
If ${{e}_{1}}$ and ${{e}_{2}}$ are the eccentricities of a hyperbola $3{{x}^{2}}-3{{y}^{2}}=25$ and its conjugate, then?
(a) ${{e}_{1}}^{2}+{{e}_{2}}^{2}=2$
(b) ${{e}_{1}}^{2}+{{e}_{2}}^{2}=4$
(c) ${{e}_{1}}+{{e}_{2}}=4$
(d) ${{e}_{1}}+{{e}_{2}}=\sqrt{2}$
Answer
506.1k+ views
Hint: Convert the given equation of the hyperbola into its general form given as $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ and compare the values of a and b. Now, write the equation of the conjugate hyperbola (for the provided hyperbola) which is given as $\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}=1$. Use the formula of eccentricity ${{e}_{1}}=\sqrt{1+\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}}$ for the given hyperbola and eccentricity ${{e}_{2}}=\sqrt{1+\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}}$ for the conjugate hyperbola. Find the correct relation between ${{e}_{1}}$ and ${{e}_{2}}$ by substituting the values of a and b.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Here we have been provided with the hyperbola $3{{x}^{2}}-3{{y}^{2}}=25$ and it is said that its eccentricity is ${{e}_{1}}$. If the eccentricity of the conjugate hyperbola is ${{e}_{2}}$ then we have to find the correct relation between ${{e}_{1}}$ and ${{e}_{2}}$.
Now, we know that the standard form of a hyperbola is given as $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$, so we can convert the given hyperbola $3{{x}^{2}}-3{{y}^{2}}=25$ into the standard form as,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{3{{x}^{2}}}{25}-\dfrac{3{{y}^{2}}}{25}=1 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{\left( \dfrac{25}{3} \right)}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{\left( \dfrac{25}{3} \right)}=1 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{\left( \dfrac{5}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{\left( \dfrac{5}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{2}}}=1 \\
\end{align}$
On comparing it with the standard form of the hyperbola we can see that we have $a=b=\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{3}}$. The eccentricity of a hyperbola of the form $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ is given by the relation $e=\sqrt{1+\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}}$, so we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{e}_{1}}=\sqrt{1+\dfrac{{{\left( \dfrac{5}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{2}}}{{{\left( \dfrac{5}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{2}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{e}_{1}}=\sqrt{1+1} \\
& \Rightarrow {{e}_{1}}=\sqrt{2} \\
\end{align}$
Now, the two hyperbolas are said to be the conjugates of each other if the transverse and conjugate axis of one hyperbola is respectively the conjugate and transverse axis of the other hyperbola. Mathematically, we say that the conjugate hyperbola of the given hyperbola $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ is given as $\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}=1$.
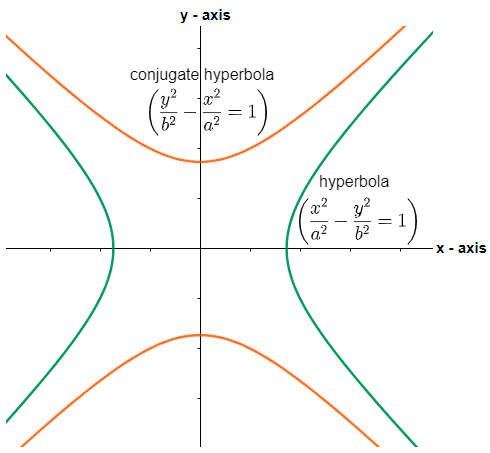
Therefore, the conjugate hyperbola of $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{\left( \dfrac{5}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{\left( \dfrac{5}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{2}}}=1$ will be given as $\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{\left( \dfrac{5}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{\left( \dfrac{5}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{2}}}=1$. The eccentricity of the hyperbola of the form $\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}=1$ is given as $e=\sqrt{1+\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}}$, so we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{e}_{2}}=\sqrt{1+\dfrac{{{\left( \dfrac{5}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{2}}}{{{\left( \dfrac{5}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{2}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{e}_{2}}=\sqrt{1+1} \\
& \Rightarrow {{e}_{2}}=\sqrt{2} \\
\end{align}$
On squaring ${{e}_{1}}$ and ${{e}_{2}}$, taking their sum we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{e}_{1}}^{2}+{{e}_{2}}^{2}=2+2 \\
& \therefore {{e}_{1}}^{2}+{{e}_{2}}^{2}=4 \\
\end{align}$
Hence, option (b) is the correct answer.
