
If in a parallelogram ABCD, the coordinates of A, B and C are respectively (1, 2), (3, 4) and (2, 5) then the equation of the diagonal AD is
Answer
607.2k+ views
Hint:Draw parallelogram ABCD and mark the given points. The diagonals of the parallelogram intersect equal. Thus the point of intersection becomes the mid – point of diagram. Find mid – point using mid – point formula then use two point formula to find equation of diagonal AD.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have been given a parallelogram ABCD. Along with this we know the coordinates of points A, B and C which are respectively A (1, 2), B (3, 4) and C (2, 5). Now let us draw a parallelogram plotting all these values.
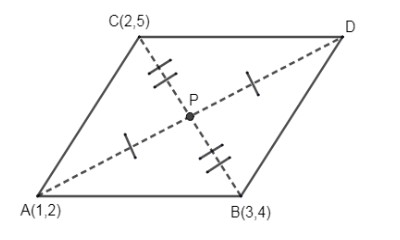
Let AD and BC be the diagonals of the parallelogram. We know that the diagonals of a parallelogram intersect equally. Thus let us mark the point where diagonals AD and BC intersect as P. From the figure you can say that P is the mid – point of the diagonal BC and AD.
Now, by using mid – point theorem, you can get the value of P. As P is the mid – point of BC, we can get the value of P, using the formula,
Mid – point of BC \[=\left( \dfrac{{{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}}{2} \right)\]
Take \[\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)=C\left( 2,5 \right)\] and \[\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)=B\left( 3,4 \right)\].
\[\therefore \] P = Mid – point of BC = \[\left( \dfrac{2+3}{2},\dfrac{5+4}{2} \right)=\left( \dfrac{5}{2},\dfrac{9}{2} \right)\]
Thus we got the coordinates of P as \[\left( \dfrac{5}{2},\dfrac{9}{2} \right)\].
Now, we need to find the equation of line AD.
We know the value of 2 points A (1, 2) and P \[\left( \dfrac{5}{2},\dfrac{9}{2} \right)\].
Thus let us use the formula for finding equation of line as,
\[\dfrac{y-{{y}_{1}}}{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}=\dfrac{x-{{x}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}\]
Put \[\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)=\left( 1,2 \right)\] and \[\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)=\left( \dfrac{5}{2},\dfrac{9}{2} \right)\].
We can rearrange the above formula as,
\[y-{{y}_{1}}=\left( \dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}} \right)\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)\]
Now let us substitute the value of \[\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\] and \[\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)\].
\[\left( y-2 \right)=\left( \dfrac{\dfrac{9}{2}-2}{\dfrac{5}{2}-1} \right)\left( x-1 \right)\Rightarrow \left( y-2 \right)=\dfrac{5}{3}\left( x-1 \right)\]
Let us cross multiply and simplify it.
\[\begin{align}
& 3\left( y-2 \right)=5\left( x-1 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 3y-6=5x-5 \\
& \Rightarrow 5x-3y-5+6=0 \\
& 5x-3y+1=0 \\
\end{align}\]
Thus we got the equation of diagonal as \[5x-3y+1=0\].
Note: In the two point formula, \[m=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}\], which represent the equation formula of slope. The formula can be written as, \[\left( y-{{y}_{1}} \right)=m\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)\]. Thus you can find slope and substitute or use the formula directly.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have been given a parallelogram ABCD. Along with this we know the coordinates of points A, B and C which are respectively A (1, 2), B (3, 4) and C (2, 5). Now let us draw a parallelogram plotting all these values.

Let AD and BC be the diagonals of the parallelogram. We know that the diagonals of a parallelogram intersect equally. Thus let us mark the point where diagonals AD and BC intersect as P. From the figure you can say that P is the mid – point of the diagonal BC and AD.
Now, by using mid – point theorem, you can get the value of P. As P is the mid – point of BC, we can get the value of P, using the formula,
Mid – point of BC \[=\left( \dfrac{{{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}}{2} \right)\]
Take \[\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)=C\left( 2,5 \right)\] and \[\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)=B\left( 3,4 \right)\].
\[\therefore \] P = Mid – point of BC = \[\left( \dfrac{2+3}{2},\dfrac{5+4}{2} \right)=\left( \dfrac{5}{2},\dfrac{9}{2} \right)\]
Thus we got the coordinates of P as \[\left( \dfrac{5}{2},\dfrac{9}{2} \right)\].
Now, we need to find the equation of line AD.
We know the value of 2 points A (1, 2) and P \[\left( \dfrac{5}{2},\dfrac{9}{2} \right)\].
Thus let us use the formula for finding equation of line as,
\[\dfrac{y-{{y}_{1}}}{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}=\dfrac{x-{{x}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}\]
Put \[\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)=\left( 1,2 \right)\] and \[\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)=\left( \dfrac{5}{2},\dfrac{9}{2} \right)\].
We can rearrange the above formula as,
\[y-{{y}_{1}}=\left( \dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}} \right)\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)\]
Now let us substitute the value of \[\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\] and \[\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)\].
\[\left( y-2 \right)=\left( \dfrac{\dfrac{9}{2}-2}{\dfrac{5}{2}-1} \right)\left( x-1 \right)\Rightarrow \left( y-2 \right)=\dfrac{5}{3}\left( x-1 \right)\]
Let us cross multiply and simplify it.
\[\begin{align}
& 3\left( y-2 \right)=5\left( x-1 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 3y-6=5x-5 \\
& \Rightarrow 5x-3y-5+6=0 \\
& 5x-3y+1=0 \\
\end{align}\]
Thus we got the equation of diagonal as \[5x-3y+1=0\].
Note: In the two point formula, \[m=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}\], which represent the equation formula of slope. The formula can be written as, \[\left( y-{{y}_{1}} \right)=m\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)\]. Thus you can find slope and substitute or use the formula directly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




