
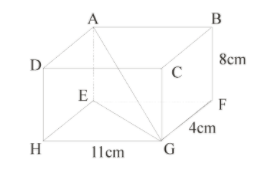
If ABCDEFGH is a cuboid , find length of AG

Answer
602.1k+ views
Hint: Cuboid – Cuboids are three-dimensional shapes which consist of six faces, eight vertices and twelve edges. Length, width and height of a cuboid are different.
Properties of cuboids.
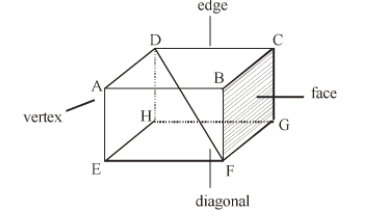
1. A cuboid is made up of six rectangles, each of the rectangles is called the face. In the figure above, ABFE, DAEH, DCGH, CBFG, ABCD and EFGH are the 6 faces of cuboid.
2. Base of cuboid – Any face of a cuboid may be called as the base of cuboid.
3. Edges – The edge of the cuboid is a line segment between any two adjacent vertices.
There are 12 edges. AB, AD, AE, HD, HE, HG, GF, GC, FE, FB, EF and CD
Opposite edges of a cuboid are equal.
4. Vertices – The point of intersection of the 3 edges of a cuboid is called the vertex of a cuboid.
A cuboid has 8 vertices
A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H
“All of a cuboid corners (vertices) are 90 degree angles”
5. Diagonal of cuboid – The length of diagonal of the cuboid of given by :
Diagonal of the cuboid $ = \sqrt {({l^2} + {b^2} + {h^2})} $
Complete step by step solution: It is given that in cuboid ABCDEFGH.
$HG = 11cm$
$FG = 4cm$
$BF = 8cm$
We have to find AG
In $\Delta EFG,$ angle $EFG = 90^\circ $
Because we know that “all of a cuboids”
And it is given that
$EF = 11cm$ (as opposite sides are equal)
$FG = 4cm$ (given)
So by using Pythagoras theorem we will find EG.
As EG is hypotenuse of triangle EFG so,
$E{G^2} = E{F^2} + F{G^2}$
$E{G^2} = {11^2} + {4^2}$
$E{G^2} = 137$
or
$EG = \sqrt {137} cm$ …..(1)
Now,
In $\Delta AEG,$ angle $AEG = 90^\circ $ (vertex of cuboid)
$AE = 8cm$ (given)
$EG = \sqrt {137} cm$ [from equation (1)]
So we can apply Pythagoras theorem in this triangle.
In $\Delta AEG$
$A{G^2} = A{E^2} + E{G^2}$
$A{G^2} = {8^2} + {(\sqrt {137} )^2}$
$A{G^2} = 64 + 137$
$A{G^2} = 201$
$AG = \sqrt {201} $
or
$AG = 14.17cm$
So, If ABCDEFGH is a cuboid. Then length of $AG = 14.17cm$
Note: We can also solve this question by the following method.
We know that in cuboid ABCDEFGH,
AG is the diagonal of cuboid.
So we can directly use the formula for cuboid diagonal.
Diagonal of the cuboid $ = \sqrt {({l^2} + {b^2} + {h^2})} $
Where
$l = length = HG = 11cm$
$b = breadth = FG = 4cm$
$h = height = BF = 8cm$
Substitute these values in above formula,
$AG = \sqrt {({{11}^2} + {4^2} + {8^2})} $
$AG = \sqrt {(121 + 16 + 64)} $
$AG = \sqrt {201} $
$AG = 14.17cm$

Properties of cuboids.
1. A cuboid is made up of six rectangles, each of the rectangles is called the face. In the figure above, ABFE, DAEH, DCGH, CBFG, ABCD and EFGH are the 6 faces of cuboid.
2. Base of cuboid – Any face of a cuboid may be called as the base of cuboid.
3. Edges – The edge of the cuboid is a line segment between any two adjacent vertices.
There are 12 edges. AB, AD, AE, HD, HE, HG, GF, GC, FE, FB, EF and CD
Opposite edges of a cuboid are equal.
4. Vertices – The point of intersection of the 3 edges of a cuboid is called the vertex of a cuboid.
A cuboid has 8 vertices
A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H
“All of a cuboid corners (vertices) are 90 degree angles”
5. Diagonal of cuboid – The length of diagonal of the cuboid of given by :
Diagonal of the cuboid $ = \sqrt {({l^2} + {b^2} + {h^2})} $
Complete step by step solution: It is given that in cuboid ABCDEFGH.
$HG = 11cm$
$FG = 4cm$
$BF = 8cm$
We have to find AG
In $\Delta EFG,$ angle $EFG = 90^\circ $
Because we know that “all of a cuboids”
And it is given that
$EF = 11cm$ (as opposite sides are equal)
$FG = 4cm$ (given)
So by using Pythagoras theorem we will find EG.
As EG is hypotenuse of triangle EFG so,
$E{G^2} = E{F^2} + F{G^2}$
$E{G^2} = {11^2} + {4^2}$
$E{G^2} = 137$
or
$EG = \sqrt {137} cm$ …..(1)
Now,
In $\Delta AEG,$ angle $AEG = 90^\circ $ (vertex of cuboid)
$AE = 8cm$ (given)
$EG = \sqrt {137} cm$ [from equation (1)]
So we can apply Pythagoras theorem in this triangle.
In $\Delta AEG$
$A{G^2} = A{E^2} + E{G^2}$
$A{G^2} = {8^2} + {(\sqrt {137} )^2}$
$A{G^2} = 64 + 137$
$A{G^2} = 201$
$AG = \sqrt {201} $
or
$AG = 14.17cm$
So, If ABCDEFGH is a cuboid. Then length of $AG = 14.17cm$
Note: We can also solve this question by the following method.
We know that in cuboid ABCDEFGH,
AG is the diagonal of cuboid.
So we can directly use the formula for cuboid diagonal.
Diagonal of the cuboid $ = \sqrt {({l^2} + {b^2} + {h^2})} $
Where
$l = length = HG = 11cm$
$b = breadth = FG = 4cm$
$h = height = BF = 8cm$
Substitute these values in above formula,
$AG = \sqrt {({{11}^2} + {4^2} + {8^2})} $
$AG = \sqrt {(121 + 16 + 64)} $
$AG = \sqrt {201} $
$AG = 14.17cm$
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the capital city of Australia? A) Sydney B) Melbourne C) Brisbane D) Canberra

How many millions make a billion class 6 maths CBSE

Give 10 examples for herbs , shrubs , climbers , creepers

Why is democracy considered as the best form of go class 6 social science CBSE

The planet nearest to earth is A Mercury B Venus C class 6 social science CBSE

Which country first gave women the right to vote?





