
If $f\left( x \right)=2{{x}^{2}}+5$ and $g\left( x \right)=3x+a$, how do you find a so that the graph of $f\left( g\left( x \right) \right)$ crosses the y-axis at 23?
Answer
533.1k+ views
Hint: We first find the composite function $f\left( g\left( x \right) \right)$. Then we find the Y-axis intercept by putting the value of $x=0$. We solve it to find the value of a. It is given that the Y intercept is 23.
Complete step by step solution:
It is given that $f\left( x \right)=2{{x}^{2}}+5$ and $g\left( x \right)=3x+a$. We first have to find the composite function of $f\left( g\left( x \right) \right)$.
Therefore, $f\left( g\left( x \right) \right)=f\left( 3x+a \right)=2{{\left( 3x+a \right)}^{2}}+5$.
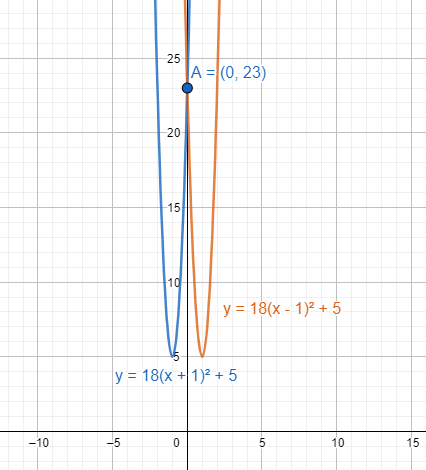
Now we have to find the value of a so that the graph of $f\left( g\left( x \right) \right)$ crosses the y-axis at 23.
We assume $y=f\left( g\left( x \right) \right)=2{{\left( 3x+a \right)}^{2}}+5$.
This means we first find the Y-axis intercepts. In that case for Y-axis, we have to take the coordinate values of x as 0. Putting the value of $x=0$ in the equation $y=2{{\left( 3x+a \right)}^{2}}+5$, we get
$\begin{align}
& y=2{{\left( 3x+a \right)}^{2}}+5 \\
& \Rightarrow y=2{{\left( 3\times 0+a \right)}^{2}}+5=2{{a}^{2}}+5 \\
\end{align}$
It is given the value of y will be 23.
This gives $2{{a}^{2}}+5=23$. We solve the quadratic to find the value of a.
We need to find the solution of the given equation $2{{a}^{2}}-18=0$.
First, we divide both sides of the equation by 2 and get $\dfrac{2{{a}^{2}}-18}{2}=0\Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}-9=0$.
Now we have a quadratic equation ${{a}^{2}}-9=0$ which gives ${{a}^{2}}-{{3}^{2}}=0$.
Now we find the factorisation of the equation ${{a}^{2}}-{{3}^{2}}=0$ using the identity of ${{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}=\left( x+y \right)\left( x-y \right)$.
Therefore, we get
$\begin{align}
& {{a}^{2}}-{{3}^{2}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \left( a+3 \right)\left( a-3 \right)=0 \\
\end{align}$
We get the values of a as either $\left( a+3 \right)=0$ or $\left( a-3 \right)=0$.
This gives $a=-3,3$.
Note: We can also apply the quadratic equation formula to solve the equation $2{{a}^{2}}-18=0$.
We know for a general equation of quadratic $a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0$, the value of the roots of x will be $x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}$.
In the given equation we have $2{{a}^{2}}-18=0$. The values of coefficients are $2,0,-18$ respectively.
We put the values and get a as $a=\dfrac{-0\pm \sqrt{{{0}^{2}}-4\times 2\times \left( -18 \right)}}{2\times 2}=\dfrac{\pm \sqrt{144}}{4}=\dfrac{\pm 12}{4}=\pm 3$.
Complete step by step solution:
It is given that $f\left( x \right)=2{{x}^{2}}+5$ and $g\left( x \right)=3x+a$. We first have to find the composite function of $f\left( g\left( x \right) \right)$.
Therefore, $f\left( g\left( x \right) \right)=f\left( 3x+a \right)=2{{\left( 3x+a \right)}^{2}}+5$.
Now we have to find the value of a so that the graph of $f\left( g\left( x \right) \right)$ crosses the y-axis at 23.
We assume $y=f\left( g\left( x \right) \right)=2{{\left( 3x+a \right)}^{2}}+5$.
This means we first find the Y-axis intercepts. In that case for Y-axis, we have to take the coordinate values of x as 0. Putting the value of $x=0$ in the equation $y=2{{\left( 3x+a \right)}^{2}}+5$, we get
$\begin{align}
& y=2{{\left( 3x+a \right)}^{2}}+5 \\
& \Rightarrow y=2{{\left( 3\times 0+a \right)}^{2}}+5=2{{a}^{2}}+5 \\
\end{align}$
It is given the value of y will be 23.
This gives $2{{a}^{2}}+5=23$. We solve the quadratic to find the value of a.
We need to find the solution of the given equation $2{{a}^{2}}-18=0$.
First, we divide both sides of the equation by 2 and get $\dfrac{2{{a}^{2}}-18}{2}=0\Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}-9=0$.
Now we have a quadratic equation ${{a}^{2}}-9=0$ which gives ${{a}^{2}}-{{3}^{2}}=0$.
Now we find the factorisation of the equation ${{a}^{2}}-{{3}^{2}}=0$ using the identity of ${{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}=\left( x+y \right)\left( x-y \right)$.
Therefore, we get
$\begin{align}
& {{a}^{2}}-{{3}^{2}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \left( a+3 \right)\left( a-3 \right)=0 \\
\end{align}$
We get the values of a as either $\left( a+3 \right)=0$ or $\left( a-3 \right)=0$.
This gives $a=-3,3$.

Note: We can also apply the quadratic equation formula to solve the equation $2{{a}^{2}}-18=0$.
We know for a general equation of quadratic $a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0$, the value of the roots of x will be $x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}$.
In the given equation we have $2{{a}^{2}}-18=0$. The values of coefficients are $2,0,-18$ respectively.
We put the values and get a as $a=\dfrac{-0\pm \sqrt{{{0}^{2}}-4\times 2\times \left( -18 \right)}}{2\times 2}=\dfrac{\pm \sqrt{144}}{4}=\dfrac{\pm 12}{4}=\pm 3$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 11 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




