
If ABCDEF is regular hexagon and O is center also $\overrightarrow { AB } +\overrightarrow { AC } +\overrightarrow { AD } +\overrightarrow { AE } +\overrightarrow { AF } =t\overrightarrow { AO }$ then find the value of t.
A. 3
B. 2
C. 6
D. 8

Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, first draw the vectors asked in the question in the given diagram. Then use the concepts of vector algebra. Use the vector addition through triangle law of vector addition in which two vectors to be added is represented as a side of triangle and resultant vector is the third side of the triangle. Using this find the terms of the expression given in the question and thus, find the value of t.
Complete answer:
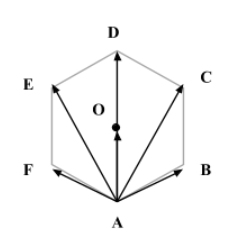
Given: $\overrightarrow { AB } +\overrightarrow { AC } +\overrightarrow { AD } +\overrightarrow { AE } +\overrightarrow { AF } =t\overrightarrow { AO }$ …(1)
From the figure drawn above, we can see $\overrightarrow {AC}$ is a resultant vector of $\overrightarrow {AO}$ and $\overrightarrow {AB}$.
$\Rightarrow \overrightarrow { AC } =\overrightarrow { AB } +\overrightarrow { AO }$ …(2)
Similarly, $\overrightarrow {AE}$ is a resultant vector of $\overrightarrow {AO}$ and $\overrightarrow {AF}$.
$\Rightarrow \overrightarrow { AE } =\overrightarrow { AF } +\overrightarrow { AO }$ …(3)
Substituting equation. (2) and (3) on the left-hand side of the equation. (1} we get,
$L.H.S= \overrightarrow { AB } +\overrightarrow { AB } +\overrightarrow {AO} +\overrightarrow { AD } +\overrightarrow { AF } +\overrightarrow { AO } +\overrightarrow { AF }$
$\Rightarrow L.H.S= 2\overrightarrow {AB}+2\overrightarrow {AO}+2\overrightarrow {AF}+\overrightarrow {AD}$ …(4)
In the figure, we can see $\overrightarrow {AD}=2\overrightarrow {AO}$
Substituting this value in the equation. (4) we get,
$ L.H.S= 2\overrightarrow {AB}+2\overrightarrow {AO}+2\overrightarrow {AF}+2\overrightarrow {AO}$
$\Rightarrow L.H.S= 2\overrightarrow {AB}+4\overrightarrow {AO}+2\overrightarrow {AF}$
$\Rightarrow L.H.S=2\left( \overrightarrow { AB } +\overrightarrow { AF } \right) +4\overrightarrow { AO }$ …(5)
From the figure drawn above, we can infer that $\overrightarrow {AO}$ is a resultant vector of $\overrightarrow {AB}$ and $\overrightarrow {AF}$.
$\Rightarrow \overrightarrow { AO } =\overrightarrow { AB } +\overrightarrow { AF }$ …(6)
Substituting equation. (6) in equation. (5) we get,
$L.H.S= 2\overrightarrow { AO } +4\overrightarrow { AO }$
$\Rightarrow L.H.S= 6\overrightarrow { AO }$ …(7)
Now, comparing equations. (7} with equation. (1) we get,
$t=6$
Hence, the value of t is 6.
Note:
To solve these types of questions, students must be aware of the use of vectors. They should also know the triangle law of vector addition. Major part of this problem could be solved without much calculation and just by using the symmetry of geometrical shape given. But it would make the problem trivial. So, it is important to solve this problem using basic principles of vector and not overcomplicate the problem.
Complete answer:

Given: $\overrightarrow { AB } +\overrightarrow { AC } +\overrightarrow { AD } +\overrightarrow { AE } +\overrightarrow { AF } =t\overrightarrow { AO }$ …(1)
From the figure drawn above, we can see $\overrightarrow {AC}$ is a resultant vector of $\overrightarrow {AO}$ and $\overrightarrow {AB}$.
$\Rightarrow \overrightarrow { AC } =\overrightarrow { AB } +\overrightarrow { AO }$ …(2)
Similarly, $\overrightarrow {AE}$ is a resultant vector of $\overrightarrow {AO}$ and $\overrightarrow {AF}$.
$\Rightarrow \overrightarrow { AE } =\overrightarrow { AF } +\overrightarrow { AO }$ …(3)
Substituting equation. (2) and (3) on the left-hand side of the equation. (1} we get,
$L.H.S= \overrightarrow { AB } +\overrightarrow { AB } +\overrightarrow {AO} +\overrightarrow { AD } +\overrightarrow { AF } +\overrightarrow { AO } +\overrightarrow { AF }$
$\Rightarrow L.H.S= 2\overrightarrow {AB}+2\overrightarrow {AO}+2\overrightarrow {AF}+\overrightarrow {AD}$ …(4)
In the figure, we can see $\overrightarrow {AD}=2\overrightarrow {AO}$
Substituting this value in the equation. (4) we get,
$ L.H.S= 2\overrightarrow {AB}+2\overrightarrow {AO}+2\overrightarrow {AF}+2\overrightarrow {AO}$
$\Rightarrow L.H.S= 2\overrightarrow {AB}+4\overrightarrow {AO}+2\overrightarrow {AF}$
$\Rightarrow L.H.S=2\left( \overrightarrow { AB } +\overrightarrow { AF } \right) +4\overrightarrow { AO }$ …(5)
From the figure drawn above, we can infer that $\overrightarrow {AO}$ is a resultant vector of $\overrightarrow {AB}$ and $\overrightarrow {AF}$.
$\Rightarrow \overrightarrow { AO } =\overrightarrow { AB } +\overrightarrow { AF }$ …(6)
Substituting equation. (6) in equation. (5) we get,
$L.H.S= 2\overrightarrow { AO } +4\overrightarrow { AO }$
$\Rightarrow L.H.S= 6\overrightarrow { AO }$ …(7)
Now, comparing equations. (7} with equation. (1) we get,
$t=6$
Hence, the value of t is 6.
Note:
To solve these types of questions, students must be aware of the use of vectors. They should also know the triangle law of vector addition. Major part of this problem could be solved without much calculation and just by using the symmetry of geometrical shape given. But it would make the problem trivial. So, it is important to solve this problem using basic principles of vector and not overcomplicate the problem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




