
If \[\cos \theta =\dfrac{5}{13}\], find the value of \[\dfrac{{{\sin }^{2}}\theta -{{\cos }^{2}}\theta }{2\sin \theta \cos \theta }\times \dfrac{1}{{{\tan }^{2}}\theta }\]
Answer
608.4k+ views
Hint:First of all consider a triangle ABC with C as the angle \[\theta \]. Now, use the Pythagoras theorem to find the remaining side. Now, find \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{P}{H}\] and \[\tan \theta =\dfrac{P}{B}\] and substitute in the given expression to get the required answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here, we are given that \[\cos \theta =\dfrac{5}{13}\]. We have to find the value of \[\dfrac{{{\sin }^{2}}\theta -{{\cos }^{2}}\theta }{2\sin \theta \cos \theta }\times \dfrac{1}{{{\tan }^{2}}\theta }\].
Let us consider the expression given in the question.
\[E=\dfrac{{{\sin }^{2}}\theta -{{\cos }^{2}}\theta }{2\sin \theta \cos \theta }\times \dfrac{1}{{{\tan }^{2}}\theta }....\left( i \right)\]
We are given that,
\[\cos \theta =\dfrac{5}{13}....\left( ii \right)\]
We know that,
\[\cos \theta =\dfrac{Base}{Hypotenuse}....\left( iii \right)\]
From equation (ii) and (iii), we get,
\[\dfrac{5}{13}=\dfrac{Base}{Hypotenuse}\]
Let us assume a triangle ABC, right-angled at B and angle C is \[\theta \].
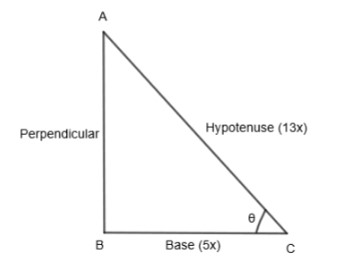
Let base BC be equal to 5x and hypotenuse equal to 13x. We know that Pythagoras theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse side is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. So, in the above triangle ABC, by applying Pythagoras theorem, we get,
\[{{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( BC \right)}^{2}}={{\left( AC \right)}^{2}}\]
By substituting the value of BC = 5x and AC = 13x, we get,
\[{{\left( 5x \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}={{\left( 13x \right)}^{2}}\]
\[25{{x}^{2}}+{{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}=169{{x}^{2}}\]
\[{{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}=169{{x}^{2}}-25{{x}^{2}}\]
\[{{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}=144{{x}^{2}}\]
\[AB=12x\]
We know that,
\[\sin \theta =\dfrac{Perpendicular}{Hypotenuse}....\left( iv \right)\]
In triangle ABC, with respect to angle \[\theta \],
Perpendicular = AB = 12x
Hypotenuse = AC = 13x
By substituting these values in equation (iv), we get,
\[\sin \theta =\dfrac{12x}{13x}=\dfrac{12}{13}\]
We also know that,
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{Perpendicular}{Base}....\left( v \right)\]
In triangle ABC, with respect to angle \[\theta \],
Perpendicular = AB = 12x
Base = BC = 5x
By substituting these values in equation (v), we get,
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{12x}{5x}=\dfrac{12}{5}\]
Now, by substituting these values of \[\cos \theta ,\sin \theta \] and \[\tan \theta \] in equation (i), we get,
\[E=\dfrac{{{\sin }^{2}}\theta -{{\cos }^{2}}\theta }{2\sin \theta \cos \theta }.\dfrac{1}{{{\tan }^{2}}\theta }\]
\[E=\dfrac{{{\left( \dfrac{12}{13} \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( \dfrac{5}{13} \right)}^{2}}}{2.\left( \dfrac{12}{13} \right).\left( \dfrac{5}{13} \right)}.\dfrac{1}{{{\left( \dfrac{12}{5} \right)}^{2}}}\]
\[E=\left[ \dfrac{\left( \dfrac{144}{169}-\dfrac{25}{169} \right)}{\dfrac{120}{169}} \right].\left( \dfrac{25}{144} \right)\]
\[E=\left[ \dfrac{\left( \dfrac{144-25}{169} \right)}{\dfrac{120}{169}} \right].\left( \dfrac{25}{144} \right)\]
\[E=\dfrac{119}{169}\times \dfrac{169}{120}\times \dfrac{25}{144}\]
\[E=\dfrac{119}{120}\times \dfrac{25}{144}\]
\[E=\dfrac{119\times 5}{24\times 144}\]
\[E=\dfrac{595}{2736}\]
So, we get the value of \[\dfrac{{{\sin }^{2}}\theta -{{\cos }^{2}}\theta }{2\sin \theta \cos \theta }\times \dfrac{1}{{{\tan }^{2}}\theta }\] as \[\dfrac{595}{2736}\].
