
If a right circular cone, having maximum volume, is inscribed in a sphere of radius 3cm, then the curved surface area $\left( in\ c{{m}^{2}} \right)$ of this cone is,
A. $8\sqrt{3}\pi $
B. $6\sqrt{2}\pi $
C. $6\sqrt{3}\pi $
D. $8\sqrt{2}\pi $
Answer
616.8k+ views
Hint: Don’t hesitate with language and words of the question, here a right circular cone states to a cone in which the altitude of a cone is perpendicular to the circle of cones. And this question is from topic maxima and minima.
Complete step by step answer:
Now, first of all we have to sketch a diagram that is easy to understand, according to the given data.
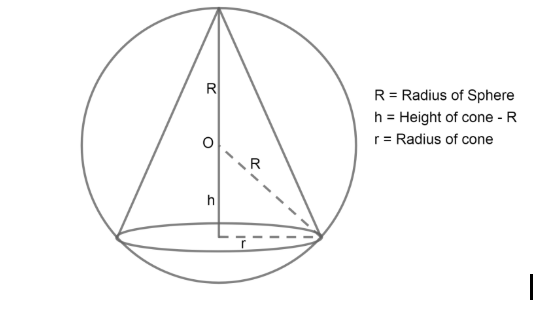
So, volume of cone V $=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{r}^{2}}H$; where r = radius of cone, H = height of cone.
$V=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \pi \times {{r}^{2}}\times \left( h+R \right)........\left( 1 \right)$
According to definition and Pythagoras Theorem,
${{r}^{2}}={{R}^{2}}-{{h}^{2}}...........\left( 2 \right)$
Using equation (1) and (2)
$V=\dfrac{\pi }{3}\times \left[ {{R}^{2}}-{{h}^{2}} \right]\times \left[ h+R \right]$
After putting R = 3cm in V the only variable remaining is ‘h’.
$V=\dfrac{\pi }{3}\times \left[ {{3}^{2}}-{{h}^{2}} \right]\times \left[ h+3 \right]......\left( 3 \right)$
Differentiate the V with respect to ‘h’ and equate to 0 (zero) to find the maxima of V.
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{dv}{dh}=\dfrac{\pi }{3}\times \left[ \left[ {{3}^{2}}-{{h}^{2}} \right]\left[ 1 \right]+\left[ -2h \right]\left[ h+3 \right] \right]=0 \\
& 9-{{h}^{2}}-2{{h}^{2}}-6h=0 \\
& 3{{h}^{2}}+6h-9=0 \\
& {{h}^{2}}+2h-3=0............\left( 4 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, find out the roots of equation (4) using formula $h=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}$ .
$\begin{align}
& h=\dfrac{-2\pm \sqrt{{{2}^{2}}-4\times 1\times \left( -3 \right)}}{2\times 1} \\
& h=\dfrac{-2\pm 4}{2}=-1\pm 2 \\
& h=-3\ and\ h=1 \\
\end{align}$
We will discard the h = 3, because we know height cannot be negative.
So, h = 1 and put h = 1 in equation (2) to get r.
$\begin{align}
& {{r}^{2}}={{3}^{2}}-{{1}^{2}}=9-1=8 \\
& r=\sqrt{8}=2\sqrt{2} \\
\end{align}$
And, there are only conical surfaces of a cone $=\pi rH$ .
$=\pi \times 2\sqrt{2}\times \left( 3+1 \right)$
So, the surface area of cone $=8\sqrt{2}\pi $.
Note: Here we didn’t check the h = 1 is a maxima or minima point because here we know the minimum possible volume of a cone inside the sphere can be zero (0).
Complete step by step answer:
Now, first of all we have to sketch a diagram that is easy to understand, according to the given data.

So, volume of cone V $=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{r}^{2}}H$; where r = radius of cone, H = height of cone.
$V=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \pi \times {{r}^{2}}\times \left( h+R \right)........\left( 1 \right)$
According to definition and Pythagoras Theorem,
${{r}^{2}}={{R}^{2}}-{{h}^{2}}...........\left( 2 \right)$
Using equation (1) and (2)
$V=\dfrac{\pi }{3}\times \left[ {{R}^{2}}-{{h}^{2}} \right]\times \left[ h+R \right]$
After putting R = 3cm in V the only variable remaining is ‘h’.
$V=\dfrac{\pi }{3}\times \left[ {{3}^{2}}-{{h}^{2}} \right]\times \left[ h+3 \right]......\left( 3 \right)$
Differentiate the V with respect to ‘h’ and equate to 0 (zero) to find the maxima of V.
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{dv}{dh}=\dfrac{\pi }{3}\times \left[ \left[ {{3}^{2}}-{{h}^{2}} \right]\left[ 1 \right]+\left[ -2h \right]\left[ h+3 \right] \right]=0 \\
& 9-{{h}^{2}}-2{{h}^{2}}-6h=0 \\
& 3{{h}^{2}}+6h-9=0 \\
& {{h}^{2}}+2h-3=0............\left( 4 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, find out the roots of equation (4) using formula $h=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}$ .
$\begin{align}
& h=\dfrac{-2\pm \sqrt{{{2}^{2}}-4\times 1\times \left( -3 \right)}}{2\times 1} \\
& h=\dfrac{-2\pm 4}{2}=-1\pm 2 \\
& h=-3\ and\ h=1 \\
\end{align}$
We will discard the h = 3, because we know height cannot be negative.
So, h = 1 and put h = 1 in equation (2) to get r.
$\begin{align}
& {{r}^{2}}={{3}^{2}}-{{1}^{2}}=9-1=8 \\
& r=\sqrt{8}=2\sqrt{2} \\
\end{align}$
And, there are only conical surfaces of a cone $=\pi rH$ .
$=\pi \times 2\sqrt{2}\times \left( 3+1 \right)$
So, the surface area of cone $=8\sqrt{2}\pi $.
Note: Here we didn’t check the h = 1 is a maxima or minima point because here we know the minimum possible volume of a cone inside the sphere can be zero (0).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




