
If in $ \vartriangle ABC $ , $ a\sin A = b\sin B $ , then the triangle is:
A) isosceles
B) right angled
C) equilateral
D) none of these
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: We can use the sine formula of the triangle to find the value of sine of angles A and B in terms of sides a and b and substitute in the given equation. The relationship between the sides a and b will tell which type of triangle given $ \vartriangle ABC $ is.
When we draw a diagram, the sides are taken opposite to the similarly named vertex or angle.
Sine formula is given as:
$ \dfrac{a}{{\sin A}} = \dfrac{b}{{\sin B}} = \dfrac{c}{{\sin C}} $
Complete step-by-step answer:
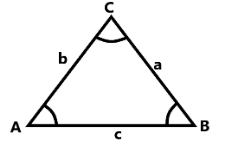
According to the sine formula for triangle, we have:
The length of side a divided by sine of angle A is equal to the similar ratios sides b and c and sine of angles B and C and it is given as:
$ \dfrac{a}{{\sin A}} = \dfrac{b}{{\sin B}} = \dfrac{c}{{\sin C}} $
We have been given the relationship between the first two components of the above, so the ratio can be equated to some constant k.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{a}{{\sin A}} = \dfrac{b}{{\sin B}} = k $
The value of sine of respective angles can be given as:
$
\Rightarrow \dfrac{a}{{\sin A}} = k \\
\Rightarrow \sin A = \dfrac{a}{k} \\
$ $
\Rightarrow \dfrac{b}{{\sin B}} = k \\
\Rightarrow \sin B = \dfrac{b}{k} \;
$
The given condition in $ \vartriangle ABC $ is $ a\sin A = b\sin B $ , substituting the values of sine of respective angles, we get:
$
\Rightarrow a \times \dfrac{a}{k} = b \times \dfrac{b}{k} \\
\Rightarrow {a^2} = {b^2} \\
\Rightarrow \sqrt {{a^2}} = \sqrt {{b^2}} \\
\Rightarrow a = \pm b \;
$
The value of side a can be equal to two values of b, one negative and the other positive. As the length of the sign cannot be negative, we will ignore it and consider only the positive one.
$ \Rightarrow a = b $
It shows that two sides of the given $ \vartriangle ABC $ are equal and when the two sides of a triangle are equal, the triangle is known as isosceles triangle.
Therefore, the given triangle is isosceles and the correct option is A).
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: We have different types of triangles which can be identified by the length of their sides. When all the sides are equal, the triangle is called equilateral, with two sides are equal, the triangle is called isosceles and when none of the sides are equal, the triangle is called scalene. The triangle is known as a right angled triangle only when one of its angle measures equal to 90°. When we take the square root of squared quantities, we always consider that it can be positive or negative because the square of both negative and positive numbers is positive.
When we draw a diagram, the sides are taken opposite to the similarly named vertex or angle.
Sine formula is given as:
$ \dfrac{a}{{\sin A}} = \dfrac{b}{{\sin B}} = \dfrac{c}{{\sin C}} $
Complete step-by-step answer:

According to the sine formula for triangle, we have:
The length of side a divided by sine of angle A is equal to the similar ratios sides b and c and sine of angles B and C and it is given as:
$ \dfrac{a}{{\sin A}} = \dfrac{b}{{\sin B}} = \dfrac{c}{{\sin C}} $
We have been given the relationship between the first two components of the above, so the ratio can be equated to some constant k.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{a}{{\sin A}} = \dfrac{b}{{\sin B}} = k $
The value of sine of respective angles can be given as:
$
\Rightarrow \dfrac{a}{{\sin A}} = k \\
\Rightarrow \sin A = \dfrac{a}{k} \\
$ $
\Rightarrow \dfrac{b}{{\sin B}} = k \\
\Rightarrow \sin B = \dfrac{b}{k} \;
$
The given condition in $ \vartriangle ABC $ is $ a\sin A = b\sin B $ , substituting the values of sine of respective angles, we get:
$
\Rightarrow a \times \dfrac{a}{k} = b \times \dfrac{b}{k} \\
\Rightarrow {a^2} = {b^2} \\
\Rightarrow \sqrt {{a^2}} = \sqrt {{b^2}} \\
\Rightarrow a = \pm b \;
$
The value of side a can be equal to two values of b, one negative and the other positive. As the length of the sign cannot be negative, we will ignore it and consider only the positive one.
$ \Rightarrow a = b $
It shows that two sides of the given $ \vartriangle ABC $ are equal and when the two sides of a triangle are equal, the triangle is known as isosceles triangle.
Therefore, the given triangle is isosceles and the correct option is A).
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: We have different types of triangles which can be identified by the length of their sides. When all the sides are equal, the triangle is called equilateral, with two sides are equal, the triangle is called isosceles and when none of the sides are equal, the triangle is called scalene. The triangle is known as a right angled triangle only when one of its angle measures equal to 90°. When we take the square root of squared quantities, we always consider that it can be positive or negative because the square of both negative and positive numbers is positive.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




