
Identify the final product, $C{H_2} = C{H_2}\xrightarrow{{C{l_2},{H_2}O}}X\xrightarrow{{aq.KOH}}Y$
A. 2-chloroethanol
B. 2-chloromethanol
C. 1-chloroethanol
D. Ethylene glycol
Answer
573k+ views
Hint:As we remember that organic chemistry is full of chemical reactions, so to solve such a type of question we should remember the working of reagent whether it is a reducing agent or an oxidising agent for product formation.
Complete answer:
We should first look at the pattern of the reaction, we know that when an alkene will react with halide like $HCl,HBr,HI$ the reaction will involve an electrophilic addition of hydride ion to alkene resulting in the formation of carbocation as an intermediate, and it will then rearrange itself in the presence of hydroxide ion. In the given reaction, ethene will react in the same manner with the reagent chlorine and water or simply hypohalous acid, HOX. Chlorine as a dihalide will break the carbon-carbon double bond and water molecule will now attack one of the carbon and $HCl$ will be released producing an intermediate as represented:
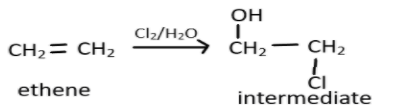
Now this intermediate will react with aqueous KOH which is an alkaline so it will give its hydroxide ion and they will act as a strong nucleophile and replace the chlorine atom from the alkyl halide. This reaction will result in the formation of alcoholic molecules, here ethylene glycol. This can be represented as:

Therefore the end product formed is Ethylene glycol and the whole reaction can be depicted by:
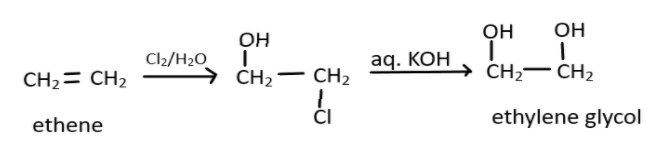
Hence the correct answer is D. Ethylene glycol.
Note:
When KOH is present in alcoholic nature, it produces \[{C_2}{H_5}{O^ - }\] ions which acts as a stronger base when compared to $O{H^ - }$ ions. These ions abstracts the hydrogen from alkyl halides and results in alkene formation. Ethylene glycol is used as a coolant and it helps in reducing overheating of car engines in summer.
Complete answer:
We should first look at the pattern of the reaction, we know that when an alkene will react with halide like $HCl,HBr,HI$ the reaction will involve an electrophilic addition of hydride ion to alkene resulting in the formation of carbocation as an intermediate, and it will then rearrange itself in the presence of hydroxide ion. In the given reaction, ethene will react in the same manner with the reagent chlorine and water or simply hypohalous acid, HOX. Chlorine as a dihalide will break the carbon-carbon double bond and water molecule will now attack one of the carbon and $HCl$ will be released producing an intermediate as represented:

Now this intermediate will react with aqueous KOH which is an alkaline so it will give its hydroxide ion and they will act as a strong nucleophile and replace the chlorine atom from the alkyl halide. This reaction will result in the formation of alcoholic molecules, here ethylene glycol. This can be represented as:

Therefore the end product formed is Ethylene glycol and the whole reaction can be depicted by:

Hence the correct answer is D. Ethylene glycol.
Note:
When KOH is present in alcoholic nature, it produces \[{C_2}{H_5}{O^ - }\] ions which acts as a stronger base when compared to $O{H^ - }$ ions. These ions abstracts the hydrogen from alkyl halides and results in alkene formation. Ethylene glycol is used as a coolant and it helps in reducing overheating of car engines in summer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




