
Hydrogen bonds are formed in many compounds e.g. ${{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}}$, HF and ${\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}$. The boiling point of such compounds depends on the strength of the hydrogen bond and the number of hydrogen bonds. The correct decreasing order of the boiling points of the above compounds is:
A.HF>${{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}}$>${\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}$
B. ${{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}}$> HF >${\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}$
C. ${\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}$>>${{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}}$
D.${\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}$>${{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}}$>HF
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: Hydrogen bond is a chemical bond in which formation of a covalent link of hydrogen atoms with other electronegative atoms, such as, fluorine, nitrogen and oxygen atoms take place in the same or another molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the extent of hydrogen bonding depends on electronegativity and the number of hydrogen atoms available for bonding. Among Fluorine, nitrogen and oxygen atoms, increasing order of electronegativities is \[{\rm{N}} < {\rm{O}} < {\rm{F}}\].
Here, we have to understand the H-bonding in HF, ${{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}}$
and ${\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}$.
Let’s understand the hydrogen bonding in case of water.
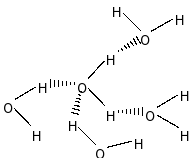
In case of water, it can form four hydrogen bonds with four other water molecules. But, ammonia can form only one hydrogen bond
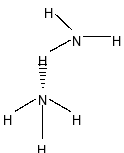
Between ammonia $\left( {{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)$ and water $\left( {{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}}} \right)$, water has more H-bonding than ammonia $\left( {{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)$ because of more number of hydrogen bond and also electronegativity of Oxygen is more than Nitrogen .
Between ammonia $\left( {{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)$and hydrogen fluoride (HF), HF has more H-bonding than ${\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}$because in ammonia, only one lone pair present which cannot satisfy all hydrogen also fluorine is more electronegative than nitrogen.
So, the decreasing order of effect of hydrogen bonding is ${{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O > HF > N}}{{\rm{H}}_3}$.
Now, we have to understand the relation of boiling point with hydrogen bonding. More the hydrogen bonding, the more the boiling point of the compound is. Therefore, decreasing order of boiling point is ${{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O > HF > N}}{{\rm{H}}_3}$.
Hence, the correct answer is option B.
Note:
It is to be noted that the extent of hydrogen bonding is in the order \[{\rm{H}} - {\rm{F}} > {\rm{H}} - {\rm{O}} > {\rm{H}} - {\rm{N}}\], that means, extent of hydrogen bonding is more in case of HF than water $\left( {{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}}} \right)$, that is, \[{\rm{HF}} > {{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}}\]. But we also have to consider the effect of the number of hydrogen bonding in the molecule. Water can form four H-bonds with four other hydrogen atoms but HF can form only one H-bond. So, HF has less effect of H-bonding than ${{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}}$.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the extent of hydrogen bonding depends on electronegativity and the number of hydrogen atoms available for bonding. Among Fluorine, nitrogen and oxygen atoms, increasing order of electronegativities is \[{\rm{N}} < {\rm{O}} < {\rm{F}}\].
Here, we have to understand the H-bonding in HF, ${{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}}$
and ${\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}$.
Let’s understand the hydrogen bonding in case of water.

In case of water, it can form four hydrogen bonds with four other water molecules. But, ammonia can form only one hydrogen bond

Between ammonia $\left( {{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)$ and water $\left( {{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}}} \right)$, water has more H-bonding than ammonia $\left( {{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)$ because of more number of hydrogen bond and also electronegativity of Oxygen is more than Nitrogen .
Between ammonia $\left( {{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)$and hydrogen fluoride (HF), HF has more H-bonding than ${\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}$because in ammonia, only one lone pair present which cannot satisfy all hydrogen also fluorine is more electronegative than nitrogen.
So, the decreasing order of effect of hydrogen bonding is ${{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O > HF > N}}{{\rm{H}}_3}$.
Now, we have to understand the relation of boiling point with hydrogen bonding. More the hydrogen bonding, the more the boiling point of the compound is. Therefore, decreasing order of boiling point is ${{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O > HF > N}}{{\rm{H}}_3}$.
Hence, the correct answer is option B.
Note:
It is to be noted that the extent of hydrogen bonding is in the order \[{\rm{H}} - {\rm{F}} > {\rm{H}} - {\rm{O}} > {\rm{H}} - {\rm{N}}\], that means, extent of hydrogen bonding is more in case of HF than water $\left( {{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}}} \right)$, that is, \[{\rm{HF}} > {{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}}\]. But we also have to consider the effect of the number of hydrogen bonding in the molecule. Water can form four H-bonds with four other hydrogen atoms but HF can form only one H-bond. So, HF has less effect of H-bonding than ${{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




