
If $a,b,c$ and $u,v,w$ are complex numbers representing the vertices of two triangles such that $c=\left( 1-r \right)a+rb$ and $w=\left( 1-r \right)u+rv$ , where $r$ is a complex number, then the two triangles.
(a) have the same area
(b) are similar
(c) are congruent
(d) none of these
Answer
611.7k+ views
Hint: For solving this question first we will see one important concept that, if there are two complex numbers ${{Z}_{1}}$ and ${{Z}_{2}}$ represented by points $P$ and $Q$ respectively. Then, the length of the segment $PQ=\left| {{Z}_{1}}-{{Z}_{2}} \right|$ . After that, we will find the length of the sides of the given triangles and try to establish a relation between them by taking their ratio and solving for the correct result.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given:
It is given that if $a,b,c$ and $u,v,w$ are complex numbers representing the vertices of two triangles such that $c=\left( 1-r \right)a+rb$ and $w=\left( 1-r \right)u+rv$ , where $r$ is a complex number.
Now, before we proceed we should know one important concept that, if there are two complex numbers ${{Z}_{1}}$ and ${{Z}_{2}}$ represented by points $P$ and $Q$ respectively. Then, the length of the segment $PQ=\left| {{Z}_{1}}-{{Z}_{2}} \right|$ . For more clarity look at the figure given below:
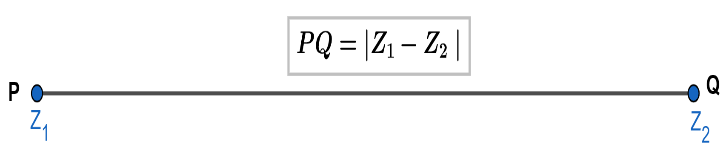
Now, we will use the above concept to solve this question.
Now, let there be a $\Delta ABC$ with vertices at complex numbers $a,b,c$ . For more clarity look at the figure given below:
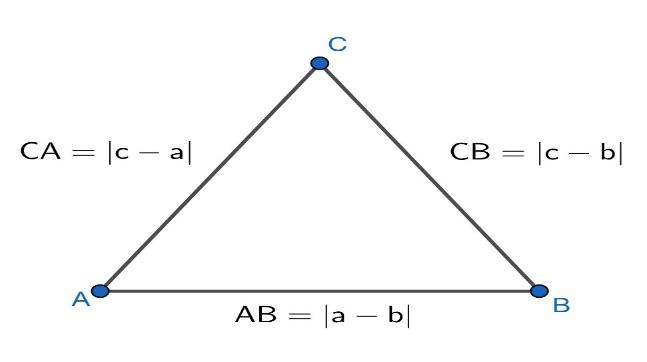
Now, as it is given that, $c=\left( 1-r \right)a+rb$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& AB=\left| a-b \right| \\
& CA=\left| c-a \right| \\
& \Rightarrow CA=\left| \left( 1-r \right)a+rb-a \right| \\
& \Rightarrow CA=\left| rb-ra \right| \\
& \Rightarrow CA=\left| r\left( b-a \right) \right| \\
& \Rightarrow CA=\left| r\left( a-b \right) \right| \\
& CB=\left| c-b \right| \\
& \Rightarrow CB=\left| \left( 1-r \right)a+rb-b \right| \\
& \Rightarrow CB=\left| \left( 1-r \right)a-\left( 1-r \right)b \right| \\
& \Rightarrow CB=\left| \left( 1-r \right)\left( a-b \right) \right| \\
\end{align}$
Now, from the above results calculate the value of $\dfrac{AB}{CA}$ and $\dfrac{AB}{CB}$ . Then,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{AB}{CA}=\dfrac{\left| a-b \right|}{\left| r\left( a-b \right) \right|} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{AB}{CA}=\dfrac{1}{\left| r \right|}.......................\left( 1 \right) \\
& \dfrac{AB}{CB}=\dfrac{\left| a-b \right|}{\left| \left( 1-r \right)\left( a-b \right) \right|} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{AB}{CB}=\dfrac{1}{\left| 1-r \right|}..................\left( 2 \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Now, let there be a $\Delta UVW$ with vertices at complex numbers $u,v,w$ . For more clarity look at the figure given below:
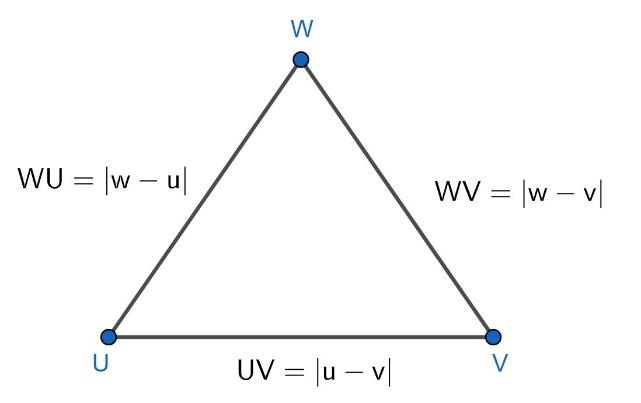
Now, as it is given that, $w=\left( 1-r \right)u+rv$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& UV=\left| u-v \right| \\
& WU=\left| w-u \right| \\
& \Rightarrow WU=\left| \left( 1-r \right)u+rv-u \right| \\
& \Rightarrow WU=\left| rv-ru \right| \\
& \Rightarrow WU=\left| r\left( v-u \right) \right| \\
