
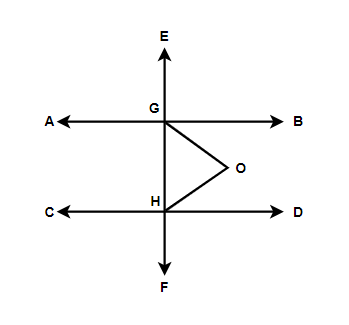
If $AB||CD$ $GO{\text{ and HO}}$ bisect $\angle BGH$ and $\angle GHD$ respectively. Prove that $\angle GOH = {90^ \circ }$ .

Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: As we can see that $GO{\text{ and HO}}$ bisects angle $\angle BGH$ and $\angle GHD$ , which means $GO{\text{ and HO}}$ cuts angle $\angle BGH$ and $\angle GHD$ into two equal angles, as $AB||CD$ so both angles will be ${90^ \circ }$ . Therefore from the property of the sum of interior angles of a triangle, we can prove that $\angle GOH = {90^ \circ }$ .
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that when two lines are parallel to each other and a line passes by two lines which are perpendicular to each other, then the angle made by the line is ${90^ \circ }$ .
So the angle \[\;\angle BGH = \angle DHG = {90^ \circ }\]
Also, it is given in the question that $GO{\text{ and HO}}$ bisects angle $\angle BGH$ and $\angle GHD$ , which means
\[\; \Rightarrow \angle BGO = \angle OGH = \angle DHO = \angle GHO = {45^ \circ }\]
Now by using the property of the sum of angles of interior angle, the sum of the interior angles of a triangle will be ${180^ \circ }$ .
Therefore, from the above property, we can say
In triangle $\vartriangle GHO$ by using the properties
\[\; \Rightarrow \angle OGH + \angle GHO + \angle HOG = {180^ \circ }\]
And we also know that \[\angle OGH = \angle GHO = {45^ \circ }\]
Therefore, the equation can be written as
\[\; \Rightarrow \angle OGH + \angle GHO + \angle HOG = {180^ \circ }\]
And on substituting the known values, we get
\[\; \Rightarrow {45^ \circ } + {45^ \circ } + \angle GOH = {180^ \circ }\]
And on solving the above equation, we get
\[\; \Rightarrow {90^ \circ } + \angle GOH = {180^ \circ }\]
Now taking the constant term to the right side of the equation, we get
\[\; \Rightarrow \angle GOH = {180^ \circ } - {90^ \circ }\]
Now on subtracting on the right side of the equation, we get
\[\; \Rightarrow \angle GOH = {90^ \circ }\]
Therefore, it is proved that \[\angle GOH = {90^ \circ }\] .
Note: Here for this question, we should always keep in mind that the sum of interior angles of a triangle is always ${180^ \circ }$ , when two lines are parallel and a line perpendicular to it cuts the parallel lines, then it cuts both at ${90^ \circ }$ . And for solving such types of problems easily we should have to remember or memorize some important geometric properties.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that when two lines are parallel to each other and a line passes by two lines which are perpendicular to each other, then the angle made by the line is ${90^ \circ }$ .
So the angle \[\;\angle BGH = \angle DHG = {90^ \circ }\]
Also, it is given in the question that $GO{\text{ and HO}}$ bisects angle $\angle BGH$ and $\angle GHD$ , which means
\[\; \Rightarrow \angle BGO = \angle OGH = \angle DHO = \angle GHO = {45^ \circ }\]
Now by using the property of the sum of angles of interior angle, the sum of the interior angles of a triangle will be ${180^ \circ }$ .
Therefore, from the above property, we can say
In triangle $\vartriangle GHO$ by using the properties
\[\; \Rightarrow \angle OGH + \angle GHO + \angle HOG = {180^ \circ }\]
And we also know that \[\angle OGH = \angle GHO = {45^ \circ }\]
Therefore, the equation can be written as
\[\; \Rightarrow \angle OGH + \angle GHO + \angle HOG = {180^ \circ }\]
And on substituting the known values, we get
\[\; \Rightarrow {45^ \circ } + {45^ \circ } + \angle GOH = {180^ \circ }\]
And on solving the above equation, we get
\[\; \Rightarrow {90^ \circ } + \angle GOH = {180^ \circ }\]
Now taking the constant term to the right side of the equation, we get
\[\; \Rightarrow \angle GOH = {180^ \circ } - {90^ \circ }\]
Now on subtracting on the right side of the equation, we get
\[\; \Rightarrow \angle GOH = {90^ \circ }\]
Therefore, it is proved that \[\angle GOH = {90^ \circ }\] .
Note: Here for this question, we should always keep in mind that the sum of interior angles of a triangle is always ${180^ \circ }$ , when two lines are parallel and a line perpendicular to it cuts the parallel lines, then it cuts both at ${90^ \circ }$ . And for solving such types of problems easily we should have to remember or memorize some important geometric properties.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE





