
Identify A and B in the given diagram showing ATP synthesis in Oxysomes
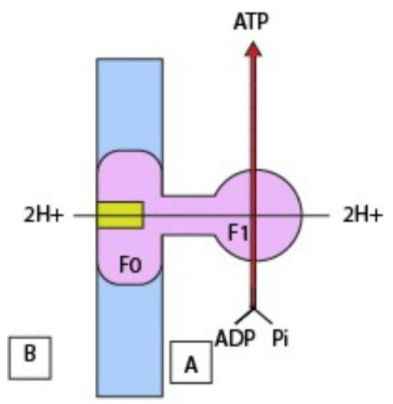
A. A = Mitochondrial matrix
B = Outer mitochondrial membrane
B. A = Mitochondrial matrix
B = Inner mitochondrial membrane
C. A = Cell cytoplasm
B = Inner mitochondrial membrane
D. A = Cell cytoplasm
B = Outer mitochondrial membrane

Answer
521.4k+ views
Hint: The exchange of electrons from the intermembranous space, through the inward layer, and back to the network is part of \[ATP\] synthesis. The exchange of electrons from the framework to the intermembranous space causes a large pH difference between the two sides of the membrane.
Complete answer:
A=It is the end product of \[ATP\] synthesis. A= \[ATP\]= It is the end product of \[ATP\] synthesis.
B=The \[F1\] particle is a peripheral membrane protein complex that contains the site for \[ATP\] synthesis from ADP and inorganic phosphate.
C=For the formation of \[ATP\], \[C\text{ }=\text{ }Pi\] is the inorganic phosphatase, which is present along with \[ADP\].
D = The \[2{{H}^{+}}\] ions move through F0 from the inner mitochondrial space to the matrix down the electrochemical proton gradient for every \[ATP\] generated during the \[ATP\] synthesis process.
E = Inner mitochondrial membrane. This is the membrane through which \[2{{H}^{+}}\] ions travel from the mitochondria to the matrix.
Mitochondrial inner membrane the interaction of oxidation and phosphorylation synthesis \[ATP\] in the mitochondria. The increased proton inclination causes an increase in the number of \[{{H}^{+}}\] in the internal mitochondrial space. The protons are pushed back into the lattice by an \[ATP\] synthase complex in the internal mitochondrial layer, which converts \[ADP\] and inorganic phosphate to \[ATP\].
Note:
\[ATP\] synthase is made up of a membrane spanning area known as the \[F0\] subunit and a bumpy projection that stretches out into the framework known as the \[F1\] subunit. The \[ATP\] synthase instrument is not what one would expect. The \[F1\]\[ATP\] synthase subunit can perform its ligase function (producing \[ATP\] from ADP and phosphate) without a proton stream into the lattice; however, the arrival of the \[ATP\] requires a proton stream through the membrane.
Complete answer:
A=It is the end product of \[ATP\] synthesis. A= \[ATP\]= It is the end product of \[ATP\] synthesis.
B=The \[F1\] particle is a peripheral membrane protein complex that contains the site for \[ATP\] synthesis from ADP and inorganic phosphate.
C=For the formation of \[ATP\], \[C\text{ }=\text{ }Pi\] is the inorganic phosphatase, which is present along with \[ADP\].
D = The \[2{{H}^{+}}\] ions move through F0 from the inner mitochondrial space to the matrix down the electrochemical proton gradient for every \[ATP\] generated during the \[ATP\] synthesis process.
E = Inner mitochondrial membrane. This is the membrane through which \[2{{H}^{+}}\] ions travel from the mitochondria to the matrix.
Mitochondrial inner membrane the interaction of oxidation and phosphorylation synthesis \[ATP\] in the mitochondria. The increased proton inclination causes an increase in the number of \[{{H}^{+}}\] in the internal mitochondrial space. The protons are pushed back into the lattice by an \[ATP\] synthase complex in the internal mitochondrial layer, which converts \[ADP\] and inorganic phosphate to \[ATP\].
Note:
\[ATP\] synthase is made up of a membrane spanning area known as the \[F0\] subunit and a bumpy projection that stretches out into the framework known as the \[F1\] subunit. The \[ATP\] synthase instrument is not what one would expect. The \[F1\]\[ATP\] synthase subunit can perform its ligase function (producing \[ATP\] from ADP and phosphate) without a proton stream into the lattice; however, the arrival of the \[ATP\] requires a proton stream through the membrane.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




