
If a tangent having slope of $-\dfrac{4}{3}$ to the ellipse $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{18}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{32}=1$ intersects the major and minor axes in points $A$ and $B$ respectively, then the area of $\Delta OAB$ is equal to ( $O$ is the centre of the ellipse)
A. $24sq.units$
B. $48sq.units$
C. $64sq.units$
D. $24sq.units$
Answer
611.4k+ views
Hint: Assume point $L$ and use the general equation of tangent. You will get the values of $a,b$ and $m$ .
Put $x=0$ and $y=0$ , you will get the points as base and height. Try it.
Complete step by step answer:
Let $({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})$ consider $L({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})$ be a point on ellipse.
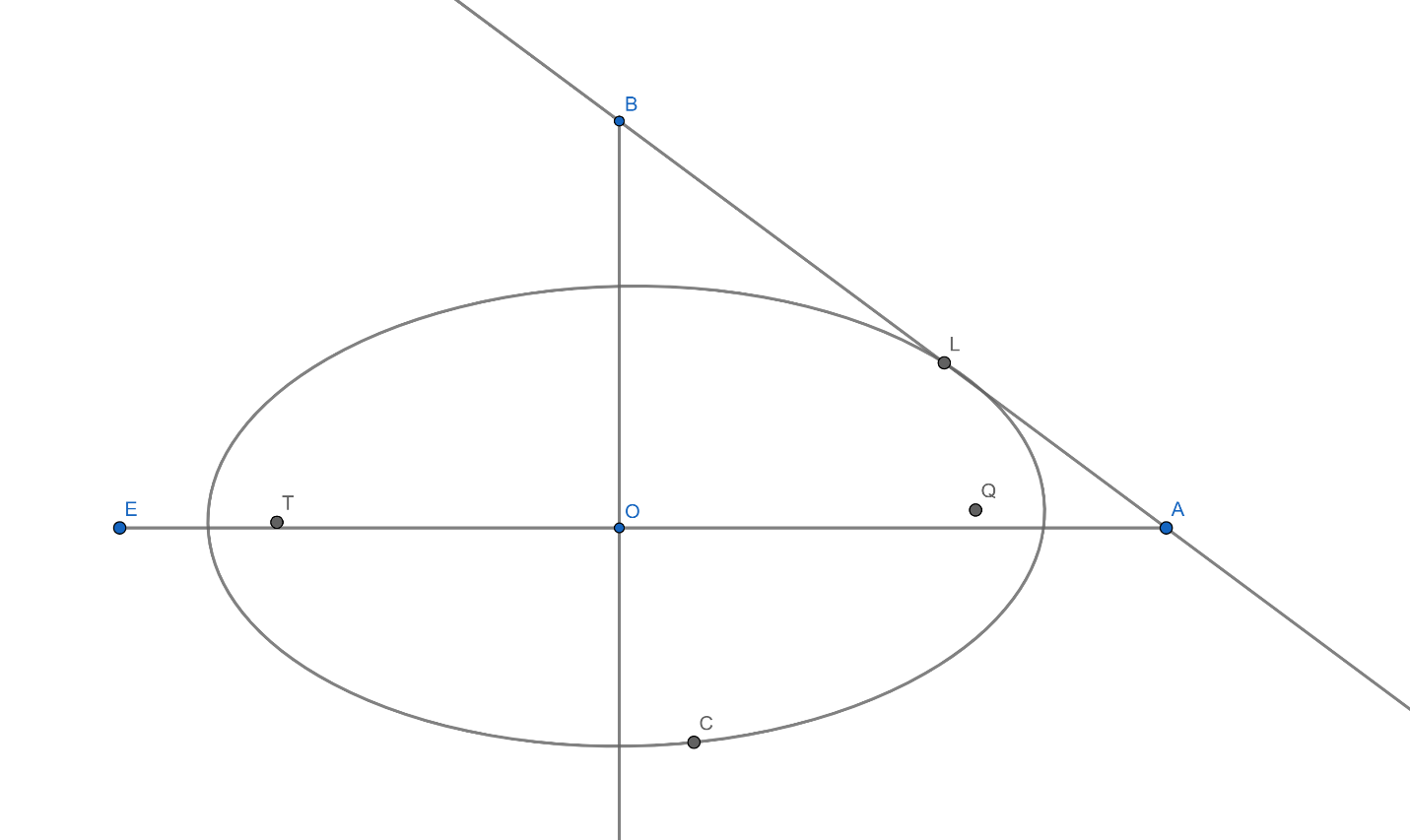
So the equation of ellipse is given as,
$\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{18}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{32}=1$………… (1)
So as the point $L$ is on ellipse so substituting $({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})$ in (1), we get,
$\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}^{2}}{18}+\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}^{2}}{32}=1$……………. (2)
So now we need the equation of tangent,
The equation of tangent to ellipse $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ at point $({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})$ is $\dfrac{x{{x}_{1}}}{a}+\dfrac{y{{y}_{1}}}{b}=1$ ,
So The equation of tangent at $({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})$ is
$\dfrac{x{{x}_{1}}}{18}+\dfrac{y{{y}_{1}}}{32}=1$,
So for above equation of tangent at $y=0$ we get $x-$ Coordinate as $\dfrac{18}{{{x}_{1}}}$ , i.e. $\left( \dfrac{18}{{{x}_{1}}},0 \right)$ .
