
If A(2,-1), B(3,4), C(-2,3) and D(-3,-2) be four points in a coordinate plane, show that ABCD is a rhombus but not a square. Find the area of the rhombus.
(a) 28 sq. units
(b) 32 sq. units
(c) 24 sq. units
(d) 20 sq. units
Answer
598.2k+ views
Hint: Start by trying to prove that the given quadrilateral is a parallelogram by showing that each pair of opposite sides are parallel. Two lines are parallel if their slopes are equal and we know that the slope of the line passing through two given points is given by $m=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}$ . Once you prove that the quadrilateral is a parallelogram, prove that the diagonals are perpendicular and the adjacent sides are not to show that it is a rhombus. Two lines are perpendicular if the product of their slopes is equal to -1.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Let us start by drawing a representative diagram of the situation given above.
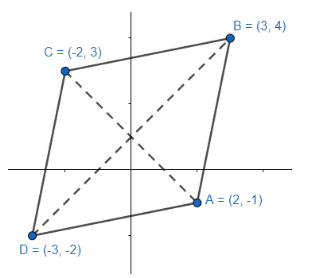
We know that the slope of the line passing through points $A({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})\text{ and }B({{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}})$ is given by $m=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}$ .
$m(AB)=\dfrac{-1-4}{2-3}=5$
$m(BC)=\dfrac{3-4}{-2-3}=\dfrac{1}{5}$
$m(CD)=\dfrac{3+2}{-2+3}=5$
$m(DA)=\dfrac{-2+1}{-3-2}=\dfrac{1}{5}$
$m(CA)=\dfrac{3+1}{-2-2}=-1$
$m(BD)=\dfrac{4+2}{3+3}=1$
As we can see that slopes of AB and CD are equal and the slopes of BC and DA are equal. So, the slopes of both the pairs of opposite sides are equal, so ABCD is a parallelogram.
Now let us move to the relation between the slope of the diagonals CA and BD. If we observe. We will find the product of their slope is equal to $-1\times 1=-1$ and we know that if the product of slope of two lines is equal to -1, then they are perpendicular. So, ABCD is a parallelogram with diagonals perpendicular, so either it is a square or a rhombus. Let us check whether the slope of adjacent sides AB and BC when multiplied gives -1 or not.
$m(AB)\times m(BC)=5\times \dfrac{1}{5}=1$
As the product is not -1, so the adjacent sides are not perpendicular, so ABCD is not a square. So, we can conclude that ABCD is a rhombus.
We know that the area of the rhombus is half of the product of its diagonal, so let us find the length of its diagonals using distance formula.
Now, according to the distance formula, the distance between two points $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\text{ and }\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ is given by $\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}}$ .
$AC=\sqrt{{{\left( -2-2 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 3+1 \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{16+16}=4\sqrt{2}\text{ units}$
$BD=\sqrt{{{\left( 3+3 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 4+2 \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{36+36}=6\sqrt{2}\text{ units}$
Therefore, the area of the rhombus is:
$\dfrac{1}{2}\times {{d}_{1}}\times {{d}_{2}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\times AC\times BD=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 4\sqrt{2}\times 6\sqrt{2}=24uni{{t}^{2}}$
Therefore, the answer to the above question is option (c).
Note: Be careful and don’t get confused between the formula of areas of rhombus and trapezium and take the area to be half of the product of height and sum of the diagonals. Also, many times it is seen that students get confused and take the difference of the x-coordinates in the numerator while finding the slope, which is completely wrong and result in the reciprocal of the slope.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Let us start by drawing a representative diagram of the situation given above.

We know that the slope of the line passing through points $A({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})\text{ and }B({{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}})$ is given by $m=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}$ .
$m(AB)=\dfrac{-1-4}{2-3}=5$
$m(BC)=\dfrac{3-4}{-2-3}=\dfrac{1}{5}$
$m(CD)=\dfrac{3+2}{-2+3}=5$
$m(DA)=\dfrac{-2+1}{-3-2}=\dfrac{1}{5}$
$m(CA)=\dfrac{3+1}{-2-2}=-1$
$m(BD)=\dfrac{4+2}{3+3}=1$
As we can see that slopes of AB and CD are equal and the slopes of BC and DA are equal. So, the slopes of both the pairs of opposite sides are equal, so ABCD is a parallelogram.
Now let us move to the relation between the slope of the diagonals CA and BD. If we observe. We will find the product of their slope is equal to $-1\times 1=-1$ and we know that if the product of slope of two lines is equal to -1, then they are perpendicular. So, ABCD is a parallelogram with diagonals perpendicular, so either it is a square or a rhombus. Let us check whether the slope of adjacent sides AB and BC when multiplied gives -1 or not.
$m(AB)\times m(BC)=5\times \dfrac{1}{5}=1$
As the product is not -1, so the adjacent sides are not perpendicular, so ABCD is not a square. So, we can conclude that ABCD is a rhombus.
We know that the area of the rhombus is half of the product of its diagonal, so let us find the length of its diagonals using distance formula.
Now, according to the distance formula, the distance between two points $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\text{ and }\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ is given by $\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}}$ .
$AC=\sqrt{{{\left( -2-2 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 3+1 \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{16+16}=4\sqrt{2}\text{ units}$
$BD=\sqrt{{{\left( 3+3 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 4+2 \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{36+36}=6\sqrt{2}\text{ units}$
Therefore, the area of the rhombus is:
$\dfrac{1}{2}\times {{d}_{1}}\times {{d}_{2}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\times AC\times BD=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 4\sqrt{2}\times 6\sqrt{2}=24uni{{t}^{2}}$
Therefore, the answer to the above question is option (c).
Note: Be careful and don’t get confused between the formula of areas of rhombus and trapezium and take the area to be half of the product of height and sum of the diagonals. Also, many times it is seen that students get confused and take the difference of the x-coordinates in the numerator while finding the slope, which is completely wrong and result in the reciprocal of the slope.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




