
How do you identify if the equation \[y = {x^2} + 3x + 1\] is a parabola, circle, ellipse, or hyperbola? How do you graph it?
Answer
539.4k+ views
Hint: First we will try to see that which form of equation fits best for the given question, whether the equation of parabola, or equation of circle, or ellipse, or hyperbola. After that we will find the vertex form of the equation and solve it to get the points. Then we will plot the graph.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The given equation is:
\[y = {x^2} + 3x + 1\]
We know that the equation of a parabola is in the form of:
\[y = a{x^2} + bx + c\] .
According to the question, it is clear that the equation is the equation of parabola.
Now, we need to graph the equation. The best way to graph this equation is to convert the equation into the vertex form. The vertex form is:
\[y = a{(x - h)^2} + k\] where (h, k) is vertex. We need to remember that a is at maxima when a>0, and a is at minima when a<0. When h=x, then it is the axis of symmetry of parabola.
The given equation is:
\[y = {x^2} + 3x + 1\]
Now, we will modify the equation. We will add and subtract some terms, and also multiply some terms, and we get:
\[ = {x^2} + 2 \times \dfrac{3}{2} \times x + {\left( {\dfrac{3}{2}} \right)^2} - {\left( {\dfrac{3}{2}} \right)^2} + 1\]
Here, we will rearrange some terms, and we get:
\[ = {x^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{3}{2}} \right)^2} + 2 \times \dfrac{3}{2} \times x - {\left( {\dfrac{3}{2}} \right)^2} + 1\]
Here, we can see that the terms are in the form of the formula:
\[{(a + b)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab\]
Here, a is ‘x’, b is \[\dfrac{3}{2}\] . So, with the help of this formula, we get:
\[ = {\left( {{x^2} + \dfrac{3}{2}} \right)^2} - {\left( {\dfrac{3}{2}} \right)^2} + 1\]
Now, when we simplify it, we get:
\[ = {\left( {x + \dfrac{3}{2}} \right)^2} - \dfrac{5}{4}\]
We can also write the answer in the form of:
\[ = {\left( {x - \left( { - \dfrac{3}{2}} \right)} \right)^2} - \dfrac{5}{4}\]
Therefore, our vertex will be \[ - \dfrac{3}{2}, - \dfrac{5}{4}\] and axis of symmetry will be \[x + \dfrac{3}{2} = 0\]
Here, we will pick various values of ‘x’ around \[ - \dfrac{3}{2}\] , and then we will find ‘y’ from the given equation. We get points, and with the help of that we can plot the graph as following:
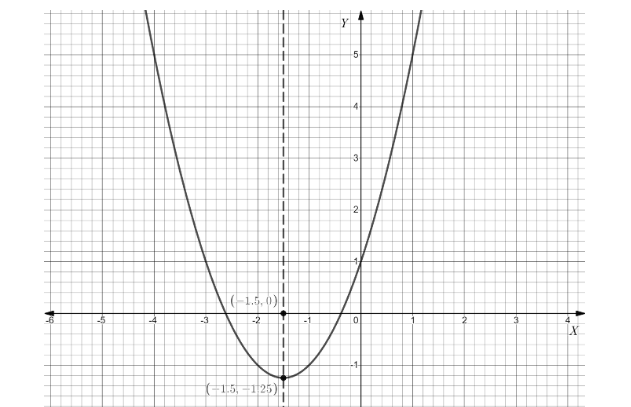
Note: There is another method to find whether the equation is a parabola, circle, ellipse or hyperbola. When we see the given equation, if \[{b^2} - 4ac = 0\] and a=0, c=0, then it is a parabola. If \[{b^2} - 4ac < 0\] and a=c, then it is a circle. If \[{b^2} - 4ac < 0\] , and \[a \ne c\] , then it is an ellipse. If \[{b^2} - 4ac > 0\] , then it is a hyperbola.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The given equation is:
\[y = {x^2} + 3x + 1\]
We know that the equation of a parabola is in the form of:
\[y = a{x^2} + bx + c\] .
According to the question, it is clear that the equation is the equation of parabola.
Now, we need to graph the equation. The best way to graph this equation is to convert the equation into the vertex form. The vertex form is:
\[y = a{(x - h)^2} + k\] where (h, k) is vertex. We need to remember that a is at maxima when a>0, and a is at minima when a<0. When h=x, then it is the axis of symmetry of parabola.
The given equation is:
\[y = {x^2} + 3x + 1\]
Now, we will modify the equation. We will add and subtract some terms, and also multiply some terms, and we get:
\[ = {x^2} + 2 \times \dfrac{3}{2} \times x + {\left( {\dfrac{3}{2}} \right)^2} - {\left( {\dfrac{3}{2}} \right)^2} + 1\]
Here, we will rearrange some terms, and we get:
\[ = {x^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{3}{2}} \right)^2} + 2 \times \dfrac{3}{2} \times x - {\left( {\dfrac{3}{2}} \right)^2} + 1\]
Here, we can see that the terms are in the form of the formula:
\[{(a + b)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab\]
Here, a is ‘x’, b is \[\dfrac{3}{2}\] . So, with the help of this formula, we get:
\[ = {\left( {{x^2} + \dfrac{3}{2}} \right)^2} - {\left( {\dfrac{3}{2}} \right)^2} + 1\]
Now, when we simplify it, we get:
\[ = {\left( {x + \dfrac{3}{2}} \right)^2} - \dfrac{5}{4}\]
We can also write the answer in the form of:
\[ = {\left( {x - \left( { - \dfrac{3}{2}} \right)} \right)^2} - \dfrac{5}{4}\]
Therefore, our vertex will be \[ - \dfrac{3}{2}, - \dfrac{5}{4}\] and axis of symmetry will be \[x + \dfrac{3}{2} = 0\]
Here, we will pick various values of ‘x’ around \[ - \dfrac{3}{2}\] , and then we will find ‘y’ from the given equation. We get points, and with the help of that we can plot the graph as following:

Note: There is another method to find whether the equation is a parabola, circle, ellipse or hyperbola. When we see the given equation, if \[{b^2} - 4ac = 0\] and a=0, c=0, then it is a parabola. If \[{b^2} - 4ac < 0\] and a=c, then it is a circle. If \[{b^2} - 4ac < 0\] , and \[a \ne c\] , then it is an ellipse. If \[{b^2} - 4ac > 0\] , then it is a hyperbola.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