And at $x=0$ we get $y-$ coordinate as $\dfrac{32}{{{y}_{1}}}$ , i.e. $\left( 0,\dfrac{32}{{{y}_{1}}} \right)$ .
So the equation of tangent meets the axes at $A\left( \dfrac{18}{{{x}_{1}}},0 \right)$ and $B\left( 0,\dfrac{32}{{{y}_{1}}} \right)$ .
Now we have given the slope of tangent at $({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})$ is $-\dfrac{4}{3}$ .
So $-\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}}{18}\times \dfrac{32}{{{y}_{1}}}=-\dfrac{4}{3}$
So now simplifying we get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{{{x}_{1}}}{{{y}_{1}}}=\dfrac{4\times 18}{32\times 3} \\
& \dfrac{{{x}_{1}}}{{{y}_{1}}}=\dfrac{6}{8} \\
\end{align}$
$\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}}{{{y}_{1}}}=\dfrac{3}{4}$
So let us write it as,
$\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}}{3}=\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}}{4}$
Let us say that $\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}}{3}=\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}}{4}=k$ .
Where k is any constant term,
So the points ${{x}_{1}}=3k$ and ${{y}_{1}}=4k$ ,
Now substituting ${{x}_{1}}$ and ${{y}_{1}}$ in equation (2) we get,
$\dfrac{{{(3k)}^{2}}}{18}+\dfrac{{{(4k)}^{2}}}{32}=1$
So simplifying we get,
$\dfrac{9{{k}^{2}}}{18}+\dfrac{16{{k}^{2}}}{32}=1$ ………………. (Here ${{\left( 3 \right)}^{2}}=9$ and ${{\left( 4 \right)}^{2}}=16$ )
Now taking ${{k}^{2}}$ as common we get,
${{k}^{2}}\left( \dfrac{9}{18}+\dfrac{16}{32} \right)=1$
So now simplifying the inner bracket we get,
$\begin{align}
& {{k}^{2}}\left( \dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{2} \right)=1 \\
& {{k}^{2}}\left( 1 \right)=1 \\
\end{align}$
So We get ${{k}^{2}}=1$ ………. (3)
So we want to find area of $\Delta OAB$ ,
So we know in general the area of the triangle is equal to $\dfrac{1}{2}\times base\times height$.
