
If \[\cot x+\cos ecx=\sqrt{3}\], then the principal value of \[(x-\dfrac{\pi }{6})\]
A. \[\dfrac{\pi }{3}\]
B. \[\dfrac{\pi }{4}\]
C. \[\dfrac{\pi }{2}\]
D. \[\dfrac{\pi }{6}\]
Answer
510.6k+ views
Hint: To solve this type of question firstly we have to notice the given equation and check if we can simplify it more with the help of some trigonometric relations. After simplifying we have to apply some trigonometric formulas and identities as per need and we will get our required answer.
Complete step by step answer:
The word trigonometry is derived from the Greek words trigonon (means “triangle”) and metron (means “to measure”).
Trigonometry can be defined as a study of the relationship of angles, lengths and heights. There are total six types of different functions in trigonometry: Sine \[(\sin )\], Cosine \[(\cos )\], Secant \[(\sec )\], Cosecant \[(\cos ec)\] , Tangent \[(\tan )\] and Cotangent \[(\cot )\]. Basically these six types of trigonometric functions define the relationship between the different sides of a right angle triangle.
Let’s understand it more:
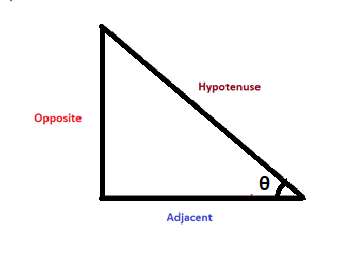
As, above figure shows a right angle triangle. So in this, Hypotenuse is the longest side of the right angle triangle. Opposite is the side that is opposite to the angle \[\theta \]. Adjacent is the side next to the angle \[\theta \]. Now the relation between these trigonometric identities with the sides of the triangles can be given as:
Sine is defined as the ratio of opposite side to the hypotenuse i.e.
\[\sin \theta =\dfrac{opposite}{hypotenuse}\]
Cosine is defined as the ratio of adjacent side to the hypotenuse i.e.
\[\cos \theta =\dfrac{adjacent}{hypotenuse}\]
Tangent can be defined as the ratio of opposite side to the adjacent side i.e.
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{opposite}{adjacent}\]
Cotangent is the reciprocal of the tangent. So it is the ratio of adjacent side to the opposite side as:
\[\cot \theta =\dfrac{adjacent}{opposite}\]
Cosecant is the reciprocal of sine. So it can be defined as the ratio of hypotenuse to the opposite side.
\[\cos ec\theta =\dfrac{hypotenuse}{opposite}\]
Secant is the reciprocal of the cosine. So it can be defined as the ratio of hypotenuse to adjacent side.
\[\sec \theta =\dfrac{hypotenuse}{adjacent}\]
Now as we have given the question \[\cot x+\cos ecx=\sqrt{3}\]
As we can represent cotangent as:
\[\cot x=\dfrac{\cos x}{\sin x}\]
And we know that Cosecant is the reciprocal of sine, so:
\[\cos ecx=\dfrac{1}{\sin x}\]
Now substituting both of these values in given equation
\[\dfrac{\cos x}{\sin x}+\dfrac{1}{\sin x}=\sqrt{3}\]
\[\dfrac{\cos x+1}{\sin x}=\sqrt{3}\]
Now we will use trigonometric formulas to simplify it further. So it becomes:
\[\dfrac{2{{\cos }^{2}}\dfrac{x}{2}}{2\sin \dfrac{x}{2}\cos \dfrac{x}{2}}=\sqrt{3}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{\cos \dfrac{x}{2}}{\sin \dfrac{x}{2}}=\sqrt{3}\]
Ratio of Cosine and Sine is Cotangent
\[\Rightarrow \cot \dfrac{x}{2}=\sqrt{3}\]
As we know reciprocal of cotangent is tangent. Therefore:
\[\tan \dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\]
\[\tan \dfrac{x}{2}=\tan (\dfrac{\pi }{6})\]
So, \[\dfrac{x}{2}=n\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{6}\]
\[\Rightarrow x=2n\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{3}\]
\[\Rightarrow x-\dfrac{\pi }{6}=2n\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{3}-\dfrac{\pi }{6}\]
\[\Rightarrow x-\dfrac{\pi }{6}=2n\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{6}\]
For \[n=0\] , principal value of:
\[x-\dfrac{\pi }{6}=\dfrac{\pi }{6}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Engineers use trigonometry to figure out the angles of the sound waves and how to design the rooms. It also has its application into the fields like physics, engineering, surveying, architecture, astronomy, satellite systems and even in the investigation of a crime scene.
