
If h, S, V be the height, curved surface area and volume of a cone respectively, then $(3\pi V {h^3} - {S^2}{h^2} + 9{V^2})$ is equal to:
A) $8$
B) $0$
C) $4\pi$
D) $32{{\pi}^2}$
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: A cone is defined as a distinctive geometric figure which has a flat surface and a surface, pointed towards the top. The pointed end of the cone is named as apex, whereas the flat surface is named as the base.
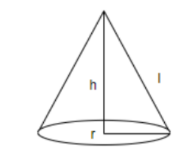
As shown in the figure we have assumed the cone which is having height = h, radius of the cone base = r and slant height of the cone = l.
(a) Volume of cone \[V{\text{ }} = \;\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h\]
(b) Curved surface area of cone \[{\text{S }} = \;\pi rl\]
(c) Total surface area of cone = \[\pi r{\text{ }}\left( {l{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}r} \right)\]
(d) Slant height of cone \[{l^2} = {r^2} + {h^2}\]
We are going to use these formulas to reduce and simplify the equation \[\left( {3\pi V{h^3} - {S^2}{h^2} + 9{V^2}} \right)\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
The given information in the question is:
h be the height of the cone
S be the curved surface area of the cone
V be the volume of a cone
Curved surface area of a cone, \[{\text{S }} = \;\pi rl\]
Volume of a cone, \[V{\text{ }} = \;\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h\]
We have to calculate the value of \[\left( {3\pi V{h^3} - {S^2}{h^2} + 9{V^2}} \right)\].
Now we will substitute the value of S and V in the above equation to get:
\[ = \left( {3\pi \left( {\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h} \right){h^3} - {{\left( {\pi rl} \right)}^2}{h^2} + 9{{\left( {\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h} \right)}^2}} \right)\]
As we know, \[{l^2} = {r^2} + {h^2}\], so now substituting the value of $l$in the above equation, we get:
\[ = \left( {3\pi \left( {\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h} \right){h^3} - {{\left( {\pi r\sqrt {{r^2} + {h^2}} } \right)}^2}{h^2} + 9{{\left( {\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h} \right)}^2}} \right)\]
Now opening the brackets and simplifying the equation, we get:
\[ = \left( {{\pi ^2}{r^2}{h^4} - {\pi ^2}{r^2}{h^2}\left( {{r^2} + {h^2}} \right) + {\pi ^2}{r^4}{h^2}} \right)\]
\[ = \left( {{\pi ^2}{r^2}{h^4} - {\pi ^2}{r^4}{h^2} - {\pi ^2}{r^2}{h^4} + {\pi ^2}{r^4}{h^2}} \right)\]
$ = 0$
If h, S, V be the height, curved surface area and volume of a cone respectively, then \[\left( {3\pi V{h^3} - {S^2}{h^2} + 9{V^2}} \right)\] is equal to $0$.
So, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note: A cone doesn’t have uniform (or congruent) cross-sections. The total surface area of a cone is calculated in two parts:
The curved surface area of a cone, which is equal to the perimeter of the cone base times one-half slant height of cone.
The flat surface area (of the base), which is equal to the area of the cone base.

As shown in the figure we have assumed the cone which is having height = h, radius of the cone base = r and slant height of the cone = l.
(a) Volume of cone \[V{\text{ }} = \;\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h\]
(b) Curved surface area of cone \[{\text{S }} = \;\pi rl\]
(c) Total surface area of cone = \[\pi r{\text{ }}\left( {l{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}r} \right)\]
(d) Slant height of cone \[{l^2} = {r^2} + {h^2}\]
We are going to use these formulas to reduce and simplify the equation \[\left( {3\pi V{h^3} - {S^2}{h^2} + 9{V^2}} \right)\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
The given information in the question is:
h be the height of the cone
S be the curved surface area of the cone
V be the volume of a cone
Curved surface area of a cone, \[{\text{S }} = \;\pi rl\]
Volume of a cone, \[V{\text{ }} = \;\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h\]
We have to calculate the value of \[\left( {3\pi V{h^3} - {S^2}{h^2} + 9{V^2}} \right)\].
Now we will substitute the value of S and V in the above equation to get:
\[ = \left( {3\pi \left( {\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h} \right){h^3} - {{\left( {\pi rl} \right)}^2}{h^2} + 9{{\left( {\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h} \right)}^2}} \right)\]
As we know, \[{l^2} = {r^2} + {h^2}\], so now substituting the value of $l$in the above equation, we get:
\[ = \left( {3\pi \left( {\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h} \right){h^3} - {{\left( {\pi r\sqrt {{r^2} + {h^2}} } \right)}^2}{h^2} + 9{{\left( {\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h} \right)}^2}} \right)\]
Now opening the brackets and simplifying the equation, we get:
\[ = \left( {{\pi ^2}{r^2}{h^4} - {\pi ^2}{r^2}{h^2}\left( {{r^2} + {h^2}} \right) + {\pi ^2}{r^4}{h^2}} \right)\]
\[ = \left( {{\pi ^2}{r^2}{h^4} - {\pi ^2}{r^4}{h^2} - {\pi ^2}{r^2}{h^4} + {\pi ^2}{r^4}{h^2}} \right)\]
$ = 0$
If h, S, V be the height, curved surface area and volume of a cone respectively, then \[\left( {3\pi V{h^3} - {S^2}{h^2} + 9{V^2}} \right)\] is equal to $0$.
So, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note: A cone doesn’t have uniform (or congruent) cross-sections. The total surface area of a cone is calculated in two parts:
The curved surface area of a cone, which is equal to the perimeter of the cone base times one-half slant height of cone.
The flat surface area (of the base), which is equal to the area of the cone base.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




