
Identify the product in the following reaction.
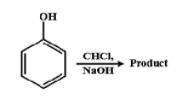


Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint: In this reaction, formation of electrophile in the presence of a strong base which substitutes on the benzene ring, forming an intermediate which undergoes basic hydrolysis to form ortho-hydroxy substituted product.
Complete step by step answer:
The reaction of the phenol with chloroform in presence of sodium hydroxide takes places as follows:
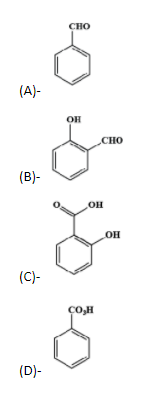
- In the presence of the strong base, NaOH, the chloroform loses the proton forming a carbanion, which further loses its $\alpha -$ chlorine atom forming dichlorocarbene, which is very reactive species and proceeds to react with the phenol.
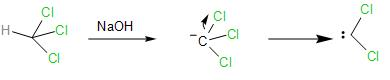
- The NaOH, strong base also, deprotonates the phenol by abstracting a proton from the O-H bond to give phenoxide ion. The negative charge acquired by the oxygen atom in the anion, it stabilised by resonance.
In the resonance structures, the negative charge is delocalised into the benzene ring, making it electron-rich at the ortho- and para-position.
- Now the nucleophilic benzene ring attacks the electrophilic carbene, at the ortho- position to form an intermediate called the di-chloromethyl substituted phenol.
- The intermediate now undergoes basic hydrolysis to lose the chloride ions and give us ortho- hydroxybenzaldehyde. This reaction of the phenol with the chloroform in the presence of sodium hydroxide to give ortho-hydroxybenzaldehyde or salicylaldehyde is known as the Reimer Tiemann reaction.
Note: The dichlorocarbene is highly electrophilic due to having six valence electrons in the carbon. Also, the two electronegative chlorine atoms which make it electron-deficient. Thus, highly attracted to the nucleophilic phenoxide ion. The ortho-position is favoured because of the hydrogen-bonding with the carbonyl group attached is more feasible than at the para- position which is further away from the hydroxyl group of the phenol.
Complete step by step answer:
The reaction of the phenol with chloroform in presence of sodium hydroxide takes places as follows:
- In the presence of the strong base, NaOH, the chloroform loses the proton forming a carbanion, which further loses its $\alpha -$ chlorine atom forming dichlorocarbene, which is very reactive species and proceeds to react with the phenol.

- The NaOH, strong base also, deprotonates the phenol by abstracting a proton from the O-H bond to give phenoxide ion. The negative charge acquired by the oxygen atom in the anion, it stabilised by resonance.
In the resonance structures, the negative charge is delocalised into the benzene ring, making it electron-rich at the ortho- and para-position.
- Now the nucleophilic benzene ring attacks the electrophilic carbene, at the ortho- position to form an intermediate called the di-chloromethyl substituted phenol.

- The intermediate now undergoes basic hydrolysis to lose the chloride ions and give us ortho- hydroxybenzaldehyde. This reaction of the phenol with the chloroform in the presence of sodium hydroxide to give ortho-hydroxybenzaldehyde or salicylaldehyde is known as the Reimer Tiemann reaction.
Note: The dichlorocarbene is highly electrophilic due to having six valence electrons in the carbon. Also, the two electronegative chlorine atoms which make it electron-deficient. Thus, highly attracted to the nucleophilic phenoxide ion. The ortho-position is favoured because of the hydrogen-bonding with the carbonyl group attached is more feasible than at the para- position which is further away from the hydroxyl group of the phenol.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