Note: Note that in the hyperbola of the form $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ the x – axis is the transverse axis and the y – axis is the conjugate axis, corresponding to which in the hyperbola of the form $\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}=1$ the y – axis is the transverse axis and the x – axis is the conjugate axis. Remember that the eccentricity of a hyperbola is always greater than 1, in an ellipse it is less than 1 and in parabola it is equal to 1.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Here we have been provided with the hyperbola $3{{x}^{2}}-3{{y}^{2}}=25$ and it is said that its eccentricity is ${{e}_{1}}$. If the eccentricity of the conjugate hyperbola is ${{e}_{2}}$ then we have to find the correct relation between ${{e}_{1}}$ and ${{e}_{2}}$.
Now, we know that the standard form of a hyperbola is given as $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$, so we can convert the given hyperbola $3{{x}^{2}}-3{{y}^{2}}=25$ into the standard form as,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{3{{x}^{2}}}{25}-\dfrac{3{{y}^{2}}}{25}=1 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{\left( \dfrac{25}{3} \right)}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{\left( \dfrac{25}{3} \right)}=1 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{\left( \dfrac{5}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{\left( \dfrac{5}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{2}}}=1 \\
\end{align}$
On comparing it with the standard form of the hyperbola we can see that we have $a=b=\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{3}}$. The eccentricity of a hyperbola of the form $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ is given by the relation $e=\sqrt{1+\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}}$, so we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{e}_{1}}=\sqrt{1+\dfrac{{{\left( \dfrac{5}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{2}}}{{{\left( \dfrac{5}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{2}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{e}_{1}}=\sqrt{1+1} \\
& \Rightarrow {{e}_{1}}=\sqrt{2} \\
\end{align}$
Now, the two hyperbolas are said to be the conjugates of each other if the transverse and conjugate axis of one hyperbola is respectively the conjugate and transverse axis of the other hyperbola. Mathematically, we say that the conjugate hyperbola of the given hyperbola $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ is given as $\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}=1$.

Therefore, the conjugate hyperbola of $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{\left( \dfrac{5}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{\left( \dfrac{5}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{2}}}=1$ will be given as $\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{\left( \dfrac{5}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{\left( \dfrac{5}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{2}}}=1$. The eccentricity of the hyperbola of the form $\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}=1$ is given as $e=\sqrt{1+\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}}$, so we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{e}_{2}}=\sqrt{1+\dfrac{{{\left( \dfrac{5}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{2}}}{{{\left( \dfrac{5}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{2}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{e}_{2}}=\sqrt{1+1} \\
& \Rightarrow {{e}_{2}}=\sqrt{2} \\
\end{align}$
On squaring ${{e}_{1}}$ and ${{e}_{2}}$, taking their sum we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{e}_{1}}^{2}+{{e}_{2}}^{2}=2+2 \\
& \therefore {{e}_{1}}^{2}+{{e}_{2}}^{2}=4 \\
\end{align}$
Hence, option (b) is the correct answer.
Note: Note that in the hyperbola of the form $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ the x – axis is the transverse axis and the y – axis is the conjugate axis, corresponding to which in the hyperbola of the form $\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}=1$ the y – axis is the transverse axis and the x – axis is the conjugate axis. Remember that the eccentricity of a hyperbola is always greater than 1, in an ellipse it is less than 1 and in parabola it is equal to 1.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




