
If $15\cot {\text{A = 8}}$ is given to us , find $\sin {\text{A}}$ and $\sec {\text{A}}$.
Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint: In this question first we will manipulate the equation given in the equation. We will take $15$ on the R.H.S in denominator and then we will find the length of adjacent side and opposite side with the help of formula of $\cot $. Now, with the help of adjacent side and opposite side we will find the length of hypotenuse using Pythagoras theorem.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The information given in the question is $\cot {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{\text{8}}}{{15}}$. Therefore, from the given information we can say that Adjacent side $ = 8$ and opposite side $ = 15$ because we know that $\cot {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{{\text{Adjacent side}}}}{{{\text{opposite side}}}}$.
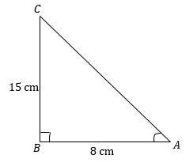
Now, we have to find out the hypotenuse of the right angle triangle with the help of the formula ${H^2} = {B^2} + {A^2}$where $H$ is hypotenuse, $B$ is the base and $A$ is the altitude of the triangle.
Now, ${H^2} = {B^2} + {A^2}\_\_(1)$
The value of $B = 8\,cm$ and the value of $A = 15\,cm$. Put this value in equation $(1)$
\[ \Rightarrow {H^2} = {8^2} + {15^2}\]
We know that ${8^2} = 64$ and ${15^2} = 225$
\[ \Rightarrow {H^2} = 64 + 225 = 289\]
We know that $289$ is the square of $17$. Therefore, we can write
\[ \Rightarrow H = \sqrt {289} = 17\]
Therefore, we got the length of the hypotenuse of the right angle triangle is $17cm$.
From the figure we can say that the length of ${\text{AC}}$is $17cm$.
Now, with the help of the hypotenuse we will able to find the $\sin {\text{A}}$and $\sec {\text{A}}$
We know that $\sin {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{{\text{opposite side}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}$. Therefore, we can write $\sin {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{{\text{BC}}}}{{{\text{AC}}}}$.
Therefore, we can write $\sin {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{{\text{BC}}}}{{{\text{AC}}}} = \dfrac{{15}}{{17}}$.
Similarly, We know that $\sec {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}{{{\text{Adjacent side}}}}$. Therefore, we can write $\sec {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{{\text{AC}}}}{{{\text{AB}}}}$.
Therefore, we can write $\sec {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{{\text{AC}}}}{{{\text{AB}}}} = \dfrac{{17}}{8}$.
Therefore, the answer is $\sin {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{15}}{{17}}$and $\sec {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{17}}{8}$.
Note: The important thing which we need is the formula of $\cot $ by which we can mark the sides of the right triangle and another important thing is the Pythagoras theorem. And be careful about the squares and square roots of the number while solving the Pythagoras theorem.
$\sin {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{{\text{Opposite}}}}{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}}$
$\cos {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{{\text{Adjacent}}}}{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}}$
$\tan {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{{\text{Opposite}}}}{{{\text{Adjacent}}}}$
$\cos ec {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}}{{{\text{Opposite}}}}$
$\sec {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}}{{{\text{Adjacent}}}}$
$\cot {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{{\text{Adjacent}}}}{{{\text{Opposite}}}}$
Complete step-by-step solution:
The information given in the question is $\cot {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{\text{8}}}{{15}}$. Therefore, from the given information we can say that Adjacent side $ = 8$ and opposite side $ = 15$ because we know that $\cot {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{{\text{Adjacent side}}}}{{{\text{opposite side}}}}$.

Now, we have to find out the hypotenuse of the right angle triangle with the help of the formula ${H^2} = {B^2} + {A^2}$where $H$ is hypotenuse, $B$ is the base and $A$ is the altitude of the triangle.
Now, ${H^2} = {B^2} + {A^2}\_\_(1)$
The value of $B = 8\,cm$ and the value of $A = 15\,cm$. Put this value in equation $(1)$
\[ \Rightarrow {H^2} = {8^2} + {15^2}\]
We know that ${8^2} = 64$ and ${15^2} = 225$
\[ \Rightarrow {H^2} = 64 + 225 = 289\]
We know that $289$ is the square of $17$. Therefore, we can write
\[ \Rightarrow H = \sqrt {289} = 17\]
Therefore, we got the length of the hypotenuse of the right angle triangle is $17cm$.
From the figure we can say that the length of ${\text{AC}}$is $17cm$.
Now, with the help of the hypotenuse we will able to find the $\sin {\text{A}}$and $\sec {\text{A}}$
We know that $\sin {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{{\text{opposite side}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}$. Therefore, we can write $\sin {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{{\text{BC}}}}{{{\text{AC}}}}$.
Therefore, we can write $\sin {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{{\text{BC}}}}{{{\text{AC}}}} = \dfrac{{15}}{{17}}$.
Similarly, We know that $\sec {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}{{{\text{Adjacent side}}}}$. Therefore, we can write $\sec {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{{\text{AC}}}}{{{\text{AB}}}}$.
Therefore, we can write $\sec {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{{\text{AC}}}}{{{\text{AB}}}} = \dfrac{{17}}{8}$.
Therefore, the answer is $\sin {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{15}}{{17}}$and $\sec {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{17}}{8}$.
Note: The important thing which we need is the formula of $\cot $ by which we can mark the sides of the right triangle and another important thing is the Pythagoras theorem. And be careful about the squares and square roots of the number while solving the Pythagoras theorem.
$\sin {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{{\text{Opposite}}}}{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}}$
$\cos {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{{\text{Adjacent}}}}{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}}$
$\tan {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{{\text{Opposite}}}}{{{\text{Adjacent}}}}$
$\cos ec {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}}{{{\text{Opposite}}}}$
$\sec {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}}{{{\text{Adjacent}}}}$
$\cot {\text{A = }}\dfrac{{{\text{Adjacent}}}}{{{\text{Opposite}}}}$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




