
Identify the correct statements regarding structure of diborane:
(This question has multiple correct options)
A. There are two bridging hydrogen atoms
B. Each boron atom forms four bonds
C. The hydrogen atoms are not in the same plane
D. Each boron atom is in \[s{{p}^{3}}\] hybridized state
Answer
600.6k+ views
Hint: Diborane has bridge bonding and it has \[3C-2{{e}^{-}}\] bond. The Boron element has \[1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{1}}\] configuration and its valency is 3. Configuration of boron in borane is \[s{{p}^{2}}\].
Step by step solution:
Diborane is formed by dimerisation of borane:
\[B{{H}_{3}}\xrightarrow{Dimerisation}{{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}\]
Diborane has non-planar structure.
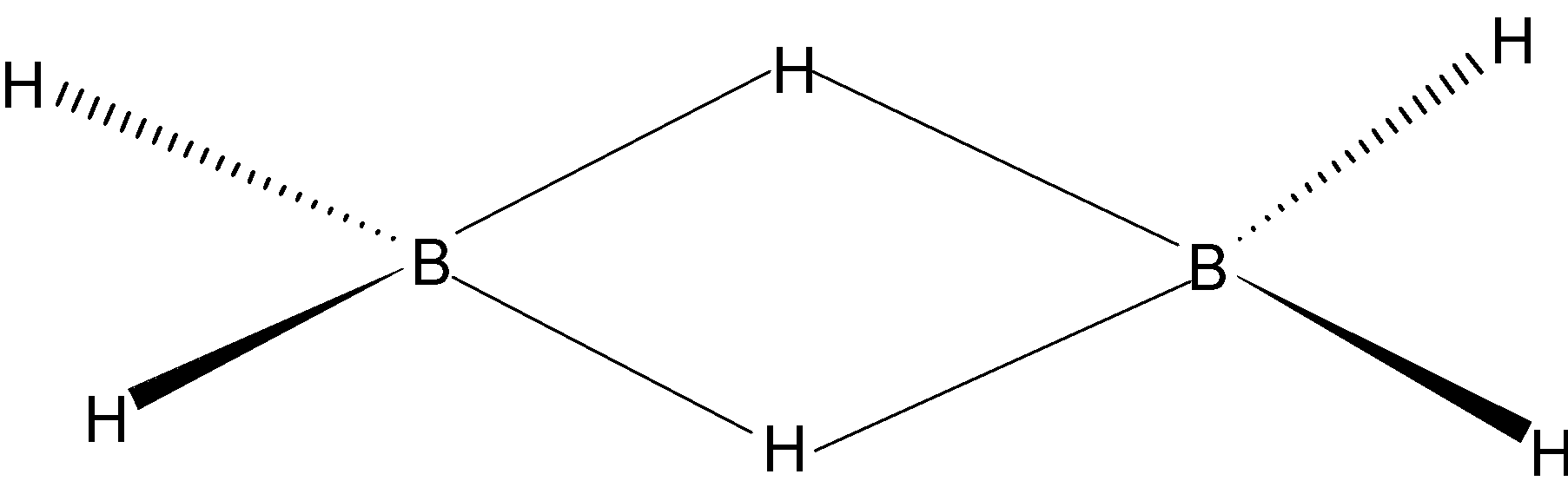
“A” is correct, because in diborane there are 6 hydrogen atoms in which 2 hydrogens are bridged and the other 4 are in the same plane.
“B” is correct, because each boron forms four bonds, two bonds with two bridged hydrogen (\[3C-2{{e}^{-}}\]) and two bonds (\[2C-2{{e}^{-}}\]) with the same planar hydrogen.
“C” is correct, because 4 hydrogens are in the same plane and two bridged hydrogens are there to reduce the bond pair – bond pair repulsion.
“D” is correct, because this molecule has a total 12 valance electrons, 3 from boron and 6 from hydrogen. Here, 8 e- are used in normal \[2C-2{{e}^{-}}\] bonds and other 4valence electrons are shared by remaining 2 hydrogens and borons for making banana bonds. Each atom contributes one orbital to form \[3C-2{{e}^{-}}\] bond. Boron uses its vacant p orbital, so its configuration is \[s{{p}^{3}}\].
Note: \[3C-2{{e}^{-}}\] bond is also known as banana bond/p-seudo bond/tau bond. It is a non-planar structure, which we can understand from the configuration of boron (\[s{{p}^{3}}\]). Banana bonds are covalent in nature, so there are 2 electrons which are shared by 3 centres.
Step by step solution:
Diborane is formed by dimerisation of borane:
\[B{{H}_{3}}\xrightarrow{Dimerisation}{{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}\]
Diborane has non-planar structure.

“A” is correct, because in diborane there are 6 hydrogen atoms in which 2 hydrogens are bridged and the other 4 are in the same plane.
“B” is correct, because each boron forms four bonds, two bonds with two bridged hydrogen (\[3C-2{{e}^{-}}\]) and two bonds (\[2C-2{{e}^{-}}\]) with the same planar hydrogen.
“C” is correct, because 4 hydrogens are in the same plane and two bridged hydrogens are there to reduce the bond pair – bond pair repulsion.
“D” is correct, because this molecule has a total 12 valance electrons, 3 from boron and 6 from hydrogen. Here, 8 e- are used in normal \[2C-2{{e}^{-}}\] bonds and other 4valence electrons are shared by remaining 2 hydrogens and borons for making banana bonds. Each atom contributes one orbital to form \[3C-2{{e}^{-}}\] bond. Boron uses its vacant p orbital, so its configuration is \[s{{p}^{3}}\].
Note: \[3C-2{{e}^{-}}\] bond is also known as banana bond/p-seudo bond/tau bond. It is a non-planar structure, which we can understand from the configuration of boron (\[s{{p}^{3}}\]). Banana bonds are covalent in nature, so there are 2 electrons which are shared by 3 centres.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