Note: In this question, students can also find \[\sin \theta \] by using \[{{\sin }^{2}}\theta +{{\cos }^{2}}\theta =1\]. After getting \[\sin \theta \], students can find \[\tan \theta \] by using \[\tan \theta =\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }\]. Also, students must keep in mind that when nothing is given about the angle, we should always consider it in the first quadrant, i.e between 0 to \[\dfrac{\pi }{2}\] and in this case all trigonometric ratios would be positive.Students should remember important trigonometric ratios for solving these types of questions.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here, we are given that \[\cos \theta =\dfrac{5}{13}\]. We have to find the value of \[\dfrac{{{\sin }^{2}}\theta -{{\cos }^{2}}\theta }{2\sin \theta \cos \theta }\times \dfrac{1}{{{\tan }^{2}}\theta }\].
Let us consider the expression given in the question.
\[E=\dfrac{{{\sin }^{2}}\theta -{{\cos }^{2}}\theta }{2\sin \theta \cos \theta }\times \dfrac{1}{{{\tan }^{2}}\theta }....\left( i \right)\]
We are given that,
\[\cos \theta =\dfrac{5}{13}....\left( ii \right)\]
We know that,
\[\cos \theta =\dfrac{Base}{Hypotenuse}....\left( iii \right)\]
From equation (ii) and (iii), we get,
\[\dfrac{5}{13}=\dfrac{Base}{Hypotenuse}\]
Let us assume a triangle ABC, right-angled at B and angle C is \[\theta \].

Let base BC be equal to 5x and hypotenuse equal to 13x. We know that Pythagoras theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse side is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. So, in the above triangle ABC, by applying Pythagoras theorem, we get,
\[{{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( BC \right)}^{2}}={{\left( AC \right)}^{2}}\]
By substituting the value of BC = 5x and AC = 13x, we get,
\[{{\left( 5x \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}={{\left( 13x \right)}^{2}}\]
\[25{{x}^{2}}+{{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}=169{{x}^{2}}\]
\[{{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}=169{{x}^{2}}-25{{x}^{2}}\]
\[{{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}=144{{x}^{2}}\]
\[AB=12x\]
We know that,
\[\sin \theta =\dfrac{Perpendicular}{Hypotenuse}....\left( iv \right)\]
In triangle ABC, with respect to angle \[\theta \],
Perpendicular = AB = 12x
Hypotenuse = AC = 13x
By substituting these values in equation (iv), we get,
\[\sin \theta =\dfrac{12x}{13x}=\dfrac{12}{13}\]
We also know that,
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{Perpendicular}{Base}....\left( v \right)\]
In triangle ABC, with respect to angle \[\theta \],
Perpendicular = AB = 12x
Base = BC = 5x
By substituting these values in equation (v), we get,
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{12x}{5x}=\dfrac{12}{5}\]
Now, by substituting these values of \[\cos \theta ,\sin \theta \] and \[\tan \theta \] in equation (i), we get,
\[E=\dfrac{{{\sin }^{2}}\theta -{{\cos }^{2}}\theta }{2\sin \theta \cos \theta }.\dfrac{1}{{{\tan }^{2}}\theta }\]
\[E=\dfrac{{{\left( \dfrac{12}{13} \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( \dfrac{5}{13} \right)}^{2}}}{2.\left( \dfrac{12}{13} \right).\left( \dfrac{5}{13} \right)}.\dfrac{1}{{{\left( \dfrac{12}{5} \right)}^{2}}}\]
\[E=\left[ \dfrac{\left( \dfrac{144}{169}-\dfrac{25}{169} \right)}{\dfrac{120}{169}} \right].\left( \dfrac{25}{144} \right)\]
\[E=\left[ \dfrac{\left( \dfrac{144-25}{169} \right)}{\dfrac{120}{169}} \right].\left( \dfrac{25}{144} \right)\]
\[E=\dfrac{119}{169}\times \dfrac{169}{120}\times \dfrac{25}{144}\]
\[E=\dfrac{119}{120}\times \dfrac{25}{144}\]
\[E=\dfrac{119\times 5}{24\times 144}\]
\[E=\dfrac{595}{2736}\]
So, we get the value of \[\dfrac{{{\sin }^{2}}\theta -{{\cos }^{2}}\theta }{2\sin \theta \cos \theta }\times \dfrac{1}{{{\tan }^{2}}\theta }\] as \[\dfrac{595}{2736}\].
Note: In this question, students can also find \[\sin \theta \] by using \[{{\sin }^{2}}\theta +{{\cos }^{2}}\theta =1\]. After getting \[\sin \theta \], students can find \[\tan \theta \] by using \[\tan \theta =\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }\]. Also, students must keep in mind that when nothing is given about the angle, we should always consider it in the first quadrant, i.e between 0 to \[\dfrac{\pi }{2}\] and in this case all trigonometric ratios would be positive.Students should remember important trigonometric ratios for solving these types of questions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 11 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




