
Identify the correct statement:
A. If $f\left( x \right)$ is differentiable at $x=a$ , $\left| f\left( x \right) \right|$ will also be differentiable at $x=a$.
B. If $f\left( x \right)$ is continuous at $x=a$ , $\left| f\left( x \right) \right|$ will also be continuous at $x=a$.
C. If $f\left( x \right)$ is discontinuous at $x=a$ , $\left| f\left( x \right) \right|$ will also be discontinuous at $x=a$.
D. If $f\left( x \right)$ is continuous at $x=a$ , $\left| f\left( x \right) \right|$ will also be continuous at $x=a$.
Answer
544.2k+ views
Hint: From the given statements, statement B is correct. Now, here we will check the consciousness of a function according to the following way as:
A function is continuous when its left hand limit, right hand limit and the value at the point exist and are equal to each other i.e.
$ \displaystyle \lim_{x \to {{a}^{-}}}f\left( x \right)=f\left( a \right)=\displaystyle \lim_{x \to {{a}^{+}}}f\left( x \right)$
Complete step by step solution:
Let the $f\left( x \right)$ be a real function and there be a positive number $a$ .
Where, $f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|$
Since, the modulus function can be defined as:
$\Rightarrow \left\{ \begin{align}
& f\left( x \right)=x,\text{ if }x>0 \\
& and \\
& f\left( x \right)=-x,\text{ if }x<0 \\
\end{align} \right\}$
To find that the modulus function to be continuous at the given point $x=a$ , we will find the value of left hand limit, right hand limit and the value at given point.
Here, we will start from left hand limit that is:
$\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=-x,\text{ if }x<0$
Now, we will apply the limit at the left hand side of function as:
$\Rightarrow \displaystyle \lim_{x \to {{a}^{-}}}f\left( x \right)$
Now, the above equation will be as:
$\Rightarrow \displaystyle \lim_{x \to {{a}^{-}}}\left( -x \right)$
Since, we already assumed $a$ as a real number. So we can write the above equation i.e. left hand limit as:
$\Rightarrow -\left( -a \right)$
Now, we will open the small bracket in the above equation so that the product of two negative must be positive as:
$\Rightarrow a$
Now, we will solve the right hand limit that is:
$\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=x,\text{ if }x>0$
We will apply the limit in the right hand side of function as:
$\Rightarrow \displaystyle \lim_{x \to {{a}^{+}}}f\left( x \right)$
Here, the above equation will be as:
$\Rightarrow \displaystyle \lim_{x \to {{a}^{+}}}x$
Since, $a$ is a positive number so that we will get the value from the above equation as:
$\Rightarrow a$
Since, we get the value for left hand limit and right hand limit. Now, we will find the value of the function at a point as:
The function is:
$\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|$
Now, after applying $x=a$ , we will have:
$\Rightarrow f\left( a \right)=\left| a \right|$
Since, modulus of a number always gives a positive number and we know that $a$ is a positive number:
$\Rightarrow f\left( a \right)=a$
Hence, we got the equal value from the left hand limit, right hand limit and at the point. Therefore, the modulus function is continuous.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Here, we try to understand the continuity of a modulus function by its graph as:
Since, we have the modulus function as:
$\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|$
And it can be derives for negative and positive values as:
$\Rightarrow \left\{ \begin{align}
& f\left( x \right)=x,\text{ if }x>0 \\
& and \\
& f\left( x \right)=-x,\text{ if }x<0 \\
\end{align} \right\}$
And for zero, it will be zero from the value of function at a point that is $0$ here as:
$\Rightarrow f\left( 0 \right)=0$
So, the graph will be as:
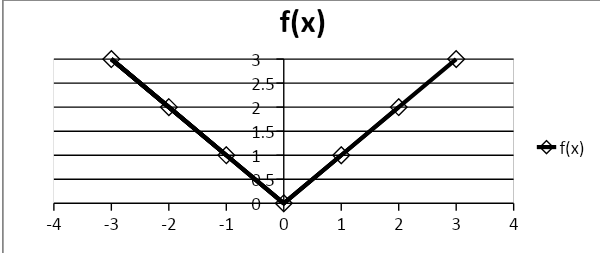
Here, we clearly see that the line is continuous for the domain. Hence, the modulus function is continuous.
A function is continuous when its left hand limit, right hand limit and the value at the point exist and are equal to each other i.e.
$ \displaystyle \lim_{x \to {{a}^{-}}}f\left( x \right)=f\left( a \right)=\displaystyle \lim_{x \to {{a}^{+}}}f\left( x \right)$
Complete step by step solution:
Let the $f\left( x \right)$ be a real function and there be a positive number $a$ .
Where, $f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|$
Since, the modulus function can be defined as:
$\Rightarrow \left\{ \begin{align}
& f\left( x \right)=x,\text{ if }x>0 \\
& and \\
& f\left( x \right)=-x,\text{ if }x<0 \\
\end{align} \right\}$
To find that the modulus function to be continuous at the given point $x=a$ , we will find the value of left hand limit, right hand limit and the value at given point.
Here, we will start from left hand limit that is:
$\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=-x,\text{ if }x<0$
Now, we will apply the limit at the left hand side of function as:
$\Rightarrow \displaystyle \lim_{x \to {{a}^{-}}}f\left( x \right)$
Now, the above equation will be as:
$\Rightarrow \displaystyle \lim_{x \to {{a}^{-}}}\left( -x \right)$
Since, we already assumed $a$ as a real number. So we can write the above equation i.e. left hand limit as:
$\Rightarrow -\left( -a \right)$
Now, we will open the small bracket in the above equation so that the product of two negative must be positive as:
$\Rightarrow a$
Now, we will solve the right hand limit that is:
$\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=x,\text{ if }x>0$
We will apply the limit in the right hand side of function as:
$\Rightarrow \displaystyle \lim_{x \to {{a}^{+}}}f\left( x \right)$
Here, the above equation will be as:
$\Rightarrow \displaystyle \lim_{x \to {{a}^{+}}}x$
Since, $a$ is a positive number so that we will get the value from the above equation as:
$\Rightarrow a$
Since, we get the value for left hand limit and right hand limit. Now, we will find the value of the function at a point as:
The function is:
$\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|$
Now, after applying $x=a$ , we will have:
$\Rightarrow f\left( a \right)=\left| a \right|$
Since, modulus of a number always gives a positive number and we know that $a$ is a positive number:
$\Rightarrow f\left( a \right)=a$
Hence, we got the equal value from the left hand limit, right hand limit and at the point. Therefore, the modulus function is continuous.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Here, we try to understand the continuity of a modulus function by its graph as:
Since, we have the modulus function as:
$\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|$
And it can be derives for negative and positive values as:
$\Rightarrow \left\{ \begin{align}
& f\left( x \right)=x,\text{ if }x>0 \\
& and \\
& f\left( x \right)=-x,\text{ if }x<0 \\
\end{align} \right\}$
And for zero, it will be zero from the value of function at a point that is $0$ here as:
$\Rightarrow f\left( 0 \right)=0$
So, the graph will be as:

Here, we clearly see that the line is continuous for the domain. Hence, the modulus function is continuous.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




