
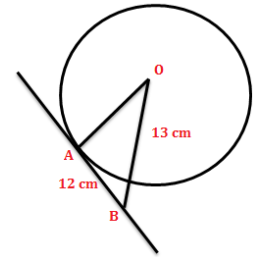
If AB is the tangent to the circle at the point A and OB = 13 cm, find the radius OA.
(a). 5 cm
(b). 7 cm
(c). 8 cm
(d). 9 cm

Answer
623.1k+ views
Hint: In a circle, tangent line and radius are always perpendicular. You can find the length of OA that is the radius of the circle by using Pythagoras theorem.
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is given that AB is the tangent to the circle at the point A and length of the OB is 13 cm.
From the figure, the length of the tangent AB is 12 cm.
We know that,
The relation between the tangent line and radius of the circle, the radius of a circle is perpendicular to the tangent line through its endpoint on the circle's circumference.
If the tangent line and radius are always perpendicular, then it makes an angle ${{90}^{0}}$.
In the figure, the triangle OAB is a right angled triangle.
Now applying the Pythagoras theorem on the triangle OAB, we get
${{(OB)}^{2}}={{(OA)}^{2}}+{{(AB)}^{2}}$
Put the length of the sides OB and AB, we get
${{(13)}^{2}}={{(OA)}^{2}}+{{(12)}^{2}}$
$169={{(OA)}^{2}}+144$
Rearranging the terms, we get
${{(OA)}^{2}}=169-144$
${{(OA)}^{2}}=25$
${{(OA)}^{2}}={{5}^{2}}$
Taking the square root on the both sides, we get
$OA=\pm 5$
Since OA is the radius of the circle, it is always positive.
$OA=5$
Hence, the radius of the given circle is 5 cm.
Therefore, the correct option for the given question is option (a).
Note: You might get confused with the converse statement of the relation between radius of the circle and tangent line. The radius of a circle is perpendicular to the tangent line through its endpoint on the circle's circumference. Conversely, the perpendicular to a radius through the same endpoint is a tangent line.
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is given that AB is the tangent to the circle at the point A and length of the OB is 13 cm.
From the figure, the length of the tangent AB is 12 cm.
We know that,
The relation between the tangent line and radius of the circle, the radius of a circle is perpendicular to the tangent line through its endpoint on the circle's circumference.
If the tangent line and radius are always perpendicular, then it makes an angle ${{90}^{0}}$.
In the figure, the triangle OAB is a right angled triangle.
Now applying the Pythagoras theorem on the triangle OAB, we get
${{(OB)}^{2}}={{(OA)}^{2}}+{{(AB)}^{2}}$
Put the length of the sides OB and AB, we get
${{(13)}^{2}}={{(OA)}^{2}}+{{(12)}^{2}}$
$169={{(OA)}^{2}}+144$
Rearranging the terms, we get
${{(OA)}^{2}}=169-144$
${{(OA)}^{2}}=25$
${{(OA)}^{2}}={{5}^{2}}$
Taking the square root on the both sides, we get
$OA=\pm 5$
Since OA is the radius of the circle, it is always positive.
$OA=5$
Hence, the radius of the given circle is 5 cm.
Therefore, the correct option for the given question is option (a).
Note: You might get confused with the converse statement of the relation between radius of the circle and tangent line. The radius of a circle is perpendicular to the tangent line through its endpoint on the circle's circumference. Conversely, the perpendicular to a radius through the same endpoint is a tangent line.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

State and explain Ohms law class 10 physics CBSE

Distinguish between soap and detergent class 10 chemistry CBSE

a Why did Mendel choose pea plants for his experiments class 10 biology CBSE

What is a "free hit" awarded for in limited-overs cricket?

Draw the diagram of the sectional view of the human class 10 biology CBSE




