
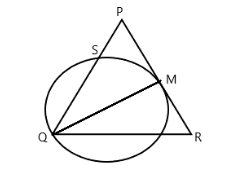
If \[\Delta PQR\] is an isosceles triangle. A circle through \[Q\] touches \[PR\] at its mid-point \[M\] and intersects \[PQ\] at \[S\] . Show that \[PQ=4\times PS\] .

Answer
541.2k+ views
Hint: In order to solve the given question, it is given in the question that \[\Delta PQR\] is an isosceles triangle and a circle through \[Q\] touches \[PR\] at its mid-point \[M\] . Therefore we will get \[PM=MR\] . Then taking the \[\Delta PQM\] and \[\Delta PMS\] , by AA similarity criteria both the triangles were similar. Later by congruence part of congruent triangle theorem, \[\dfrac{PQ}{PM}=\dfrac{PM}{PS}\] . Now, simplifying this by substituting values we will get the required answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is given in the question,
\[\Delta PQR\] is an isosceles triangle.
And
A circle through \[Q\] touches \[PR\] at its mid-point \[M\] .
Therefore,
\[PM=MR\]
Now,
Taking the \[\Delta PQM\] and \[\Delta PMS\] ,
\[\angle QPM=\angle MPQ\] (Common angle in both the triangle)
\[\angle PQM=\angle PMQ\] (Angle between a chord and a tangent is equal to the angle subtended by that chord in the alternate segment are equal)
Therefore,
By \[AA\] similarity criteria,
\[\Delta PQM\sim \Delta PMS\]
Thus,
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{PQ}{PM}=\dfrac{PM}{PS}\] (Corresponding parts of congruent triangle)
Therefore,
By performing the cross-multiplication,
\[\Rightarrow PQ\cdot PS={{\left( PM \right)}^{2}}\]
As we know that,
\[PM=\dfrac{\operatorname{P}R}{2}\]
Substituting the value in the above equation, we will get
\[\Rightarrow PQ\cdot PS={{\left( \dfrac{\operatorname{P}R}{2} \right)}^{2}}\]
Solving the above, we will get
\[\Rightarrow PQ\cdot PS=\dfrac{{{\left( \operatorname{P}R \right)}^{2}}}{4}\]
Now,
We know that,
\[PR=PQ\]
Substituting this value in the above equation, we will get
\[\Rightarrow PQ\cdot PS=\dfrac{{{\left( PQ \right)}^{2}}}{4}\]
\[\Rightarrow PS=\dfrac{{{\left( PQ \right)}^{2}}}{4PQ}\]
\[\Rightarrow PS=\dfrac{PQ}{4}\]
Multiplying both the sides by 4, we will get
\[\Rightarrow PQ=4\times PS\]
Hence, we get the required answer.
Note: While solving the question, students should need to know the properties of triangles so that they are able to prove the given triangles are similar. In this question, one main point that students must know is that the angle between a chord and a tangent is equal to the angle subtended by that chord in the alternate segment. Students should need to kind in mind the required result that is needed to be proven and accordingly simplify the question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is given in the question,
\[\Delta PQR\] is an isosceles triangle.
And
A circle through \[Q\] touches \[PR\] at its mid-point \[M\] .
Therefore,
\[PM=MR\]
Now,
Taking the \[\Delta PQM\] and \[\Delta PMS\] ,
\[\angle QPM=\angle MPQ\] (Common angle in both the triangle)
\[\angle PQM=\angle PMQ\] (Angle between a chord and a tangent is equal to the angle subtended by that chord in the alternate segment are equal)
Therefore,
By \[AA\] similarity criteria,
\[\Delta PQM\sim \Delta PMS\]
Thus,
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{PQ}{PM}=\dfrac{PM}{PS}\] (Corresponding parts of congruent triangle)
Therefore,
By performing the cross-multiplication,
\[\Rightarrow PQ\cdot PS={{\left( PM \right)}^{2}}\]
As we know that,
\[PM=\dfrac{\operatorname{P}R}{2}\]
Substituting the value in the above equation, we will get
\[\Rightarrow PQ\cdot PS={{\left( \dfrac{\operatorname{P}R}{2} \right)}^{2}}\]
Solving the above, we will get
\[\Rightarrow PQ\cdot PS=\dfrac{{{\left( \operatorname{P}R \right)}^{2}}}{4}\]
Now,
We know that,
\[PR=PQ\]
Substituting this value in the above equation, we will get
\[\Rightarrow PQ\cdot PS=\dfrac{{{\left( PQ \right)}^{2}}}{4}\]
\[\Rightarrow PS=\dfrac{{{\left( PQ \right)}^{2}}}{4PQ}\]
\[\Rightarrow PS=\dfrac{PQ}{4}\]
Multiplying both the sides by 4, we will get
\[\Rightarrow PQ=4\times PS\]
Hence, we get the required answer.
Note: While solving the question, students should need to know the properties of triangles so that they are able to prove the given triangles are similar. In this question, one main point that students must know is that the angle between a chord and a tangent is equal to the angle subtended by that chord in the alternate segment. Students should need to kind in mind the required result that is needed to be proven and accordingly simplify the question.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE





