
If b > a, then prove that the length of the tangent drawn from any point on circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+a=0$ to the circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+b=0$ is $\sqrt{b-a}$.
Answer
616.5k+ views
Hint: For solving this problem, we first show the condition of the length of tangent using a diagram. Also, the relation between tangent and equation of a circle at a point is important. Then by using this property, we can prove the desired result.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the question, we are given two equations of a circle. So, let the inner circle with constant as a be equation (1) and outer circle with constant b be (2):
$\begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+a=0\ldots (1) \\
& {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+b=0\ldots (2) \\
\end{align}$
Now, the length of the tangent can be shown by using the diagram as:
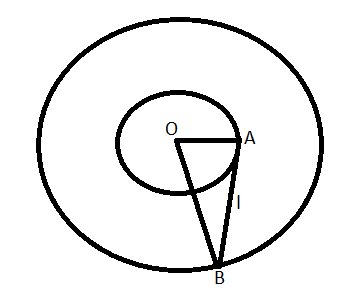
Also, we know that length of tangent to any circle at a point is equal to the square root value of the circle at that point. This can be mathematically expressed as:
For a circle with equation ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+c=0$, the length of tangent at (l, m) would be:
$Length=\sqrt{{{l}^{2}}+{{m}^{2}}+2gl+2fm+c}$
Consider a point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ on the inner circle such that it satisfies the circle equation. Therefore, we form equation (3) as:
$\begin{align}
& {{x}_{1}}^{2}+{{y}_{1}}^{2}+2g{{x}_{1}}+2f{{y}_{1}}+a=0 \\
& \therefore {{x}_{1}}^{2}+{{y}_{1}}^{2}+2g{{x}_{1}}+2f{{y}_{1}}=-a\ldots (3) \\
\end{align}$
Now, the length of tangent from point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ to outer circle would be:
$l=\sqrt{{{x}_{1}}^{2}+{{y}_{1}}^{2}+2g{{x}_{1}}+2f{{y}_{1}}+b}\ldots (4)$
Putting the values from equation (3) into (4), we get
$l=\sqrt{b-a}$
Since the left-hand side and right-hand side of the equation are equal, we proved the equivalence of both sides. So, we obtain the desired result.
Note: The key concept for solving this problem is the knowledge of length of tangent at a point on any circle. It is a very important property of geometry and is very helpful in solving complex problems without dealing with much calculation. So, the length of tangent is obtained easily
Complete step by step answer:
According to the question, we are given two equations of a circle. So, let the inner circle with constant as a be equation (1) and outer circle with constant b be (2):
$\begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+a=0\ldots (1) \\
& {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+b=0\ldots (2) \\
\end{align}$
Now, the length of the tangent can be shown by using the diagram as:

Also, we know that length of tangent to any circle at a point is equal to the square root value of the circle at that point. This can be mathematically expressed as:
For a circle with equation ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+c=0$, the length of tangent at (l, m) would be:
$Length=\sqrt{{{l}^{2}}+{{m}^{2}}+2gl+2fm+c}$
Consider a point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ on the inner circle such that it satisfies the circle equation. Therefore, we form equation (3) as:
$\begin{align}
& {{x}_{1}}^{2}+{{y}_{1}}^{2}+2g{{x}_{1}}+2f{{y}_{1}}+a=0 \\
& \therefore {{x}_{1}}^{2}+{{y}_{1}}^{2}+2g{{x}_{1}}+2f{{y}_{1}}=-a\ldots (3) \\
\end{align}$
Now, the length of tangent from point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ to outer circle would be:
$l=\sqrt{{{x}_{1}}^{2}+{{y}_{1}}^{2}+2g{{x}_{1}}+2f{{y}_{1}}+b}\ldots (4)$
Putting the values from equation (3) into (4), we get
$l=\sqrt{b-a}$
Since the left-hand side and right-hand side of the equation are equal, we proved the equivalence of both sides. So, we obtain the desired result.
Note: The key concept for solving this problem is the knowledge of length of tangent at a point on any circle. It is a very important property of geometry and is very helpful in solving complex problems without dealing with much calculation. So, the length of tangent is obtained easily
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




