
Identify which functional groups are not present in the given compound?
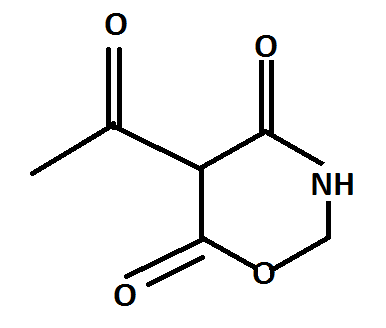
(A) Ketone
(B) Ester
(C) Amide
(D) ether

Answer
527.1k+ views
Hint: A class of organic molecules that has a carbon atom joined to an oxygen atom by a double bond. This is commonly known as a carbonyl group. The trigonal planar of carbon in the carbonyl group is attached to two other elements that lead to the subfamilies like aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids and esters.
Complete answer:
All the functional groups except ether are present. Hence the correct answer is option is, Option D.
Let us see all these functional groups as follow:
Aldehydes and ketone: This functional group contains carbonyl groups. It’s a functional group which has a carbon-oxygen double bond. The names are derived with the help of nomenclature rules of alkanes and alcohols, and also include the class that identifies the suffixes –al and -one
When it comes to aldehyde, the carbonyl group bonds with at least one hydrogen atom, whereas in ketone, it is bonded to two carbon atoms.
Esters: it contains a carbonyl group with a second oxygen atom which is bonded to a carbon atom in the atom in the carbonyl group with a single bond. The second oxygen atom is bonded to another carbon atom. The prefixes indicates the length of the carbon
Note:
Functional groups that are related to carbonyl group includes –CHO group of aldehyde, -CO of a ketone, $ - CO{}_2H $ group represents the carboxylic acid, and $ - CO{}_2R $ group represents an ester. All of these compounds have oxidized carbon atoms relative to the carbon atom of an alcohol group.
Complete answer:
All the functional groups except ether are present. Hence the correct answer is option is, Option D.
Let us see all these functional groups as follow:
Aldehydes and ketone: This functional group contains carbonyl groups. It’s a functional group which has a carbon-oxygen double bond. The names are derived with the help of nomenclature rules of alkanes and alcohols, and also include the class that identifies the suffixes –al and -one
When it comes to aldehyde, the carbonyl group bonds with at least one hydrogen atom, whereas in ketone, it is bonded to two carbon atoms.
Esters: it contains a carbonyl group with a second oxygen atom which is bonded to a carbon atom in the atom in the carbonyl group with a single bond. The second oxygen atom is bonded to another carbon atom. The prefixes indicates the length of the carbon
Note:
Functional groups that are related to carbonyl group includes –CHO group of aldehyde, -CO of a ketone, $ - CO{}_2H $ group represents the carboxylic acid, and $ - CO{}_2R $ group represents an ester. All of these compounds have oxidized carbon atoms relative to the carbon atom of an alcohol group.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




