
What is the hybridization state of each carbon atom in ${H_2}C = C = C{H_2}$?
Answer
504k+ views
Hint: We know that the redistribution of energy of orbitals of individual atoms takes place to form orbitals of equivalent energy that happens when the two atomic orbitals combine to form hybrid orbital in a molecule and this process is known as hybridization.
Complete answer:
In organic chemistry, the hybridization state of the carbon atom is determined by the number of sigma bonds and pi bonds associated with that carbon atom. If a carbon atom consists of Only sigma bonds which means hybrid orbitals show head-to-head overlapping and match the symmetry of atom’s atomic orbital. So, the carbon atom with only sigma bonds is $s{p^3}$ overlapping. If a carbon atom consists of one pi and three sigma bonds, then the hybridization of carbon atom is observed to be $s{p^2}$ and if the carbon atom consists of two sigma and two pi bonds, then the carbon atom is said to be $sp$ hybridized.
Now, for determining the hybridization of each carbon atom in the given compound, we first need to count the number of sigma and pi bonds associated with each carbon atom. The sigma and pi bonds in the given organic compound are represented as follows:
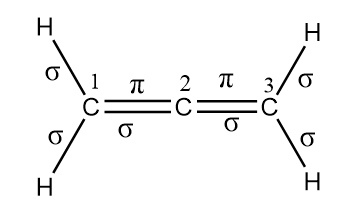
Therefore, the number of sigma and pi bonds for each carbon atoms are as follows:
Carbon-1: Sigma bonds $ = 3$ and pi bonds $ = 1$
Carbon-2: Sigma bonds $ = 2$ and pi bonds $ = 2$
Carbon-3: Sigma bonds $ = 3$ and pi bonds $ = 1$
Thus, we can conclude that the hybridization state of each carbon atom in the given compound is as follows:
Carbon-1: $s{p^2}$
Carbon-2: $sp$
Carbon-3: $s{p^2}$
Note:
Remember to never make assumptions of the hybridization state of carbon just by looking at the type of bond i.e., single, double or triple bond as it may lead to inaccurate results. As per above compound, the central carbon is bonded to two double bonds but it is not $s{p^2}$ hybridized instead it is $sp$ hybridized. Thus, always calculate the number of sigma and pi bonds before stating the hybridization state.
Complete answer:
In organic chemistry, the hybridization state of the carbon atom is determined by the number of sigma bonds and pi bonds associated with that carbon atom. If a carbon atom consists of Only sigma bonds which means hybrid orbitals show head-to-head overlapping and match the symmetry of atom’s atomic orbital. So, the carbon atom with only sigma bonds is $s{p^3}$ overlapping. If a carbon atom consists of one pi and three sigma bonds, then the hybridization of carbon atom is observed to be $s{p^2}$ and if the carbon atom consists of two sigma and two pi bonds, then the carbon atom is said to be $sp$ hybridized.
Now, for determining the hybridization of each carbon atom in the given compound, we first need to count the number of sigma and pi bonds associated with each carbon atom. The sigma and pi bonds in the given organic compound are represented as follows:

Therefore, the number of sigma and pi bonds for each carbon atoms are as follows:
Carbon-1: Sigma bonds $ = 3$ and pi bonds $ = 1$
Carbon-2: Sigma bonds $ = 2$ and pi bonds $ = 2$
Carbon-3: Sigma bonds $ = 3$ and pi bonds $ = 1$
Thus, we can conclude that the hybridization state of each carbon atom in the given compound is as follows:
Carbon-1: $s{p^2}$
Carbon-2: $sp$
Carbon-3: $s{p^2}$
Note:
Remember to never make assumptions of the hybridization state of carbon just by looking at the type of bond i.e., single, double or triple bond as it may lead to inaccurate results. As per above compound, the central carbon is bonded to two double bonds but it is not $s{p^2}$ hybridized instead it is $sp$ hybridized. Thus, always calculate the number of sigma and pi bonds before stating the hybridization state.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




