
If $A( - 2, - 1)$, $B(a,0)$ ,$C(4,b)$ and $D(1,2)$ are the vertices of a parallelogram, then the values of $a$ and $b$ are
A. 2,1
B. 1,3
C. -1,-3
D. 2,-3
Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint: In this question, we have to find values of vertices $a$ and $b$ of the parallelogram.
Diagonal is the line segment joining two vertices that are not on the same edges.
The midpoint of a line divides the line segment into two equal parts.
When the diagonals of the parallelogram bisect each other their intersection point is the midpoint of each diagonal.
Find the midpoint of the diagonals whose vertices are given and equate to each other.
Midpoint formula of the line:
$({x_m},{y_m}) = \left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)$
$({x_m},{y_m})$=midpoint coordinates
$({x_1},{y_1})$=coordinate of first vertex
$({x_2},{y_2})$=coordinate of second vertex
Complete step-by-step answer:
Consider $A( - 2, - 1)$, $B(a,0)$ ,$C(4,b)$ and $D(1,2)$ are the vertices of a parallelogram.
According to the properties of the parallelogram, the diagonal of the parallelogram bisect each other.
$\therefore$ The Midpoint of the diagonals are the same.
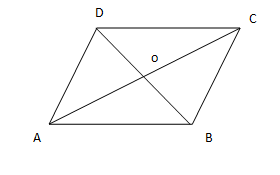
Consider the diagonals are $AC$ and $BD$, and the midpoint is $o$.
Determine the midpoint of the diagonal $AC$, given is $A( - 2, - 1)$, and $C(4,b)$ ,
$ \Rightarrow ({x_1},{y_1}) = ( - 2, - 1)$ and $({x_2},{y_2}) = (4,b)$
Midpoints $({x_m},{y_m}) = \left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)$
Substitute $({x_1},{y_1}) = ( - 2, - 1)$ and, $({x_2},{y_2}) = (4,b)$ into $({x_m},{y_m}) = \left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)$,
$({x_m},{y_m}) = \left( {\dfrac{{ - 2 + 4}}{2},\dfrac{{ - 1 + b}}{2}} \right)$
$({x_m},{y_m}) = \left( {1,\dfrac{{ - 1 + b}}{2}} \right) \ldots (1)$
Determine the midpoint of the diagonal $BD$, given is $B(a,0)$, and $D(1,2)$
$ \Rightarrow ({x_1},{y_1}) = (a,0)$ and, $({x_2},{y_2}) = (1,2)$
Midpoints $({x_m},{y_m}) = \left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)$
Substitute $({x_1},{y_1}) = (a,0)$ and, $({x_2},{y_2}) = (1,2)$into $({x_m},{y_m}) = \left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)$,
$({x_m},{y_m}) = \left( {\dfrac{{a + 1}}{2},\dfrac{{0 + 2}}{2}} \right)$
$({x_m},{y_m}) = \left( {\dfrac{{a + 1}}{2},1} \right) \ldots (2)$
Equate equations $(1)$ and $(2)$,
$\left( {\dfrac{{a + 1}}{2},1} \right) = \left( {1,\dfrac{{ - 1 + b}}{2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{a + 1}}{2} = 1$ and $\dfrac{{ - 1 + b}}{2} = 1$
Solve $\dfrac{{a + 1}}{2} = 1$ by cross multiplication,
$a + 1 = 2$
$ \Rightarrow a = 1$
Solve $\dfrac{{ - 1 + b}}{2} = 1$ by cross multiplication,
$ - 1 + b = 2$
$ \Rightarrow b = 3$
Correct Answer: B. 1,3
Note:
The important step is that When the diagonals of the parallelogram bisect each other their intersection point is the midpoint of each diagonal.
The midpoint of two points $({x_1},{y_1})$ and $({x_2},{y_2})$ is the point \[M\] found by the following formula,
$M = \left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)$
You basically are averaging the \[X\] and \[Y\] values.
Diagonal is the line segment joining two vertices that are not on the same edges.
The midpoint of a line divides the line segment into two equal parts.
When the diagonals of the parallelogram bisect each other their intersection point is the midpoint of each diagonal.
Find the midpoint of the diagonals whose vertices are given and equate to each other.
Midpoint formula of the line:
$({x_m},{y_m}) = \left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)$
$({x_m},{y_m})$=midpoint coordinates
$({x_1},{y_1})$=coordinate of first vertex
$({x_2},{y_2})$=coordinate of second vertex
Complete step-by-step answer:
Consider $A( - 2, - 1)$, $B(a,0)$ ,$C(4,b)$ and $D(1,2)$ are the vertices of a parallelogram.
According to the properties of the parallelogram, the diagonal of the parallelogram bisect each other.
$\therefore$ The Midpoint of the diagonals are the same.

Consider the diagonals are $AC$ and $BD$, and the midpoint is $o$.
Determine the midpoint of the diagonal $AC$, given is $A( - 2, - 1)$, and $C(4,b)$ ,
$ \Rightarrow ({x_1},{y_1}) = ( - 2, - 1)$ and $({x_2},{y_2}) = (4,b)$
Midpoints $({x_m},{y_m}) = \left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)$
Substitute $({x_1},{y_1}) = ( - 2, - 1)$ and, $({x_2},{y_2}) = (4,b)$ into $({x_m},{y_m}) = \left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)$,
$({x_m},{y_m}) = \left( {\dfrac{{ - 2 + 4}}{2},\dfrac{{ - 1 + b}}{2}} \right)$
$({x_m},{y_m}) = \left( {1,\dfrac{{ - 1 + b}}{2}} \right) \ldots (1)$
Determine the midpoint of the diagonal $BD$, given is $B(a,0)$, and $D(1,2)$
$ \Rightarrow ({x_1},{y_1}) = (a,0)$ and, $({x_2},{y_2}) = (1,2)$
Midpoints $({x_m},{y_m}) = \left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)$
Substitute $({x_1},{y_1}) = (a,0)$ and, $({x_2},{y_2}) = (1,2)$into $({x_m},{y_m}) = \left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)$,
$({x_m},{y_m}) = \left( {\dfrac{{a + 1}}{2},\dfrac{{0 + 2}}{2}} \right)$
$({x_m},{y_m}) = \left( {\dfrac{{a + 1}}{2},1} \right) \ldots (2)$
Equate equations $(1)$ and $(2)$,
$\left( {\dfrac{{a + 1}}{2},1} \right) = \left( {1,\dfrac{{ - 1 + b}}{2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{a + 1}}{2} = 1$ and $\dfrac{{ - 1 + b}}{2} = 1$
Solve $\dfrac{{a + 1}}{2} = 1$ by cross multiplication,
$a + 1 = 2$
$ \Rightarrow a = 1$
Solve $\dfrac{{ - 1 + b}}{2} = 1$ by cross multiplication,
$ - 1 + b = 2$
$ \Rightarrow b = 3$
Correct Answer: B. 1,3
Note:
The important step is that When the diagonals of the parallelogram bisect each other their intersection point is the midpoint of each diagonal.
The midpoint of two points $({x_1},{y_1})$ and $({x_2},{y_2})$ is the point \[M\] found by the following formula,
$M = \left( {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)$
You basically are averaging the \[X\] and \[Y\] values.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

State and explain Ohms law class 10 physics CBSE

Write a letter to the editor of a newspaper explaining class 10 english CBSE

Distinguish between soap and detergent class 10 chemistry CBSE

a Why did Mendel choose pea plants for his experiments class 10 biology CBSE

What is a "free hit" awarded for in limited-overs cricket?




