
If A and B are two exhaustive events such that $P(A)=\dfrac{1}{2}$ and $P(B)=\dfrac{2}{3}$ , then
A.$P(A\cup B)\ge \dfrac{2}{3}$
B.$P(A\cap \overline{B})\le \dfrac{1}{3}$
C.$\dfrac{1}{6}\le P(A\cap B)\le \dfrac{1}{2}$
D.$\dfrac{1}{6}\le P(\overline{A}\cap B)\le \dfrac{1}{2}$
Answer
606.3k+ views
Hint: Treat P(A) and P(B) as two sets and form the Venn diagrams for each case. Also, focus on the meaning of the word exhaustive used in the question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Before moving to the question, let us talk about probability.
Probability in simple words is the possibility of an event to occur.
Probability can be mathematically defined as $=\dfrac{\text{number of favourable outcomes}}{\text{total number of outcomes}}$ .
Now, let’s move to the solution to the above question.
As it is given that the two events are exhaustive and two or more events are exhaustive when at least one of the events occurs compulsorily from the list of events, i.e., the probability of at least one of the events to occur is 1. So, we can say that $P\left( A\cup B \right)=1$ and 1 is greater than $\dfrac{2}{3}$ . Therefore, option (a) is correct.
Now we will treat P(A) and P(B) as two sets and try to represent the condition in the form of a Venn diagram. On doing so we get:
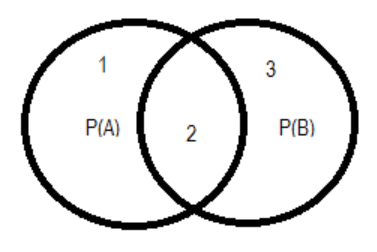
Region 1 represents $P(A)-P(A\cap B)$ , whole region 2 represents $P(A\cap B)$ and region 3 represents $P(B)-P(A\cap B)$.
Now we know that the sum of the regions 1, 2 and 3 is equal to 1. So, we get
$P(A)+P(B)-P(A\cap B)=1$
Now we will put the values given in the question. On doing so, we get
$\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{2}{3}-P(A\cap B)=1$
$\Rightarrow P(A\cap B)=\dfrac{1}{6}$
Therefore, option (c) is also correct. Also, we conclude that region 1 $=P(A)-P(A\cap B)=\dfrac{1}{3}$ and region 3 = $\dfrac{1}{2}$ .
Now $P(A\cap \overline{B})$ represents region 1, so its value $=P(A)-P(A\cap B)=\dfrac{1}{3}$ and $P(\overline{A}\cap B)$ represents region 3 which makes it equal to $\dfrac{1}{2}$ . Therefore, option (b) and option (d) are also correct.
So, all the options are correct.
Note: It is preferred that while solving a question as above always take the approach using the Venn diagram as it gives you a better visualisation of the question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Before moving to the question, let us talk about probability.
Probability in simple words is the possibility of an event to occur.
Probability can be mathematically defined as $=\dfrac{\text{number of favourable outcomes}}{\text{total number of outcomes}}$ .
Now, let’s move to the solution to the above question.
As it is given that the two events are exhaustive and two or more events are exhaustive when at least one of the events occurs compulsorily from the list of events, i.e., the probability of at least one of the events to occur is 1. So, we can say that $P\left( A\cup B \right)=1$ and 1 is greater than $\dfrac{2}{3}$ . Therefore, option (a) is correct.
Now we will treat P(A) and P(B) as two sets and try to represent the condition in the form of a Venn diagram. On doing so we get:

Region 1 represents $P(A)-P(A\cap B)$ , whole region 2 represents $P(A\cap B)$ and region 3 represents $P(B)-P(A\cap B)$.
Now we know that the sum of the regions 1, 2 and 3 is equal to 1. So, we get
$P(A)+P(B)-P(A\cap B)=1$
Now we will put the values given in the question. On doing so, we get
$\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{2}{3}-P(A\cap B)=1$
$\Rightarrow P(A\cap B)=\dfrac{1}{6}$
Therefore, option (c) is also correct. Also, we conclude that region 1 $=P(A)-P(A\cap B)=\dfrac{1}{3}$ and region 3 = $\dfrac{1}{2}$ .
Now $P(A\cap \overline{B})$ represents region 1, so its value $=P(A)-P(A\cap B)=\dfrac{1}{3}$ and $P(\overline{A}\cap B)$ represents region 3 which makes it equal to $\dfrac{1}{2}$ . Therefore, option (b) and option (d) are also correct.
So, all the options are correct.
Note: It is preferred that while solving a question as above always take the approach using the Venn diagram as it gives you a better visualisation of the question.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 12 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Complete reduction of benzene diazonium chloride with class 12 chemistry CBSE

How can you identify optical isomers class 12 chemistry CBSE

Trending doubts
What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

RNA and DNA are chiral molecules their chirality is class 12 chemistry CBSE

India is a sovereign socialist secular democratic republic class 12 social science CBSE

How many states of matter are there in total class 12 chemistry CBSE




