
If $\hat u$ and $\hat v$ are the unit vectors and $\theta $ is the acute angle between them, then $2\hat u \times 3\hat v$ is a unit vector for
A.Exactly two values of $\theta $
B.More than two values of $\theta $
C.No value of $\theta $
D.Exactly one value of $\theta $
Answer
576k+ views
Hint: At first, we will learn about the cross product, and its formula i.e. \[\vec a \times \vec b = \left( {\left| {\vec a} \right|\left| {\vec b} \right|\sin \beta } \right)\hat n\].Using this we will simplify the given expression, from where we will get an equation in $\theta $ or in the function of $\theta $, therefore solving that equation we will get our answer.
We know that the magnitude of the cross product of 2 vectors a and b is given by \[\left| {\vec a \times \vec b} \right| = \left| {\vec a} \right|\left| {\vec b} \right|\sin \theta \] where $\theta $ is the angle between the two vectors. Then we can find the magnitude of the cross product of the given vectors. Then we can equate it to unity and solve for the angle $\theta $. Then the number of solutions of $\theta $ will give the required option.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given that $\hat u$ and $\hat v$ are two unit vectors and $\theta $ is the acute angle between them
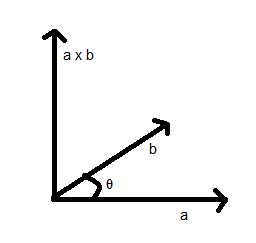
We know that the cross product of two vectors is also a vector perpendicular to both the vectors. We know that the magnitude of the cross product of 2 vectors a and b is given by \[\left| {\vec a \times \vec b} \right| = \left| {\vec a} \right|\left| {\vec b} \right|\sin \theta \] where $\theta $ is the angle between the two vectors.
We are given the vectors $\hat u$ and $\hat v$
We can find the magnitude of $2\hat u \times 3\hat v$.
$ \Rightarrow \left| {2\hat u \times 3\hat v} \right| = \left| {2\hat u} \right|\left| {3\hat v} \right|\sin \theta $
We know that $\left| {c\vec a} \right| = c\left| {\vec a} \right|$. So, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \left| {2\hat u \times 3\hat v} \right| = 2\left| {\hat u} \right| \times 3\left| {\hat v} \right| \times \sin \theta $
Since it is given that $\hat u$ and $\hat v$ is the unit vectors i.e. \[\left| {\hat u} \right| = \left| {\hat v} \right| = 1\]. So, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \left| {2\hat u \times 3\hat v} \right| = 2 \times 3 \times \sin \theta $
On simplification we get,
$ \Rightarrow \left| {2\hat u \times 3\hat v} \right| = 6\sin \theta $ … (1)
We need to find the angle when the cross product will give a unit vector. For $2\hat u \times 3\hat v$ to be a unit vector, its modulus should be equal to 1.
i.e. $ \Rightarrow \left| {2\hat u \times 3\hat v} \right| = 1$ …. (2)
On equating (1) and (2), we get,
$ \Rightarrow 1 = 6\sin \theta $
On dividing the equation by 6 we get,
$ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{1}{6}$
Taking both side expression as a function of ${\sin ^{ - 1}}$
$ \Rightarrow \theta = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{6}$
Therefore $\theta $ has only one value which makes it an acute angle.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D.
Note: While solving the equation for $\theta $ most of the students take the value of $\theta $ as $\theta = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{6}$ and $\theta = \pi - {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{6}$, but it is mentioned the question that the $\theta $ is an acute angle so it cannot take the value $\theta = \pi - {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{6}$, and will have only one solution, so remember to apply all the given data to get a more accurate answer.
The vector product of two vectors will give another vector. The resultant vector will be perpendicular to both the vectors. It will be zero if the vectors are parallel. The scalar product of two vectors will give a scalar quantity. It will be zero if the vectors are perpendicular to each other.
We know that the magnitude of the cross product of 2 vectors a and b is given by \[\left| {\vec a \times \vec b} \right| = \left| {\vec a} \right|\left| {\vec b} \right|\sin \theta \] where $\theta $ is the angle between the two vectors. Then we can find the magnitude of the cross product of the given vectors. Then we can equate it to unity and solve for the angle $\theta $. Then the number of solutions of $\theta $ will give the required option.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given that $\hat u$ and $\hat v$ are two unit vectors and $\theta $ is the acute angle between them

We know that the cross product of two vectors is also a vector perpendicular to both the vectors. We know that the magnitude of the cross product of 2 vectors a and b is given by \[\left| {\vec a \times \vec b} \right| = \left| {\vec a} \right|\left| {\vec b} \right|\sin \theta \] where $\theta $ is the angle between the two vectors.
We are given the vectors $\hat u$ and $\hat v$
We can find the magnitude of $2\hat u \times 3\hat v$.
$ \Rightarrow \left| {2\hat u \times 3\hat v} \right| = \left| {2\hat u} \right|\left| {3\hat v} \right|\sin \theta $
We know that $\left| {c\vec a} \right| = c\left| {\vec a} \right|$. So, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \left| {2\hat u \times 3\hat v} \right| = 2\left| {\hat u} \right| \times 3\left| {\hat v} \right| \times \sin \theta $
Since it is given that $\hat u$ and $\hat v$ is the unit vectors i.e. \[\left| {\hat u} \right| = \left| {\hat v} \right| = 1\]. So, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \left| {2\hat u \times 3\hat v} \right| = 2 \times 3 \times \sin \theta $
On simplification we get,
$ \Rightarrow \left| {2\hat u \times 3\hat v} \right| = 6\sin \theta $ … (1)
We need to find the angle when the cross product will give a unit vector. For $2\hat u \times 3\hat v$ to be a unit vector, its modulus should be equal to 1.
i.e. $ \Rightarrow \left| {2\hat u \times 3\hat v} \right| = 1$ …. (2)
On equating (1) and (2), we get,
$ \Rightarrow 1 = 6\sin \theta $
On dividing the equation by 6 we get,
$ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{1}{6}$
Taking both side expression as a function of ${\sin ^{ - 1}}$
$ \Rightarrow \theta = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{6}$
Therefore $\theta $ has only one value which makes it an acute angle.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D.
Note: While solving the equation for $\theta $ most of the students take the value of $\theta $ as $\theta = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{6}$ and $\theta = \pi - {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{6}$, but it is mentioned the question that the $\theta $ is an acute angle so it cannot take the value $\theta = \pi - {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{6}$, and will have only one solution, so remember to apply all the given data to get a more accurate answer.
The vector product of two vectors will give another vector. The resultant vector will be perpendicular to both the vectors. It will be zero if the vectors are parallel. The scalar product of two vectors will give a scalar quantity. It will be zero if the vectors are perpendicular to each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




