
(I) Fruit is the product of fertilization.Is there any fruit formed without the act of fertilization?
(II) Represent the classification of fruits in a diagrammatic sketch.
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: The seed-bearing structure in flowering plants (also known as angiosperms) produced after flowering from the ovary is a fruit. A fruit results from the maturation of one or more flowers, and all or part of the fruit forms the gynecium of the flower(s).
Complete answer:
(I) Yes, there is a certain type of fruit that is produced without the fertilisation act.
Explanation:-A parthenocarpic fruit is considered a fruit that grows without fertilization. They are distinguished by a lack of seeds and are commonly referred to as seedless fruits. Through this phenomenon, fruits such as bananas, grapes, oranges and watermelons are produced. Different changes in a flower are caused by fertilisation: the anthers and stigma wither, the petals drop off, and the sepals can be shed or altered; the ovary enlarges and the ovules grow into seeds, each containing an embryo plant. Protection and propagation of the seed is the principal function of the fruit.Fruits are important sources of dietary fibre, antioxidants, and vitamins (especially vitamin C). While fresh fruits are subject to spoilage, refrigeration or the removal of oxygen from their storage or packaging containers can extend their shelf life.
b)
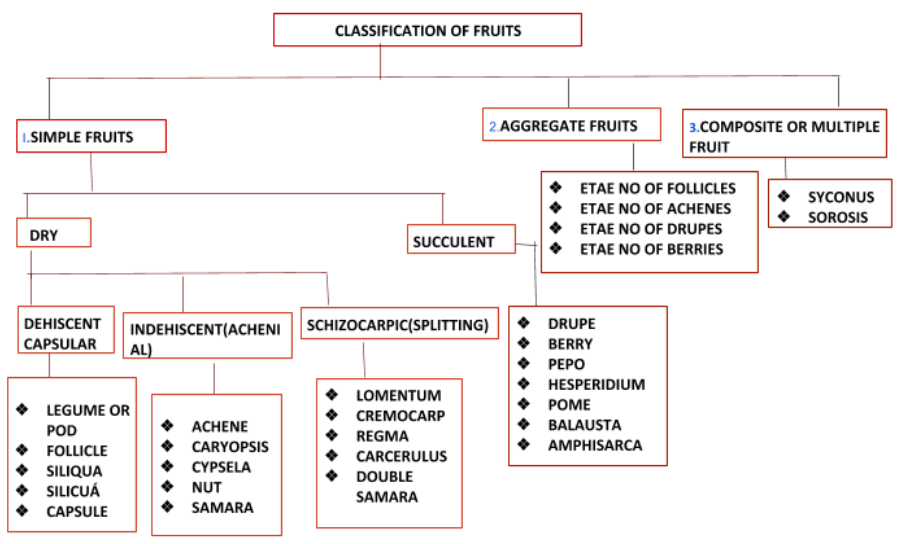
Note: Since fruits have been such a major component of the human diet, various cultures have established several different uses for different fruits that they do not rely on as edible. Several dry fruits, such as unicorn plants, lotus, wheat, yearly honesty and milkweed, are used as decorations or in dried flower arrangements. For their colourful fruits, including holly, pyracantha, viburnum, skimmia, beautyberry, and cotoneaster, ornamental trees and shrubs are also cultivated.
Complete answer:
(I) Yes, there is a certain type of fruit that is produced without the fertilisation act.
Explanation:-A parthenocarpic fruit is considered a fruit that grows without fertilization. They are distinguished by a lack of seeds and are commonly referred to as seedless fruits. Through this phenomenon, fruits such as bananas, grapes, oranges and watermelons are produced. Different changes in a flower are caused by fertilisation: the anthers and stigma wither, the petals drop off, and the sepals can be shed or altered; the ovary enlarges and the ovules grow into seeds, each containing an embryo plant. Protection and propagation of the seed is the principal function of the fruit.Fruits are important sources of dietary fibre, antioxidants, and vitamins (especially vitamin C). While fresh fruits are subject to spoilage, refrigeration or the removal of oxygen from their storage or packaging containers can extend their shelf life.
b)

Note: Since fruits have been such a major component of the human diet, various cultures have established several different uses for different fruits that they do not rely on as edible. Several dry fruits, such as unicorn plants, lotus, wheat, yearly honesty and milkweed, are used as decorations or in dried flower arrangements. For their colourful fruits, including holly, pyracantha, viburnum, skimmia, beautyberry, and cotoneaster, ornamental trees and shrubs are also cultivated.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




