
How is hydrogen bonding among water molecules related to the structure of the water molecule?
Answer
537.9k+ views
Hint:We know that hydrogen bonding is one of the strongest molecular forces (second only to ionic bonding). Hydrogen bonding does influence the water molecules when they are in bulk or in solution as they have strong interaction between themselves.
Complete step-by-step answer: Let’s understand how the structure of water molecules plays a role in hydrogen bonding.
Also, oxygen and hydrogen atoms are connected by a covalent bond where a shared pair of electrons is pulled by an oxygen atom and becomes partially negative-charged. So, ultimately, the H atom will become partially positive-charged. When we talk about the bulk of water molecules, then there occurs an interaction between the positive charge of H atom of one molecule and negative charge of O atom of the neighboring molecule. This interaction is very strong and hence named hydrogen bonding.
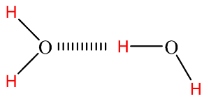
Hydrogen bonding is the reason behind adhesion and cohesion property of water as well as its surface tension.
Generally hydrogen bonding would not occur if there is only a single molecule of water. This hydrogen bonding leads to some unusual but important properties. It helps to give distinctive properties to water and ice (as ice (${{H}_{2}}O$) has lower density than liquid (${{H}_{2}}O$)). Due to strong hydrogen bonds, water molecules are able to stay condensed in liquid state.
Note: Remember that Hydrogen bonding can occur in those molecules where hydrogen atom is covalently bonded to highly electronegative atoms such as Fluorine, Oxygen or Nitrogen because they tend to withdraw electron density of the covalent bond with Hydrogen atom, making itself completely electron deficient. Hence H atoms tend to act like a proton which gets attracted towards lone pairs easily.
Complete step-by-step answer: Let’s understand how the structure of water molecules plays a role in hydrogen bonding.
Also, oxygen and hydrogen atoms are connected by a covalent bond where a shared pair of electrons is pulled by an oxygen atom and becomes partially negative-charged. So, ultimately, the H atom will become partially positive-charged. When we talk about the bulk of water molecules, then there occurs an interaction between the positive charge of H atom of one molecule and negative charge of O atom of the neighboring molecule. This interaction is very strong and hence named hydrogen bonding.

Hydrogen bonding is the reason behind adhesion and cohesion property of water as well as its surface tension.
Generally hydrogen bonding would not occur if there is only a single molecule of water. This hydrogen bonding leads to some unusual but important properties. It helps to give distinctive properties to water and ice (as ice (${{H}_{2}}O$) has lower density than liquid (${{H}_{2}}O$)). Due to strong hydrogen bonds, water molecules are able to stay condensed in liquid state.
Note: Remember that Hydrogen bonding can occur in those molecules where hydrogen atom is covalently bonded to highly electronegative atoms such as Fluorine, Oxygen or Nitrogen because they tend to withdraw electron density of the covalent bond with Hydrogen atom, making itself completely electron deficient. Hence H atoms tend to act like a proton which gets attracted towards lone pairs easily.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