Complete step by step answer:
The word trigonometry is derived from the Greek words trigonon (means “triangle”) and metron (means “to measure”).
Trigonometry can be defined as a study of the relationship of angles, lengths and heights. There are total six types of different functions in trigonometry: Sine \[(\sin )\], Cosine \[(\cos )\], Secant \[(\sec )\], Cosecant \[(\cos ec)\] , Tangent \[(\tan )\] and Cotangent \[(\cot )\]. Basically these six types of trigonometric functions define the relationship between the different sides of a right angle triangle.
Let’s understand it more:

As, above figure shows a right angle triangle. So in this, Hypotenuse is the longest side of the right angle triangle. Opposite is the side that is opposite to the angle \[\theta \]. Adjacent is the side next to the angle \[\theta \]. Now the relation between these trigonometric identities with the sides of the triangles can be given as:
Sine is defined as the ratio of opposite side to the hypotenuse i.e.
\[\sin \theta =\dfrac{opposite}{hypotenuse}\]
Cosine is defined as the ratio of adjacent side to the hypotenuse i.e.
\[\cos \theta =\dfrac{adjacent}{hypotenuse}\]
Tangent can be defined as the ratio of opposite side to the adjacent side i.e.
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{opposite}{adjacent}\]
Cotangent is the reciprocal of the tangent. So it is the ratio of adjacent side to the opposite side as:
\[\cot \theta =\dfrac{adjacent}{opposite}\]
Cosecant is the reciprocal of sine. So it can be defined as the ratio of hypotenuse to the opposite side.
\[\cos ec\theta =\dfrac{hypotenuse}{opposite}\]
Secant is the reciprocal of the cosine. So it can be defined as the ratio of hypotenuse to adjacent side.
\[\sec \theta =\dfrac{hypotenuse}{adjacent}\]
Now as we have given the question \[\cot x+\cos ecx=\sqrt{3}\]
As we can represent cotangent as:
\[\cot x=\dfrac{\cos x}{\sin x}\]
And we know that Cosecant is the reciprocal of sine, so:
\[\cos ecx=\dfrac{1}{\sin x}\]
Now substituting both of these values in given equation
\[\dfrac{\cos x}{\sin x}+\dfrac{1}{\sin x}=\sqrt{3}\]
\[\dfrac{\cos x+1}{\sin x}=\sqrt{3}\]
Now we will use trigonometric formulas to simplify it further. So it becomes:
\[\dfrac{2{{\cos }^{2}}\dfrac{x}{2}}{2\sin \dfrac{x}{2}\cos \dfrac{x}{2}}=\sqrt{3}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{\cos \dfrac{x}{2}}{\sin \dfrac{x}{2}}=\sqrt{3}\]
Ratio of Cosine and Sine is Cotangent
\[\Rightarrow \cot \dfrac{x}{2}=\sqrt{3}\]
As we know reciprocal of cotangent is tangent. Therefore:
\[\tan \dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\]
\[\tan \dfrac{x}{2}=\tan (\dfrac{\pi }{6})\]
So, \[\dfrac{x}{2}=n\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{6}\]
\[\Rightarrow x=2n\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{3}\]
\[\Rightarrow x-\dfrac{\pi }{6}=2n\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{3}-\dfrac{\pi }{6}\]
\[\Rightarrow x-\dfrac{\pi }{6}=2n\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{6}\]
For \[n=0\] , principal value of:
\[x-\dfrac{\pi }{6}=\dfrac{\pi }{6}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Engineers use trigonometry to figure out the angles of the sound waves and how to design the rooms. It also has its application into the fields like physics, engineering, surveying, architecture, astronomy, satellite systems and even in the investigation of a crime scene.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




