
If both the roots of $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$ are negative, then
$
{\text{A}}{\text{. }}\Delta {\text{ > 0,ab > 0,bc < 0}} \\
{\text{B}}{\text{. }}\Delta {\text{ > 0,a,b,c,have same sign}} \\
{\text{C}}{\text{. }}\Delta {\text{ < 0,ab > 0,ac < 0}} \\
{\text{D}}{\text{. }}\Delta {\text{ < 0,ab > 0,bc > 0}} \\
$
Answer
613.2k+ views
Hint:- To solve this question we have to make diagram to understand clearly and here two diagram is possible for both roots negative one will be upward parabola and another will be downward parabola depending on value of a that means on coefficient of ${x^2}$.
Complete step-by-step solution -
We have,
$a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$
Since both roots are negative, then the diagram of equation $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$ that is parabola lies to the left of y-axis. Now, here two cases are possible: one will be an upward parabola for(a>0) and another will be the downward parabola(a<0).
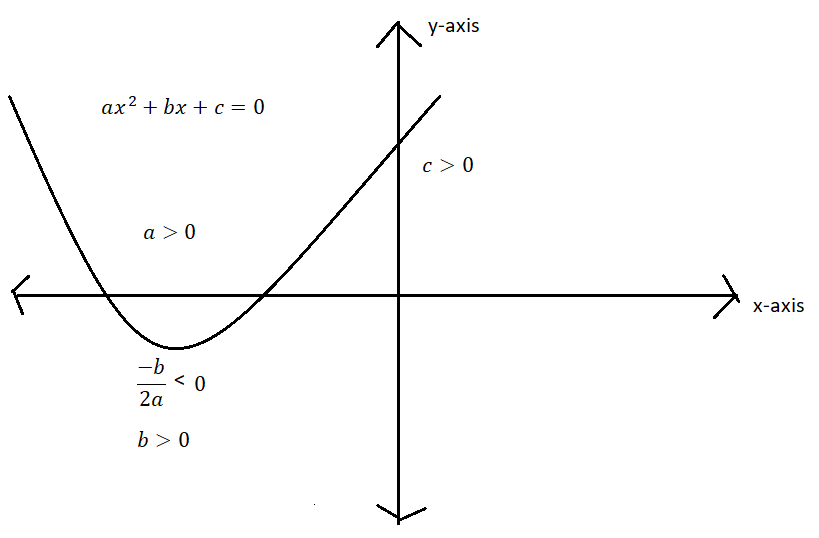
Consider the case in which $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$ is upward parabola because it depends on the coefficient
of ${x^2}$that is a > 0. On forming its diagram as seen below we can observe that the y intercept i.e. when x=0 the equation gives us the c>0. And the point where differentiation of equation $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$ is equal to gives us the condition that $\dfrac{{ - b}}{{2a}} < 0$. Since a>0 then b>0. Since, the diagram of $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$ cuts the x-axis at two real points then $\Delta > 0$.
From above discussion we can write that
$a > 0,b > 0,c > 0{\text{ and }}\Delta > 0$ eq.1
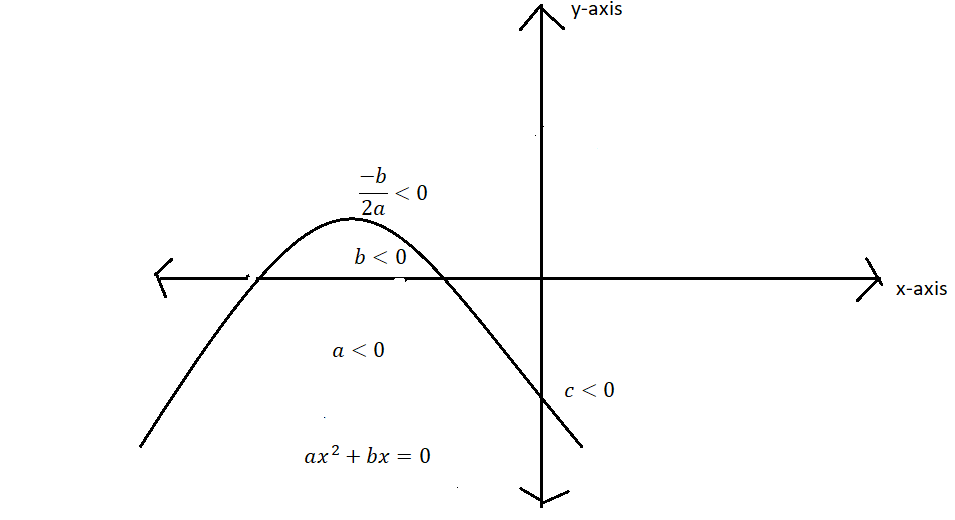
Now, consider the second case in which $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$ is downward parabola because it depends on the coefficient of ${x^2}$that is a < 0. On forming its diagram as seen below we can observe that the y intercept i.e. when x=0 the equation gives us a condition that c<0 . And the point where differentiation of equation $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$ is equal to zero gives us the condition that $\dfrac{{ - b}}{{2a}} < 0$. Since, a < 0 then b < 0. Since, the diagram of $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$ cuts the x-axis at two real points then $\Delta > 0$.
From above discussion we can write that
$a < 0,b < 0,c < 0{\text{ and }}\Delta > 0$ eq.2
From, eq.1 and eq.2 we can write that
$\Delta > 0,{\text{ }}a,b,c{\text{ have the same sign}}$.
Hence, option B. is correct.
Note:- Whenever you get this type of question the key concept to solve this is to learn the different diagrams of equation $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$ under different conditions. And one more thing to be remember is that if graph of some equation intersect y-axis below x-axis then y-intercept is negative and if intersect y-axis above x-axis then y-intercept is positive.
Complete step-by-step solution -
We have,
$a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$
Since both roots are negative, then the diagram of equation $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$ that is parabola lies to the left of y-axis. Now, here two cases are possible: one will be an upward parabola for(a>0) and another will be the downward parabola(a<0).
Consider the case in which $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$ is upward parabola because it depends on the coefficient
of ${x^2}$that is a > 0. On forming its diagram as seen below we can observe that the y intercept i.e. when x=0 the equation gives us the c>0. And the point where differentiation of equation $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$ is equal to gives us the condition that $\dfrac{{ - b}}{{2a}} < 0$. Since a>0 then b>0. Since, the diagram of $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$ cuts the x-axis at two real points then $\Delta > 0$.
From above discussion we can write that
$a > 0,b > 0,c > 0{\text{ and }}\Delta > 0$ eq.1

Now, consider the second case in which $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$ is downward parabola because it depends on the coefficient of ${x^2}$that is a < 0. On forming its diagram as seen below we can observe that the y intercept i.e. when x=0 the equation gives us a condition that c<0 . And the point where differentiation of equation $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$ is equal to zero gives us the condition that $\dfrac{{ - b}}{{2a}} < 0$. Since, a < 0 then b < 0. Since, the diagram of $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$ cuts the x-axis at two real points then $\Delta > 0$.
From above discussion we can write that
$a < 0,b < 0,c < 0{\text{ and }}\Delta > 0$ eq.2

From, eq.1 and eq.2 we can write that
$\Delta > 0,{\text{ }}a,b,c{\text{ have the same sign}}$.
Hence, option B. is correct.
Note:- Whenever you get this type of question the key concept to solve this is to learn the different diagrams of equation $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$ under different conditions. And one more thing to be remember is that if graph of some equation intersect y-axis below x-axis then y-intercept is negative and if intersect y-axis above x-axis then y-intercept is positive.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




