
If \[A\left( { - 2,1} \right),B\left( {a,0} \right),C\left( {4,b} \right){\text{ }}and{\text{ }}D\left( {1,2} \right)\]are the vertices of a parallelogram ABCD, find the values of a and b. Hence find the lengths of its sides.
Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint: As this is a parallelogram, then we using the property of a parallelogram that diagonals bisect each other. Then to find the coordinates of an intersecting point of a parallelogram we will use a midpoint formula. For every coordinate of an intersecting point we will get two equations as we have two diagonals. Then substituting them we will get the value of a and b. Then by using distance formula we will find the length of the sides.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given sides of parallelogram \[A\left( { - 2,1} \right),B\left( {a,0} \right),C\left( {4,b} \right){\text{ }}and{\text{ }}D\left( {1,2} \right)\]
We know that diagonals of Parallelogram bisect each other.
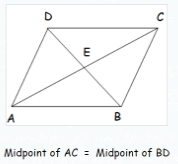
Mid-point let say E of diagonal AC is given by
\[x = \dfrac{{({x_1} + {x_2})}}{2}and\;y = \dfrac{{({y_1} + {y_2})}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{( - 2 + 4)}}{2}and\;y = \dfrac{{(1 + b)}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = 1\;and\;y = \dfrac{{(1 + b)}}{2}\] …………………..(1)
So, the coordinates of E are $\left( {1,\dfrac{{1 + b}}{2}} \right)$
Mid-point let say E of diagonal BD is given by
\[x = \dfrac{{({x_1} + {x_2})}}{2}and\;y = \dfrac{{({y_1} + {y_2})}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{(a + 1)}}{2}and\;y = \dfrac{{(0 + 2)}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{(a + 1)}}{2}and\;y = 1\]…………………..(2)
So, the coordinates of E are $\left( {\dfrac{{a + 1}}{2},1} \right)$
Equating the corresponding coordinates of both midpoints, we get the value of a and b
Lets equate the value of x first and try to find the value of a from equation (1) and equation (2).
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{a + 1}}{2} = 1$
$ \Rightarrow a = 1$
Lets equate the value of y now and try to find the value of b from equation (1) and equation (2).
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{1 + b}}{2} = 1$
$ \Rightarrow b = 1$
Now the Given coordinates of the parallelogram are written as
\[A\left( { - 2,1} \right),B\left( {1,0} \right),C\left( {4,1} \right){\text{ }}and{\text{ }}D\left( {1,2} \right)\]
By distance formula, \[\sqrt {{{\left( {{x_{2}} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}} \]
we can find the length of each side
\[ \Rightarrow AB = \sqrt {{{\left( { - 2 - 2} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {1 - 0} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {10} \]………………………………..(3)
AB = CD (As they are pair of opposite sides of the parallelogram)……………………………..(4)
\[ \Rightarrow BC = \sqrt {{{\left( {4 - 1} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {1 - 0} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {10} \]………………………………(5)
BC = AD (As they are pair of opposite sides of the parallelogram)……………………………..(6)
By combining the equation (3), equation (4), equation (5) and equation (6) we get:-
$ \Rightarrow AB = BC = CD = AD = \sqrt {10} $
So, this implies that ABCD is a Rhombus.
The length of the sides is equal to 10.
Note: Just remember some of the important points while solving these kind of questions:-
In the ordered pair (a, b) order is important, ‘a' represents x coordinate and ‘b’ represents y coordinate Cross Check whether you have correctly substituted the coordinates.
Do not perform many steps at a time. Solve systematically.
You should know the conditions:
Vertices of right triangle: sides satisfy Pythagoras theorem.
Vertices of square: All sides & both the diagonals are equal.
Circumcentre: Distance between circumcentre & point on circle is radius.
Vertices of rectangle: Opposite sides are equal & satisfies Pythagoras theorem
Diagonals of Parallelogram bisect each other.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given sides of parallelogram \[A\left( { - 2,1} \right),B\left( {a,0} \right),C\left( {4,b} \right){\text{ }}and{\text{ }}D\left( {1,2} \right)\]
We know that diagonals of Parallelogram bisect each other.

Mid-point let say E of diagonal AC is given by
\[x = \dfrac{{({x_1} + {x_2})}}{2}and\;y = \dfrac{{({y_1} + {y_2})}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{( - 2 + 4)}}{2}and\;y = \dfrac{{(1 + b)}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = 1\;and\;y = \dfrac{{(1 + b)}}{2}\] …………………..(1)
So, the coordinates of E are $\left( {1,\dfrac{{1 + b}}{2}} \right)$
Mid-point let say E of diagonal BD is given by
\[x = \dfrac{{({x_1} + {x_2})}}{2}and\;y = \dfrac{{({y_1} + {y_2})}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{(a + 1)}}{2}and\;y = \dfrac{{(0 + 2)}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{(a + 1)}}{2}and\;y = 1\]…………………..(2)
So, the coordinates of E are $\left( {\dfrac{{a + 1}}{2},1} \right)$
Equating the corresponding coordinates of both midpoints, we get the value of a and b
Lets equate the value of x first and try to find the value of a from equation (1) and equation (2).
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{a + 1}}{2} = 1$
$ \Rightarrow a = 1$
Lets equate the value of y now and try to find the value of b from equation (1) and equation (2).
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{1 + b}}{2} = 1$
$ \Rightarrow b = 1$
Now the Given coordinates of the parallelogram are written as
\[A\left( { - 2,1} \right),B\left( {1,0} \right),C\left( {4,1} \right){\text{ }}and{\text{ }}D\left( {1,2} \right)\]
By distance formula, \[\sqrt {{{\left( {{x_{2}} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}} \]
we can find the length of each side
\[ \Rightarrow AB = \sqrt {{{\left( { - 2 - 2} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {1 - 0} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {10} \]………………………………..(3)
AB = CD (As they are pair of opposite sides of the parallelogram)……………………………..(4)
\[ \Rightarrow BC = \sqrt {{{\left( {4 - 1} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {1 - 0} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {10} \]………………………………(5)
BC = AD (As they are pair of opposite sides of the parallelogram)……………………………..(6)
By combining the equation (3), equation (4), equation (5) and equation (6) we get:-
$ \Rightarrow AB = BC = CD = AD = \sqrt {10} $
So, this implies that ABCD is a Rhombus.
The length of the sides is equal to 10.
Note: Just remember some of the important points while solving these kind of questions:-
In the ordered pair (a, b) order is important, ‘a' represents x coordinate and ‘b’ represents y coordinate Cross Check whether you have correctly substituted the coordinates.
Do not perform many steps at a time. Solve systematically.
You should know the conditions:
Vertices of right triangle: sides satisfy Pythagoras theorem.
Vertices of square: All sides & both the diagonals are equal.
Circumcentre: Distance between circumcentre & point on circle is radius.
Vertices of rectangle: Opposite sides are equal & satisfies Pythagoras theorem
Diagonals of Parallelogram bisect each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE





