
If $f\left( x \right)=\left| \begin{matrix}
\cos \left( 2x \right) & \cos \left( 2x \right) & \sin \left( 2x \right) \\
-\cos x & \cos x & -\sin x \\
\sin x & \sin x & \cos x \\
\end{matrix} \right|$, then:
(a) ${f}'\left( x \right)=0$ at exactly three points in $\left( -\pi ,\pi \right)$
(b) ${f}'\left( x \right)=0$ at more than three points in $\left( -\pi ,\pi \right)$
(c) f(x) attains its maximum at x=0
(d) f(x) attains its minimum at x=0
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: First, before proceeding for this, we must start by expanding the determinant along the first row to get the answer of f(x). Then, by using the trigonometric identity as ${{\sin }^{2}}x+{{\cos }^{2}}x=1$, $2\sin x\cos x=\sin 2x$ and ${{\cos }^{2}}x-{{\sin }^{2}}x=\cos 2x$, we get value of f(x). Then, we can see that ${f}'\left( x \right)$is required, so the differentiation of the function f(x) and then equating it with 0, we get the first answer. Then, we need to get that function has maximum or minimum value by again differentiating the function.
Complete step by step answer:
In this question, we are supposed to find the value of the determinant given as:$f\left( x \right)=\left| \begin{matrix}
\cos \left( 2x \right) & \cos \left( 2x \right) & \sin \left( 2x \right) \\
-\cos x & \cos x & -\sin x \\
\sin x & \sin x & \cos x \\
\end{matrix} \right|$
So, before proceeding for this, we must start by expanding the determinant along first row to get the answer of f(x) as:
$f\left( x \right)=\cos 2x\left( \cos x\times \cos x+\sin x\times \sin x \right)-\cos 2x\left( -\cos x\times \cos x+\sin x\times \sin x \right)+\sin 2x\left( -\cos x\times \sin x-\cos x\times \sin x \right)$Then, by solving the above expression, we get:
$f\left( x \right)=\cos 2x\left( {{\cos }^{2}}x+{{\sin }^{2}}x \right)-\cos 2x\left( -{{\cos }^{2}}x+{{\sin }^{2}}x \right)+\sin 2x\left( -2\cos x\sin x \right)$
Now, by using the trigonometric identity as ${{\sin }^{2}}x+{{\cos }^{2}}x=1$, we get:
$f\left( x \right)=\cos 2x+\cos 2x\left( {{\cos }^{2}}x-{{\sin }^{2}}x \right)-\sin 2x\left( 2\cos x\sin x \right)$
Now, again by using the trigonometric identities as $2\sin x\cos x=\sin 2x$ and ${{\cos }^{2}}x-{{\sin }^{2}}x=\cos 2x$, we get:
$f\left( x \right)=\cos 2x+{{\cos }^{2}}2x-{{\sin }^{2}}2x$
Then, by again applying the same identity as ${{\cos }^{2}}2x-{{\sin }^{2}}2x=\cos 4x$, we get:
$f\left( x \right)=\cos 2x+\cos 4x$
Now, in the options, we can see that ${f}'\left( x \right)$is required, so the differentiation of the function f(x) is as:
${f}'\left( x \right)=-2\sin 2x-4\sin 4x$
Now, b y solving the above expression and equating it with zero, we get:
$\begin{align}
& -2\sin 2x-4\left( 2\sin 2xcos2x \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow -2\sin 2x\left( 1+4\cos 2x \right)=0 \\
\end{align}$
So, it gives us with the two conditions that are as:
$\sin 2x=0$ or $\begin{align}
& 1+4\cos 2x=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \cos 2x=\dfrac{-1}{4} \\
\end{align}$
So, we can get the roots for $\sin 2x=0$by using the graph as:
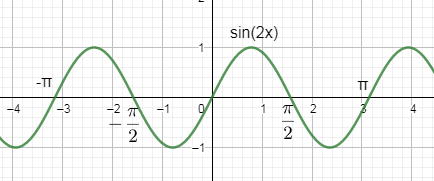
So, we get the roots of $\sin 2x$ in the range $\left( -\pi ,\pi \right)$as $x=\dfrac{-\pi }{2},0,\dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
Now, by doing the same for the function $\cos 2x=\dfrac{-1}{4}$, we get:
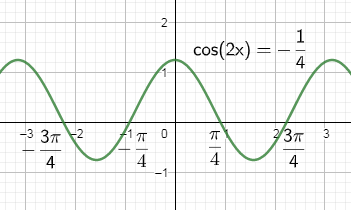
So, we get the roots of $\cos 2x=\dfrac{-1}{4}$ in the range $\left( -\pi ,\pi \right)$as $x=\dfrac{-3\pi }{4},\dfrac{-\pi }{4},\dfrac{\pi }{4},\dfrac{3\pi }{4}$.
So, the function ${f}'\left( x \right)$has more than three values in the range $\left( -\pi ,\pi \right)$.
