
Identify the type of root given in the figure, from the given option
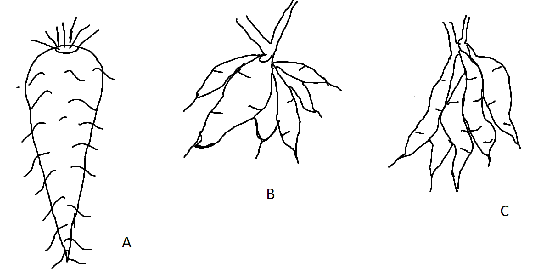
A) A- Fusiform, radish;B- Napiform, turmeric; C. Tuberous,sweet potato.
B) A. Conical,turnip; B. Nodulated,sweet potato; C. Tuberous, Curcuma amada
C) A. Conical,carrot; B. Tuberous,sweet potato; C. Fasciculated, Dahlia
D) A. Napiform, carrot; B. Tuberous,sweet potato; C. Fasciculated, Dahlia

Answer
537.9k+ views
Hint: Roots provide nutrition to the plant, but in some plants the roots are modified. The modified roots perform additional functions than normal roots. These include storage of food, respiration and support.
Complete answer:
The plant roots play a vital role in conveying water, absorption and transport of nutrients from soil to the plant. There are two types of root system in plants, tap root system and adventitious root system. These root systems undergo modification in order to perform additional function of storage and vegetative propagation.
The tap root modifications have swollen tap roots and are fleshy with stored food. The secondary roots remain thin and the stem is reduced, discoid in the beginning bearing radical leaves. There are different types of tap roots depending upon the shape.
1) Conical : The tap roots are in a cone shape, therefore called conical. They are thickest towards the base and gradually tapering towards the apex. Example Daucus carota (carrot).
2) Fusiform: They have fleshy roots which are like spindles. They are thick in the middle and narrow towards its base and apex as well. Raphanus sativus (Radish) is a common example.
3) Napiform: They have a very thick fleshy root at base which is almost spherical. They appear thin at apex. Examples include Beet (Beta vulgaris), Turnip (Brassica rapa).
4) Tuberous Roots: Root are thick and fleshy but do not have any definite shape. Examples include Mirabilis jalapa (Four O` clock).
The adventitious roots are the roots that develop from unusual places other than radical or its branches.The fleshy adventitious root appears swollen, fleshy due to storage of the food. There are several types depending upon shape and place of swollen part.
1) Tuberous Root: These do not have definite shape and occur singly, e.g. Sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas)
2) Fasciculated fleshy roots: They occur in clusters. They are lying at the base of the stem or may occur as seen in Dahlia or they occur at intervals on normal roots as seen in Asparagus.
3) Palmata roots: These are thickened fleshy roots like the palm of the human hand and are similarly finger-like outgrowths. Examples include Orchids.
4) Nodulose roots: They are swollen only near the tips. Examples include Curucuma amada, (Mango ginger), Turmeric.
Hence, the carrot is conical in shape; Sweet potato belongs to tuberous root and Dahlia has a Fasciculate fleshy type of root.
Therefore, the correct answer is option ‘C’ i.e, A. Conical, carrot; B. Tuberous, sweet potato; C. Fasciculated, Dahlia.
Note: The tap roots have main root and through which lateral root develops while adventitious root does not have main root. The tap root develops from the radicle whereas adventitious roots can develop from any part including leaves.
Complete answer:
The plant roots play a vital role in conveying water, absorption and transport of nutrients from soil to the plant. There are two types of root system in plants, tap root system and adventitious root system. These root systems undergo modification in order to perform additional function of storage and vegetative propagation.
The tap root modifications have swollen tap roots and are fleshy with stored food. The secondary roots remain thin and the stem is reduced, discoid in the beginning bearing radical leaves. There are different types of tap roots depending upon the shape.
1) Conical : The tap roots are in a cone shape, therefore called conical. They are thickest towards the base and gradually tapering towards the apex. Example Daucus carota (carrot).
2) Fusiform: They have fleshy roots which are like spindles. They are thick in the middle and narrow towards its base and apex as well. Raphanus sativus (Radish) is a common example.
3) Napiform: They have a very thick fleshy root at base which is almost spherical. They appear thin at apex. Examples include Beet (Beta vulgaris), Turnip (Brassica rapa).
4) Tuberous Roots: Root are thick and fleshy but do not have any definite shape. Examples include Mirabilis jalapa (Four O` clock).
The adventitious roots are the roots that develop from unusual places other than radical or its branches.The fleshy adventitious root appears swollen, fleshy due to storage of the food. There are several types depending upon shape and place of swollen part.
1) Tuberous Root: These do not have definite shape and occur singly, e.g. Sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas)
2) Fasciculated fleshy roots: They occur in clusters. They are lying at the base of the stem or may occur as seen in Dahlia or they occur at intervals on normal roots as seen in Asparagus.
3) Palmata roots: These are thickened fleshy roots like the palm of the human hand and are similarly finger-like outgrowths. Examples include Orchids.
4) Nodulose roots: They are swollen only near the tips. Examples include Curucuma amada, (Mango ginger), Turmeric.
Hence, the carrot is conical in shape; Sweet potato belongs to tuberous root and Dahlia has a Fasciculate fleshy type of root.
Therefore, the correct answer is option ‘C’ i.e, A. Conical, carrot; B. Tuberous, sweet potato; C. Fasciculated, Dahlia.
Note: The tap roots have main root and through which lateral root develops while adventitious root does not have main root. The tap root develops from the radicle whereas adventitious roots can develop from any part including leaves.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




