
I am very confused about the anti-bonding orbitals. How do they form? I mean when two atomic orbitals produce bonding orbital + anti -bonding orbital ? please clear my basics. I am really worried. Please solve my problem?
Answer
558.6k+ views
Hint: Anti-bonding orbitals are simply formed by the subtraction of the overlapping and are completely opposite in comparison to the bonding orbitals which are formed by the addition of the overlapping. Now answer the given statement accordingly.
Complete step by step answer:
The anti-bonding molecular orbitals are formed by the subtraction of the overlap of the two atomic orbitals ( those orbitals which the electron is under the influence of the only one positive nucleus).
Example:- Consider the formation of the anti-bonding molecular orbital which is formed by the subtraction of overlapping of two 1s-orbitals as:
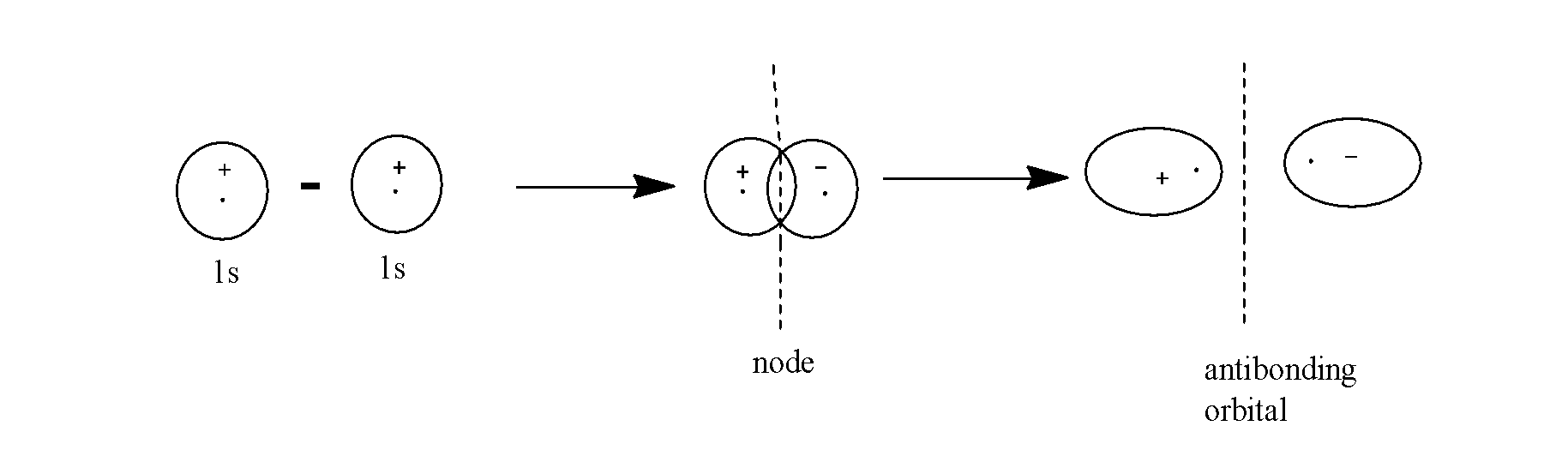
- The antibonding molecular orbitals have lesser electron density in the region between the two nuclei of the atoms.
- The forces in this orbital push the nuclei apart and thus, the electrons in the antibonding molecular orbitals contribute to repulsion between the atoms.
- These orbitals possess higher energy than the isolated atomic orbitals from which they are formed.
Note: Don’t get confused in the bonding and the anti-molecular orbitals. The bonding molecular orbitals are formed by the addition overlap of the atomic orbitals and have greater electron density but possess lower energy than the isolated atomic orbitals whereas on the contrary antibonding molecular orbitals are formed by the subtraction of the atomic orbitals.
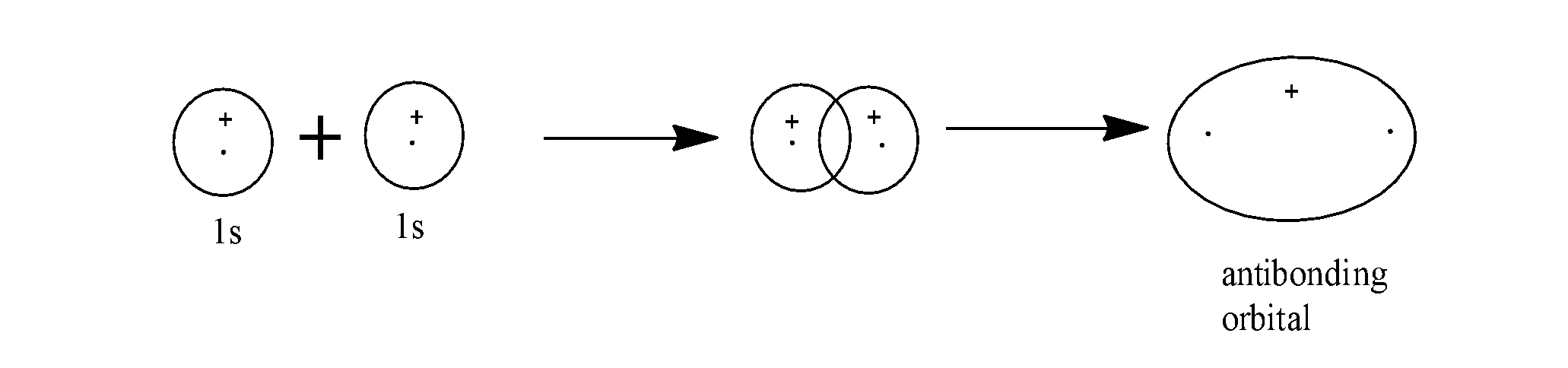
- The formation of the bonding molecular orbitals occur as:
Complete step by step answer:
The anti-bonding molecular orbitals are formed by the subtraction of the overlap of the two atomic orbitals ( those orbitals which the electron is under the influence of the only one positive nucleus).
Example:- Consider the formation of the anti-bonding molecular orbital which is formed by the subtraction of overlapping of two 1s-orbitals as:

- The antibonding molecular orbitals have lesser electron density in the region between the two nuclei of the atoms.
- The forces in this orbital push the nuclei apart and thus, the electrons in the antibonding molecular orbitals contribute to repulsion between the atoms.
- These orbitals possess higher energy than the isolated atomic orbitals from which they are formed.
Note: Don’t get confused in the bonding and the anti-molecular orbitals. The bonding molecular orbitals are formed by the addition overlap of the atomic orbitals and have greater electron density but possess lower energy than the isolated atomic orbitals whereas on the contrary antibonding molecular orbitals are formed by the subtraction of the atomic orbitals.
- The formation of the bonding molecular orbitals occur as:

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