Then, we need to get that function has maximum or minimum value by again differentiating the function as:
${{f}'}'\left( x \right)=-4\cos 2x-16\cos 4x$
Now, by substituting the value of x as 0 to get the condition as:
$\begin{align}
& {{f}'}'\left( x \right)=-4\cos 2\left( 0 \right)-16\cos 4\left( 0 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{f}'}'\left( x \right)=-20 \\
& \Rightarrow {{f}'}'\left( x \right)<0 \\
\end{align}$
So, we know the condition that if ${{f}'}'\left( x \right)<0$, then the function f(x) attains the maximum at x=0.
Hence, options (b) and (c) are correct.
Note: Now, to solve these type of the questions we need not to expand with first row only as we can expand at any row or column to calculate the determinant of the given matrix. So, it will not create any difference if we expand with any other row or column and we get the same answer. Moreover, some basic differentiations are:
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{d}{dx}\sin x=\cos x \\
& \dfrac{d}{dx}\cos x=-\sin x \\
\end{align}$
Complete step by step answer:
In this question, we are supposed to find the value of the determinant given as:$f\left( x \right)=\left| \begin{matrix}
\cos \left( 2x \right) & \cos \left( 2x \right) & \sin \left( 2x \right) \\
-\cos x & \cos x & -\sin x \\
\sin x & \sin x & \cos x \\
\end{matrix} \right|$
So, before proceeding for this, we must start by expanding the determinant along first row to get the answer of f(x) as:
$f\left( x \right)=\cos 2x\left( \cos x\times \cos x+\sin x\times \sin x \right)-\cos 2x\left( -\cos x\times \cos x+\sin x\times \sin x \right)+\sin 2x\left( -\cos x\times \sin x-\cos x\times \sin x \right)$Then, by solving the above expression, we get:
$f\left( x \right)=\cos 2x\left( {{\cos }^{2}}x+{{\sin }^{2}}x \right)-\cos 2x\left( -{{\cos }^{2}}x+{{\sin }^{2}}x \right)+\sin 2x\left( -2\cos x\sin x \right)$
Now, by using the trigonometric identity as ${{\sin }^{2}}x+{{\cos }^{2}}x=1$, we get:
$f\left( x \right)=\cos 2x+\cos 2x\left( {{\cos }^{2}}x-{{\sin }^{2}}x \right)-\sin 2x\left( 2\cos x\sin x \right)$
Now, again by using the trigonometric identities as $2\sin x\cos x=\sin 2x$ and ${{\cos }^{2}}x-{{\sin }^{2}}x=\cos 2x$, we get:
$f\left( x \right)=\cos 2x+{{\cos }^{2}}2x-{{\sin }^{2}}2x$
Then, by again applying the same identity as ${{\cos }^{2}}2x-{{\sin }^{2}}2x=\cos 4x$, we get:
$f\left( x \right)=\cos 2x+\cos 4x$
Now, in the options, we can see that ${f}'\left( x \right)$is required, so the differentiation of the function f(x) is as:
${f}'\left( x \right)=-2\sin 2x-4\sin 4x$
Now, b y solving the above expression and equating it with zero, we get:
$\begin{align}
& -2\sin 2x-4\left( 2\sin 2xcos2x \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow -2\sin 2x\left( 1+4\cos 2x \right)=0 \\
\end{align}$
So, it gives us with the two conditions that are as:
$\sin 2x=0$ or $\begin{align}
& 1+4\cos 2x=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \cos 2x=\dfrac{-1}{4} \\
\end{align}$
So, we can get the roots for $\sin 2x=0$by using the graph as:

So, we get the roots of $\sin 2x$ in the range $\left( -\pi ,\pi \right)$as $x=\dfrac{-\pi }{2},0,\dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
Now, by doing the same for the function $\cos 2x=\dfrac{-1}{4}$, we get:

So, we get the roots of $\cos 2x=\dfrac{-1}{4}$ in the range $\left( -\pi ,\pi \right)$as $x=\dfrac{-3\pi }{4},\dfrac{-\pi }{4},\dfrac{\pi }{4},\dfrac{3\pi }{4}$.
So, the function ${f}'\left( x \right)$has more than three values in the range $\left( -\pi ,\pi \right)$.
Then, we need to get that function has maximum or minimum value by again differentiating the function as:
${{f}'}'\left( x \right)=-4\cos 2x-16\cos 4x$
Now, by substituting the value of x as 0 to get the condition as:
$\begin{align}
& {{f}'}'\left( x \right)=-4\cos 2\left( 0 \right)-16\cos 4\left( 0 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{f}'}'\left( x \right)=-20 \\
& \Rightarrow {{f}'}'\left( x \right)<0 \\
\end{align}$
So, we know the condition that if ${{f}'}'\left( x \right)<0$, then the function f(x) attains the maximum at x=0.
Hence, options (b) and (c) are correct.
Note: Now, to solve these type of the questions we need not to expand with first row only as we can expand at any row or column to calculate the determinant of the given matrix. So, it will not create any difference if we expand with any other row or column and we get the same answer. Moreover, some basic differentiations are:
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{d}{dx}\sin x=\cos x \\
& \dfrac{d}{dx}\cos x=-\sin x \\
\end{align}$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




