
How can we identify ethane from ethene?
Answer
496.8k+ views
Hint: We know that Alkanes, alkenes and alkynes are straightforward hydrocarbon chains with no practical gatherings. The least complex natural mixtures are the alkanes. Alkanes have just single connections between carbon molecules and are called immersed hydrocarbons. Alkenes have at any rate one carbon-carbon double bond.
Complete answer:
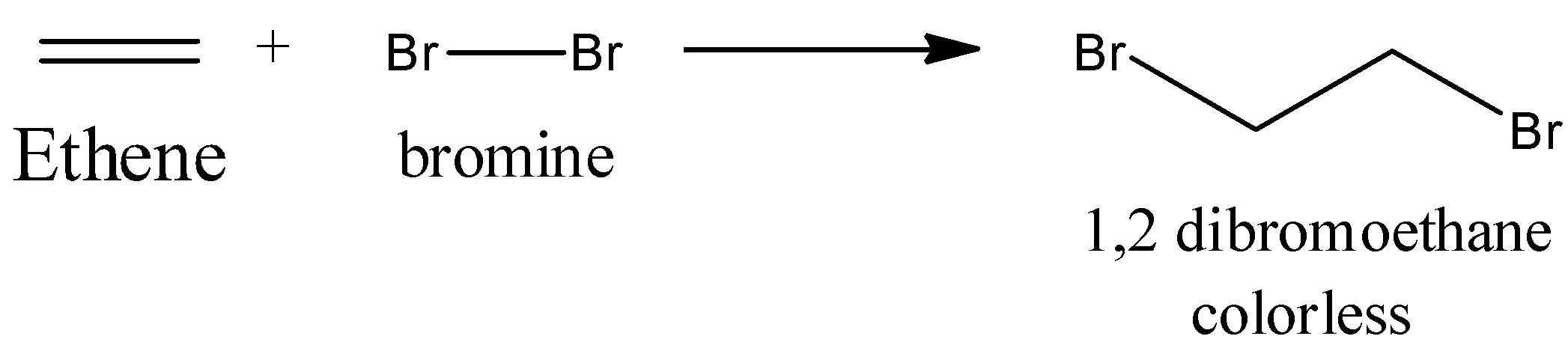
We have to know that ethane is an alkane and as such is immersed, which means it has every single bond. Ethene is an alkene and as such is unsaturated, which means it has one carbon to carbon double bond. So they can be distinguished by their shown formulae, as ethene has the double bond utilitarian gathering.
Chemically, they can be recognized most effectively by the response with bromine water, which is orange/red in shading. Add a couple of drops to ethene and bromine water is decolorized as 1, 2-dibromoethane, an immersed compound structure. There is no noticeable indication of response when bromine is added to an alkane.
Note:
The least difficult natural mixtures contain just the components carbon and hydrogen, and are called hydrocarbons. Despite the fact that they are made out of just two sorts of molecules, there is a wide assortment of hydrocarbons since they may consist of changing lengths of chains, spread chains, and rings of carbon particles, or blends of these constructions. What's more, hydrocarbons may contrast in the kinds of carbon-carbon bonds present in their particles. Numerous hydrocarbons are found in plants, creatures, and their fossils; different hydrocarbons have been set up in the research center. We use hydrocarbons consistently, essentially as fills, like petroleum gas, acetylene, propane, butane, and the central parts of gas, diesel fuel, and warming oil. The natural plastics polyethylene, polypropylene, and polystyrene are likewise hydrocarbons. We can recognize a few kinds of hydrocarbons by contrasts in the holding between carbon iotas. This prompts contrasts in calculations and in the hybridization of the carbon orbitals.
Complete answer:
We have to know that ethane is an alkane and as such is immersed, which means it has every single bond. Ethene is an alkene and as such is unsaturated, which means it has one carbon to carbon double bond. So they can be distinguished by their shown formulae, as ethene has the double bond utilitarian gathering.
Chemically, they can be recognized most effectively by the response with bromine water, which is orange/red in shading. Add a couple of drops to ethene and bromine water is decolorized as 1, 2-dibromoethane, an immersed compound structure. There is no noticeable indication of response when bromine is added to an alkane.

Note:
The least difficult natural mixtures contain just the components carbon and hydrogen, and are called hydrocarbons. Despite the fact that they are made out of just two sorts of molecules, there is a wide assortment of hydrocarbons since they may consist of changing lengths of chains, spread chains, and rings of carbon particles, or blends of these constructions. What's more, hydrocarbons may contrast in the kinds of carbon-carbon bonds present in their particles. Numerous hydrocarbons are found in plants, creatures, and their fossils; different hydrocarbons have been set up in the research center. We use hydrocarbons consistently, essentially as fills, like petroleum gas, acetylene, propane, butane, and the central parts of gas, diesel fuel, and warming oil. The natural plastics polyethylene, polypropylene, and polystyrene are likewise hydrocarbons. We can recognize a few kinds of hydrocarbons by contrasts in the holding between carbon iotas. This prompts contrasts in calculations and in the hybridization of the carbon orbitals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