& \Rightarrow WU=\left| r\left( u-v \right) \right| \\
& WV=\left| w-v \right| \\
& \Rightarrow WV=\left| \left( 1-r \right)u+rv-v \right| \\
& \Rightarrow WV=\left| \left( 1-r \right)u-\left( 1-r \right)v \right| \\
& \Rightarrow WV=\left| \left( 1-r \right)\left( u-v \right) \right| \\
\end{align}$
Now, from the above results calculate the value of $\dfrac{UV}{WU}$ and $\dfrac{UV}{WV}$ . Then,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{UV}{WU}=\dfrac{\left| u-v \right|}{\left| r\left( u-v \right) \right|} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{UV}{WU}=\dfrac{1}{\left| r \right|}.......................\left( 3 \right) \\
& \dfrac{UV}{WV}=\dfrac{\left| u-v \right|}{\left| \left( 1-r \right)\left( u-v \right) \right|} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{UV}{WV}=\dfrac{1}{\left| 1-r \right|}..................\left( 4 \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Now, compare equation (1) and (3). Then,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{AB}{CA}=\dfrac{UV}{WU}=\dfrac{1}{\left| r \right|} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{AB}{CA}=\dfrac{UV}{WU}.................\left( 5 \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Now, compare equation (2) and (4). Then,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{AB}{CB}=\dfrac{UV}{WV}=\dfrac{1}{\left| 1-r \right|} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{AB}{CB}=\dfrac{UV}{WV}....................\left( 6 \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Now, in $\Delta ABC$ and $\Delta UVW$ , we have the following results:
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{AB}{CA}=\dfrac{UV}{WU} \\
& \dfrac{AB}{CB}=\dfrac{UV}{WV} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{CB}{AB}=\dfrac{WV}{UV} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{CB}{AB}\times \dfrac{AB}{CA}=\dfrac{WV}{UV}\times \dfrac{WV}{WU} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{CB}{CA}=\dfrac{UV}{WU} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, from the above result, we can say that in $\Delta ABC$ and $\Delta UVW$ the ratio of corresponding sides is equal.
Now, we conclude that $\Delta ABC\sim \Delta UVW$ .
Thus, the two triangles will be similar.
Hence, (b) is the correct option.
Note: Here, the student should first understand what is asked in the problem and then proceed in the right direction. Moreover, we should apply the concept of length of the segment between any two complex numbers correctly. After that, we should proceed stepwise without any mistake and solve for the correct answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given:
It is given that if $a,b,c$ and $u,v,w$ are complex numbers representing the vertices of two triangles such that $c=\left( 1-r \right)a+rb$ and $w=\left( 1-r \right)u+rv$ , where $r$ is a complex number.
Now, before we proceed we should know one important concept that, if there are two complex numbers ${{Z}_{1}}$ and ${{Z}_{2}}$ represented by points $P$ and $Q$ respectively. Then, the length of the segment $PQ=\left| {{Z}_{1}}-{{Z}_{2}} \right|$ . For more clarity look at the figure given below:
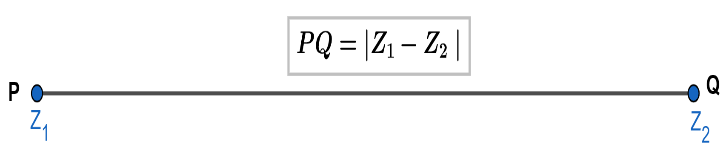
Now, we will use the above concept to solve this question.
