
Hyper conjugation is:
A. $\sigma - \pi $ conjugation
B.Delocalization of $\sigma $ and $\pi $ bond
C.No bond resonance
D.All of the above
Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint: Basically, hyper conjugation is a permanent effect in which the localization of sigma electrons of C-H bond of an alkyl group is directly attached to an atom of the unsaturated system. Further, it stabilizes the carbocation as it helps in the dispersal of positive charges.
Complete step by step answer:
Hyper conjugation refers to the delocalization of the electrons with the participation of bonds of primary sigma character. Moreover, it is a permanent effect in which the localization of sigma electrons of \[C - H\] bond of an alkyl group is directly attached to an atom of the unsaturated system or to an atom with an unshared p orbital.
Now, from the above options, all the options are correct. Basically it is a delocalization of $\sigma $ and $\pi $ bonds and as a result it ends in the addition of bonds where there is no bond between C and H .Therefore, it is also called as no bond resonance. The hyper conjugation is as shown:
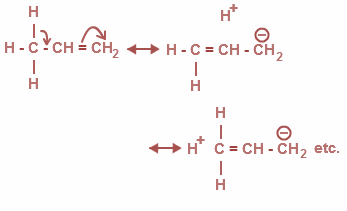
Moreover, the Baker-Nathan effect is used synonymously for hyper conjugation. It is a specific application for certain chemical reactions and types of structures.
Hence, option D is correct.
Note:Hyper conjugation is used to rationalize a variety of chemical phenomena such as gauche effect, anomeric effect, beta-silicon effect, relative stability of carbocation, the rotational barrier of ethane and many more. Moreover, it has several properties such as bond length, dipole moments, heat of formation etc.
Complete step by step answer:
Hyper conjugation refers to the delocalization of the electrons with the participation of bonds of primary sigma character. Moreover, it is a permanent effect in which the localization of sigma electrons of \[C - H\] bond of an alkyl group is directly attached to an atom of the unsaturated system or to an atom with an unshared p orbital.
Now, from the above options, all the options are correct. Basically it is a delocalization of $\sigma $ and $\pi $ bonds and as a result it ends in the addition of bonds where there is no bond between C and H .Therefore, it is also called as no bond resonance. The hyper conjugation is as shown:

Moreover, the Baker-Nathan effect is used synonymously for hyper conjugation. It is a specific application for certain chemical reactions and types of structures.
Hence, option D is correct.
Note:Hyper conjugation is used to rationalize a variety of chemical phenomena such as gauche effect, anomeric effect, beta-silicon effect, relative stability of carbocation, the rotational barrier of ethane and many more. Moreover, it has several properties such as bond length, dipole moments, heat of formation etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