Area of $\Delta OAB$ $=\dfrac{1}{2}\times base\times height$
So in figure we can see that in $\Delta OAB$ ,
$\begin{align}
& OA=base=\dfrac{18}{{{x}_{1}}} \\
& OB=height=\dfrac{32}{{{y}_{1}}} \\
\end{align}$
So Area of $\Delta OAB$ $=\dfrac{1}{2}\times OA\times OB$
Area of $\Delta OAB$ $=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{18}{{{x}_{1}}}\times \dfrac{32}{{{y}_{1}}}$
We have calculated the value of ${{x}_{1}}$ and ${{y}_{1}}$ ,We know that value of ${{x}_{1}}=3k$ and ${{y}_{1}}=4k$ ,
So substituting the values of ${{x}_{1}}$ and ${{y}_{1}}$ , we get,
Area of $\Delta OAB$ $=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{18}{3k}\times \dfrac{32}{4k}$
Area of $\Delta OAB$ $=\dfrac{9\times 32}{3\times 4\times {{k}^{2}}}$
So simplifying it in simple manner we get,
Area of $\Delta OAB$ $=\dfrac{3\times 32}{4\times {{k}^{2}}}$
Area of $\Delta OAB$ $=\dfrac{3\times 8}{{{k}^{2}}}$
Area of $\Delta OAB$ $=\dfrac{24}{{{k}^{2}}}$
So we have found out the value of ${{k}^{2}}=1$ , from (3)
So substituting the value of ${{k}^{2}}$ in above we get,
Area of $\Delta OAB$ $=\dfrac{24}{{{1}^{2}}}$
Area of $\Delta OAB$ $=24sq.units$
So we got the Area of $\Delta OAB$ as $24sq.units$.
So the area of $\Delta OAB$ is $24sq.units$.
Note: So in the above problem read the question carefully. So be thorough with the concept as I have considered point $L$ so you should understand why I have considered it. So we can solve this problem by other method such as we know general equation of tangent $y=mx+\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}{{m}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}$
So $a=18,b=32$ and $m=-\dfrac{4}{3}$.
So substituting all values in above equation we get,
So we get final equation as,
$y=-\dfrac{4}{3}x+8$
So putting $x=0$ we get $y-coordinate$ as $8$ ,so $A(6,0)$ .
And that of $y=0$ we get $x-coordinate$as $6$, so $B(0,8)$.
So here $base=6$and $height=8$
So Area of $\Delta OAB$ $=\dfrac{1}{2}\times base\times height$
Area of $\Delta OAB$ $=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 6\times 8=24sq.units$
So in this way you can solve it.
Put $x=0$ and $y=0$ , you will get the points as base and height. Try it.
Complete step by step answer:
Let $({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})$ consider $L({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})$ be a point on ellipse.

So the equation of ellipse is given as,
$\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{18}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{32}=1$………… (1)
So as the point $L$ is on ellipse so substituting $({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})$ in (1), we get,
$\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}^{2}}{18}+\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}^{2}}{32}=1$……………. (2)
So now we need the equation of tangent,
The equation of tangent to ellipse $\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1$ at point $({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})$ is $\dfrac{x{{x}_{1}}}{a}+\dfrac{y{{y}_{1}}}{b}=1$ ,
So The equation of tangent at $({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})$ is
$\dfrac{x{{x}_{1}}}{18}+\dfrac{y{{y}_{1}}}{32}=1$,
So for above equation of tangent at $y=0$ we get $x-$ Coordinate as $\dfrac{18}{{{x}_{1}}}$ , i.e. $\left( \dfrac{18}{{{x}_{1}}},0 \right)$ .
And at $x=0$ we get $y-$ coordinate as $\dfrac{32}{{{y}_{1}}}$ , i.e. $\left( 0,\dfrac{32}{{{y}_{1}}} \right)$ .
So the equation of tangent meets the axes at $A\left( \dfrac{18}{{{x}_{1}}},0 \right)$ and $B\left( 0,\dfrac{32}{{{y}_{1}}} \right)$ .
Now we have given the slope of tangent at $({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})$ is $-\dfrac{4}{3}$ .
So $-\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}}{18}\times \dfrac{32}{{{y}_{1}}}=-\dfrac{4}{3}$
So now simplifying we get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{{{x}_{1}}}{{{y}_{1}}}=\dfrac{4\times 18}{32\times 3} \\
& \dfrac{{{x}_{1}}}{{{y}_{1}}}=\dfrac{6}{8} \\
\end{align}$
$\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}}{{{y}_{1}}}=\dfrac{3}{4}$
So let us write it as,
$\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}}{3}=\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}}{4}$
Let us say that $\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}}{3}=\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}}{4}=k$ .
