
If ABCD is a quadrilateral such that $ \overline{AB}=2\widehat{i}-3\widehat{j}+\widehat{k} $ , $ \overline{BC}=\widehat{i}+\widehat{j}+\widehat{k} $ , $ \overline{CD}=4\widehat{i}-7\widehat{j} $ . Then find $ \overline{AD} $ .
Answer
595.8k+ views
Hint: As ABCD is a quadrilateral, we can use the rule of vector addition of a polygon to solve the above question. According to the rule the sum of the vectors forming all the sides of the polygon such that the tail of one vector coincides with the head of the other vector is zero. Also, use the identity that $ \overline{DA}=-\overline{AD} $ .
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us start the solution to the above question by drawing a representative diagram of the situation given in the question.
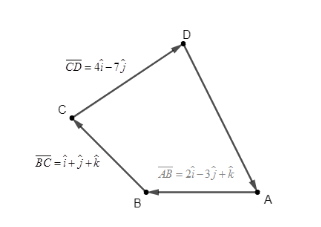
We know that according to the polygon law of vector addition the sum of the vectors forming all the sides of the polygon such that the tail of one vector coincides with the head of the other vector is zero. So, if we apply this on quadrilateral ABCD, we get
$ \overline{AB}+\overline{BC}+\overline{CD}+\overline{DA}=0 $
Now it is given that $ \overline{AB}=2\widehat{i}-3\widehat{j}+\widehat{k} $ , $ \overline{BC}=\widehat{i}+\widehat{j}+\widehat{k} $ , $ \overline{CD}=4\widehat{i}-7\widehat{j} $ . So, if we put this values in the above equation, we get
\[2\widehat{i}-3\widehat{j}+\widehat{k}+\widehat{i}+\widehat{j}+\widehat{k}+4\widehat{i}-7\widehat{j}+\overline{DA}=0\]
We also know that $ \overline{DA}=-\overline{AD} $ .
\[2\widehat{i}-3\widehat{j}+\widehat{k}+\widehat{i}+\widehat{j}+\widehat{k}+4\widehat{i}-7\widehat{j}-\overline{AD}=0\]
\[\Rightarrow 7\widehat{i}-9\widehat{j}+2\widehat{k}=\overline{AD}\]
Hence, the answer to the above question is \[\overline{AD}=7\widehat{i}-9\widehat{j}+2\widehat{k}\] .
Note: While adding the vectors, remember that the coefficients of $ \widehat{i},\widehat{j}\text{ and }\widehat{k} $ are added separately and reported. Also, you should know that polygon law is an extension of triangle law of vector addition and the above question could have been solved using triangle law as well, but that would have been a bit lengthier. Also, remember that for applying the polygon law, the head of one vector must coincide with the tail of the other and directions of vectors are very important.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us start the solution to the above question by drawing a representative diagram of the situation given in the question.

We know that according to the polygon law of vector addition the sum of the vectors forming all the sides of the polygon such that the tail of one vector coincides with the head of the other vector is zero. So, if we apply this on quadrilateral ABCD, we get
$ \overline{AB}+\overline{BC}+\overline{CD}+\overline{DA}=0 $
Now it is given that $ \overline{AB}=2\widehat{i}-3\widehat{j}+\widehat{k} $ , $ \overline{BC}=\widehat{i}+\widehat{j}+\widehat{k} $ , $ \overline{CD}=4\widehat{i}-7\widehat{j} $ . So, if we put this values in the above equation, we get
\[2\widehat{i}-3\widehat{j}+\widehat{k}+\widehat{i}+\widehat{j}+\widehat{k}+4\widehat{i}-7\widehat{j}+\overline{DA}=0\]
We also know that $ \overline{DA}=-\overline{AD} $ .
\[2\widehat{i}-3\widehat{j}+\widehat{k}+\widehat{i}+\widehat{j}+\widehat{k}+4\widehat{i}-7\widehat{j}-\overline{AD}=0\]
\[\Rightarrow 7\widehat{i}-9\widehat{j}+2\widehat{k}=\overline{AD}\]
Hence, the answer to the above question is \[\overline{AD}=7\widehat{i}-9\widehat{j}+2\widehat{k}\] .
Note: While adding the vectors, remember that the coefficients of $ \widehat{i},\widehat{j}\text{ and }\widehat{k} $ are added separately and reported. Also, you should know that polygon law is an extension of triangle law of vector addition and the above question could have been solved using triangle law as well, but that would have been a bit lengthier. Also, remember that for applying the polygon law, the head of one vector must coincide with the tail of the other and directions of vectors are very important.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




