
If \[\Delta LMN \sim \Delta RST\] and A\[(\Delta LMN) = 100\] sq. cm, A\[(\Delta RST) = 144\] sq. cm. and \[LM = 5\]cm. Then find RS.
Answer
596.1k+ views
Hint: The symbol “\[ \sim \]” is used to indicate the similarity of two triangles.
Here we are going to use area of similar theorem and find the similarity in the sides of both the triangle and solve them to find\[RS.\]
Used theorems: Area of similar triangle theorem: If two triangles are similar, then the ratio of the area of both triangles are proportional to the square of the ratio of their corresponding sides.
Let us consider two triangles \[ABC\] and \[PQR\] are similar to each other. Then, by area of similar triangle theorem we get,
\[\dfrac{{A(ABC)}}{{A(PQR)}} = {(\dfrac{{AB}}{{PQ}})^2} = {(\dfrac{{BC}}{{QR}})^2} = {(\dfrac{{CA}}{{RP}})^2}\]
Complete step by step answer:
It is given that, \[\Delta LMN \sim \Delta RST\]which means \[\Delta LMN,\Delta RST\] are two similar triangles. Also, it is given that, A\[(\Delta LMN) = 100\] sq. cm and A\[(\Delta RST) = 144\] sq. cm. and \[LM = 5\]cm. we need to find the length of \[RS.\]
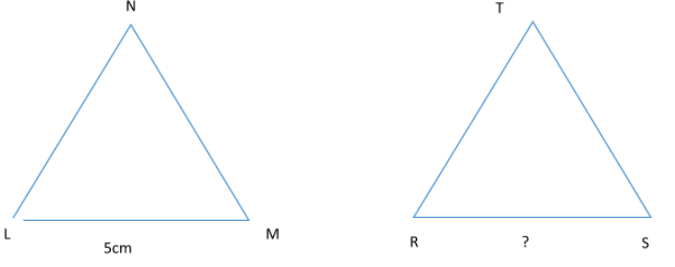
To find the length of \[RS\], we will apply the area of similar triangle theorem.
Applying, area of similar triangle theorem on triangles \[\Delta LMN,\Delta RST\]we get,
\[\dfrac{{A(LMN)}}{{A(RST)}} = {(\dfrac{{LM}}{{RS}})^2} = {(\dfrac{{MN}}{{ST}})^2} = {(\dfrac{{NL}}{{TR}})^2}\]
To find the length of \[RS\], we will consider the first two ratios.
That is, \[\dfrac{{A(LMN)}}{{A(RST)}} = {(\dfrac{{LM}}{{RS}})^2}\]
Substitute the values of the areas of the triangle and the length of the given side that is A\[(\Delta LMN) = 100\] sq. cm, A\[(\Delta RST) = 144\] sq. cm, and \[LM = 5\] cm, we get,
\[\dfrac{{100}}{{144}} = {(\dfrac{5}{{RS}})^2}\]
Solving we get,
\[\dfrac{{100}}{{144}} = \dfrac{{25}}{{R{S^2}}}\]
Simplifying we get,
\[R{S^2} = \dfrac{{144}}{{100}} \times 25 = 36\]
Taking square root of both sides we get,
\[RS = \sqrt {36} = 6\]
Hence, the length of the side \[RS = 6cm.\]
Note:
Two triangles are said to be similar if their corresponding angles are congruent and the corresponding sides are in proportion. In other ways we can say that, similar triangle is in the same shape but not necessarily in the same size.
Let us consider, two triangles \[ABC\]and \[PQR\] are similar to each other. Then
\[\dfrac{{AB}}{{PQ}} = \dfrac{{BC}}{{QR}} = \dfrac{{CA}}{{RP}}\]
Again, \[RS = \sqrt {36} = \pm 6\]
We consider the positive values since the length of a side is always positive.
Here we are going to use area of similar theorem and find the similarity in the sides of both the triangle and solve them to find\[RS.\]
Used theorems: Area of similar triangle theorem: If two triangles are similar, then the ratio of the area of both triangles are proportional to the square of the ratio of their corresponding sides.
Let us consider two triangles \[ABC\] and \[PQR\] are similar to each other. Then, by area of similar triangle theorem we get,
\[\dfrac{{A(ABC)}}{{A(PQR)}} = {(\dfrac{{AB}}{{PQ}})^2} = {(\dfrac{{BC}}{{QR}})^2} = {(\dfrac{{CA}}{{RP}})^2}\]
Complete step by step answer:
It is given that, \[\Delta LMN \sim \Delta RST\]which means \[\Delta LMN,\Delta RST\] are two similar triangles. Also, it is given that, A\[(\Delta LMN) = 100\] sq. cm and A\[(\Delta RST) = 144\] sq. cm. and \[LM = 5\]cm. we need to find the length of \[RS.\]

To find the length of \[RS\], we will apply the area of similar triangle theorem.
Applying, area of similar triangle theorem on triangles \[\Delta LMN,\Delta RST\]we get,
\[\dfrac{{A(LMN)}}{{A(RST)}} = {(\dfrac{{LM}}{{RS}})^2} = {(\dfrac{{MN}}{{ST}})^2} = {(\dfrac{{NL}}{{TR}})^2}\]
To find the length of \[RS\], we will consider the first two ratios.
That is, \[\dfrac{{A(LMN)}}{{A(RST)}} = {(\dfrac{{LM}}{{RS}})^2}\]
Substitute the values of the areas of the triangle and the length of the given side that is A\[(\Delta LMN) = 100\] sq. cm, A\[(\Delta RST) = 144\] sq. cm, and \[LM = 5\] cm, we get,
\[\dfrac{{100}}{{144}} = {(\dfrac{5}{{RS}})^2}\]
Solving we get,
\[\dfrac{{100}}{{144}} = \dfrac{{25}}{{R{S^2}}}\]
Simplifying we get,
\[R{S^2} = \dfrac{{144}}{{100}} \times 25 = 36\]
Taking square root of both sides we get,
\[RS = \sqrt {36} = 6\]
Hence, the length of the side \[RS = 6cm.\]
Note:
Two triangles are said to be similar if their corresponding angles are congruent and the corresponding sides are in proportion. In other ways we can say that, similar triangle is in the same shape but not necessarily in the same size.
Let us consider, two triangles \[ABC\]and \[PQR\] are similar to each other. Then
\[\dfrac{{AB}}{{PQ}} = \dfrac{{BC}}{{QR}} = \dfrac{{CA}}{{RP}}\]
Again, \[RS = \sqrt {36} = \pm 6\]
We consider the positive values since the length of a side is always positive.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 7 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What are the factors of 100 class 7 maths CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

Convert 200 Million dollars in rupees class 7 maths CBSE

AIM To prepare stained temporary mount of onion peel class 7 biology CBSE

Write a letter to the editor of the national daily class 7 english CBSE

List of coprime numbers from 1 to 100 class 7 maths CBSE





