
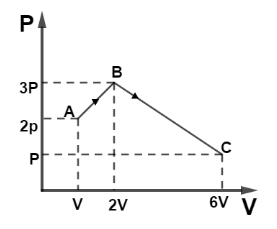
(i) Find total work by the gas during process ABC.
(ii) Find $\Delta {U_{ABC}}$ if the gas is monatomic.

Answer
503.4k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question we need to understand the thermodynamic process. A thermodynamic process is defined as a process in which the state of gas changes, it can be either reversible or irreversible. Reversible process is one in which we can achieve each step involved in state transition while repeating from final state to initial state; these processes are slow and are known as quasi-static processes. Irreversible processes are one step which cannot be achieved while returning back from final to initial state. There are different types of processes like isochoric, adiabatic, isobaric and isothermal processes. Also the first law of thermodynamics is conservation of energy.
Complete step by step answer:
(i) Work done by gas in a changing state is defined as the area under curve P-V. So area under curve ABC can be divided as shown,
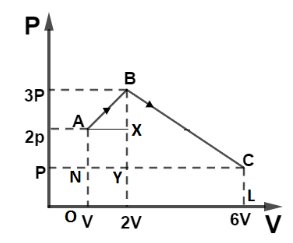
So, Area of $\Delta AXB$ is given by, $\Delta AXB = \dfrac{1}{2}(AX)(XB)$
From figure, $AX = V$ and $XB = P$
So, $\Delta AXB = \dfrac{1}{2}PV$
Area of $\Delta BYC$ is given by, $\Delta BYC = \dfrac{1}{2}(YC)(BY)$
From figure, $YC = 4V$ and $BY = 2P$
So, $\Delta BYC = \dfrac{1}{2}(4V)(2P)$
$\Delta BYC = 4PV$
Area of square $AXYN$ is given by, $ar(AXNY) = (NY)(AN)$
From figure, $AN = P$ and $NY = V$
So, $ar(AXNY) = PV$
Area of rectangle $ar(NCLO)$ is given by, $ar(NCLO) = (NC)(CL)$
From figure, $NC = 5V$ and $CL = P$
So, $ar(NCLO) = 5PV$
So total area is $\Delta AXB + \Delta BYC + ar(AXYN) + ar(NCLO)$
Putting values we get, ${W_{ABC}} = \dfrac{1}{2}PV + 4PV + PV + 5PV$
$\therefore {W_{ABC}} = 10.5\,PV$
So work done by the gas is, ${W_{ABC}} = 10.5\,PV$.
(ii) Internal energy only depends on the final and initial point as it does not depend upon path travelled. Since gas is monatomic, so specific heat at constant volume is given by, ${C_V} = \dfrac{3}{2}RT$
Also Using Ideal gas equation at point A we get, $(2P)(V) = nR{T_A}$
${T_A} = \dfrac{{2PV}}{{nR}}$
And using ideal gas equation at point B we get, $(P)(6V) = nR{T_B}$
${T_B} = \dfrac{{6PV}}{{nR}}$
So temperature difference is given by, $\Delta T = {T_B} - {T_A}$
Putting values we get, $\Delta T = \dfrac{{6PV}}{{nR}} - \dfrac{{2PV}}{{nR}}$
$\Delta T = \dfrac{{4PV}}{{nR}}$
So internal energy is given by, $U = n{C_V}\Delta T$
Putting values we get, $U = n(\dfrac{3}{2}R)(\dfrac{{4PV}}{{nR}})$
$\therefore U = 6\,PV$
So internal energy is $U = 6\,PV$.
Note: It should be remembered that internal energy is path independent but the work done depends on the path travelled. So internal energy only depends upon final and initial points. Also Isothermal processes in which the gas state changes upon keeping temperature constant, isochoric process is one in which gas state changes by keeping volume constant and isobaric process in which gas state changes by keeping pressure constant.
Complete step by step answer:
(i) Work done by gas in a changing state is defined as the area under curve P-V. So area under curve ABC can be divided as shown,

So, Area of $\Delta AXB$ is given by, $\Delta AXB = \dfrac{1}{2}(AX)(XB)$
From figure, $AX = V$ and $XB = P$
So, $\Delta AXB = \dfrac{1}{2}PV$
Area of $\Delta BYC$ is given by, $\Delta BYC = \dfrac{1}{2}(YC)(BY)$
From figure, $YC = 4V$ and $BY = 2P$
So, $\Delta BYC = \dfrac{1}{2}(4V)(2P)$
$\Delta BYC = 4PV$
Area of square $AXYN$ is given by, $ar(AXNY) = (NY)(AN)$
From figure, $AN = P$ and $NY = V$
So, $ar(AXNY) = PV$
Area of rectangle $ar(NCLO)$ is given by, $ar(NCLO) = (NC)(CL)$
From figure, $NC = 5V$ and $CL = P$
So, $ar(NCLO) = 5PV$
So total area is $\Delta AXB + \Delta BYC + ar(AXYN) + ar(NCLO)$
Putting values we get, ${W_{ABC}} = \dfrac{1}{2}PV + 4PV + PV + 5PV$
$\therefore {W_{ABC}} = 10.5\,PV$
So work done by the gas is, ${W_{ABC}} = 10.5\,PV$.
(ii) Internal energy only depends on the final and initial point as it does not depend upon path travelled. Since gas is monatomic, so specific heat at constant volume is given by, ${C_V} = \dfrac{3}{2}RT$
Also Using Ideal gas equation at point A we get, $(2P)(V) = nR{T_A}$
${T_A} = \dfrac{{2PV}}{{nR}}$
And using ideal gas equation at point B we get, $(P)(6V) = nR{T_B}$
${T_B} = \dfrac{{6PV}}{{nR}}$
So temperature difference is given by, $\Delta T = {T_B} - {T_A}$
Putting values we get, $\Delta T = \dfrac{{6PV}}{{nR}} - \dfrac{{2PV}}{{nR}}$
$\Delta T = \dfrac{{4PV}}{{nR}}$
So internal energy is given by, $U = n{C_V}\Delta T$
Putting values we get, $U = n(\dfrac{3}{2}R)(\dfrac{{4PV}}{{nR}})$
$\therefore U = 6\,PV$
So internal energy is $U = 6\,PV$.
Note: It should be remembered that internal energy is path independent but the work done depends on the path travelled. So internal energy only depends upon final and initial points. Also Isothermal processes in which the gas state changes upon keeping temperature constant, isochoric process is one in which gas state changes by keeping volume constant and isobaric process in which gas state changes by keeping pressure constant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