Where k is any constant term,
So the points ${{x}_{1}}=3k$ and ${{y}_{1}}=4k$ ,
Now substituting ${{x}_{1}}$ and ${{y}_{1}}$ in equation (2) we get,
$\dfrac{{{(3k)}^{2}}}{18}+\dfrac{{{(4k)}^{2}}}{32}=1$
So simplifying we get,
$\dfrac{9{{k}^{2}}}{18}+\dfrac{16{{k}^{2}}}{32}=1$ ………………. (Here ${{\left( 3 \right)}^{2}}=9$ and ${{\left( 4 \right)}^{2}}=16$ )
Now taking ${{k}^{2}}$ as common we get,
${{k}^{2}}\left( \dfrac{9}{18}+\dfrac{16}{32} \right)=1$
So now simplifying the inner bracket we get,
$\begin{align}
& {{k}^{2}}\left( \dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{2} \right)=1 \\
& {{k}^{2}}\left( 1 \right)=1 \\
\end{align}$
So We get ${{k}^{2}}=1$ ………. (3)
So we want to find area of $\Delta OAB$ ,
So we know in general the area of the triangle is equal to $\dfrac{1}{2}\times base\times height$.
Area of $\Delta OAB$ $=\dfrac{1}{2}\times base\times height$
So in figure we can see that in $\Delta OAB$ ,
$\begin{align}
& OA=base=\dfrac{18}{{{x}_{1}}} \\
& OB=height=\dfrac{32}{{{y}_{1}}} \\
\end{align}$
So Area of $\Delta OAB$ $=\dfrac{1}{2}\times OA\times OB$
Area of $\Delta OAB$ $=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{18}{{{x}_{1}}}\times \dfrac{32}{{{y}_{1}}}$
We have calculated the value of ${{x}_{1}}$ and ${{y}_{1}}$ ,We know that value of ${{x}_{1}}=3k$ and ${{y}_{1}}=4k$ ,
So substituting the values of ${{x}_{1}}$ and ${{y}_{1}}$ , we get,
Area of $\Delta OAB$ $=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{18}{3k}\times \dfrac{32}{4k}$
Area of $\Delta OAB$ $=\dfrac{9\times 32}{3\times 4\times {{k}^{2}}}$
So simplifying it in simple manner we get,
Area of $\Delta OAB$ $=\dfrac{3\times 32}{4\times {{k}^{2}}}$
Area of $\Delta OAB$ $=\dfrac{3\times 8}{{{k}^{2}}}$
Area of $\Delta OAB$ $=\dfrac{24}{{{k}^{2}}}$
So we have found out the value of ${{k}^{2}}=1$ , from (3)
So substituting the value of ${{k}^{2}}$ in above we get,
Area of $\Delta OAB$ $=\dfrac{24}{{{1}^{2}}}$
Area of $\Delta OAB$ $=24sq.units$
So we got the Area of $\Delta OAB$ as $24sq.units$.
So the area of $\Delta OAB$ is $24sq.units$.
Note: So in the above problem read the question carefully. So be thorough with the concept as I have considered point $L$ so you should understand why I have considered it. So we can solve this problem by other method such as we know general equation of tangent $y=mx+\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}{{m}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}}$
So $a=18,b=32$ and $m=-\dfrac{4}{3}$.
So substituting all values in above equation we get,
So we get final equation as,
$y=-\dfrac{4}{3}x+8$
So putting $x=0$ we get $y-coordinate$ as $8$ ,so $A(6,0)$ .
And that of $y=0$ we get $x-coordinate$as $6$, so $B(0,8)$.
So here $base=6$and $height=8$
So Area of $\Delta OAB$ $=\dfrac{1}{2}\times base\times height$
Area of $\Delta OAB$ $=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 6\times 8=24sq.units$
So in this way you can solve it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