Now, let there be a $\Delta ABC$ with vertices at complex numbers $a,b,c$ . For more clarity look at the figure given below:

Now, as it is given that, $c=\left( 1-r \right)a+rb$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& AB=\left| a-b \right| \\
& CA=\left| c-a \right| \\
& \Rightarrow CA=\left| \left( 1-r \right)a+rb-a \right| \\
& \Rightarrow CA=\left| rb-ra \right| \\
& \Rightarrow CA=\left| r\left( b-a \right) \right| \\
& \Rightarrow CA=\left| r\left( a-b \right) \right| \\
& CB=\left| c-b \right| \\
& \Rightarrow CB=\left| \left( 1-r \right)a+rb-b \right| \\
& \Rightarrow CB=\left| \left( 1-r \right)a-\left( 1-r \right)b \right| \\
& \Rightarrow CB=\left| \left( 1-r \right)\left( a-b \right) \right| \\
\end{align}$
Now, from the above results calculate the value of $\dfrac{AB}{CA}$ and $\dfrac{AB}{CB}$ . Then,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{AB}{CA}=\dfrac{\left| a-b \right|}{\left| r\left( a-b \right) \right|} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{AB}{CA}=\dfrac{1}{\left| r \right|}.......................\left( 1 \right) \\
& \dfrac{AB}{CB}=\dfrac{\left| a-b \right|}{\left| \left( 1-r \right)\left( a-b \right) \right|} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{AB}{CB}=\dfrac{1}{\left| 1-r \right|}..................\left( 2 \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Now, let there be a $\Delta UVW$ with vertices at complex numbers $u,v,w$ . For more clarity look at the figure given below:

Now, as it is given that, $w=\left( 1-r \right)u+rv$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& UV=\left| u-v \right| \\
& WU=\left| w-u \right| \\
& \Rightarrow WU=\left| \left( 1-r \right)u+rv-u \right| \\
& \Rightarrow WU=\left| rv-ru \right| \\
& \Rightarrow WU=\left| r\left( v-u \right) \right| \\
& \Rightarrow WU=\left| r\left( u-v \right) \right| \\
& WV=\left| w-v \right| \\
& \Rightarrow WV=\left| \left( 1-r \right)u+rv-v \right| \\
& \Rightarrow WV=\left| \left( 1-r \right)u-\left( 1-r \right)v \right| \\
& \Rightarrow WV=\left| \left( 1-r \right)\left( u-v \right) \right| \\
\end{align}$
Now, from the above results calculate the value of $\dfrac{UV}{WU}$ and $\dfrac{UV}{WV}$ . Then,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{UV}{WU}=\dfrac{\left| u-v \right|}{\left| r\left( u-v \right) \right|} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{UV}{WU}=\dfrac{1}{\left| r \right|}.......................\left( 3 \right) \\
& \dfrac{UV}{WV}=\dfrac{\left| u-v \right|}{\left| \left( 1-r \right)\left( u-v \right) \right|} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{UV}{WV}=\dfrac{1}{\left| 1-r \right|}..................\left( 4 \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Now, compare equation (1) and (3). Then,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{AB}{CA}=\dfrac{UV}{WU}=\dfrac{1}{\left| r \right|} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{AB}{CA}=\dfrac{UV}{WU}.................\left( 5 \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Now, compare equation (2) and (4). Then,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{AB}{CB}=\dfrac{UV}{WV}=\dfrac{1}{\left| 1-r \right|} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{AB}{CB}=\dfrac{UV}{WV}....................\left( 6 \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Now, in $\Delta ABC$ and $\Delta UVW$ , we have the following results:
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{AB}{CA}=\dfrac{UV}{WU} \\
& \dfrac{AB}{CB}=\dfrac{UV}{WV} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{CB}{AB}=\dfrac{WV}{UV} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{CB}{AB}\times \dfrac{AB}{CA}=\dfrac{WV}{UV}\times \dfrac{WV}{WU} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{CB}{CA}=\dfrac{UV}{WU} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, from the above result, we can say that in $\Delta ABC$ and $\Delta UVW$ the ratio of corresponding sides is equal.
Now, we conclude that $\Delta ABC\sim \Delta UVW$ .
Thus, the two triangles will be similar.
Hence, (b) is the correct option.
Note: Here, the student should first understand what is asked in the problem and then proceed in the right direction. Moreover, we should apply the concept of length of the segment between any two complex numbers correctly. After that, we should proceed stepwise without any mistake and solve for the correct answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

The draft of the Preamble of the Indian Constitution class 10 social science CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who gave "Inqilab Zindabad" slogan?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?




