
Hybridization on the carbon atoms in diamond is:
A. $\text{sp}$
B. $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{2}}$
C. $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{3}}$
D. $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{3}}\text{d}$
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: Diamond is actually a solid form of pure carbon in which its carbon atoms are arranged in a crystal. In diamond, its basic element carbon, atoms are arranged in tetrahedral structure. In this structure, each atom is bonded to four nearest neighbours. Due to its structure, it's highly rigid and incompressible.
Complete step by step answer:
Diamond is one of the allotrope of carbon other than graphite and coal. Diamond is entirely made of carbon atoms and in the cubic crystal lattice of diamond, carbon atoms are arranged. This arrangement of carbon is obtained due to high pressure and immense heat.
Let us discuss the physical properties of diamond and structure formation of diamond:
1. The hybridisation of carbon here is $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{3}}$. Thus, it has a tetrahedral structure.
Its structural unit is like
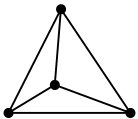
2. All four valencies of carbon atom are satisfied, as it is $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{3}}$hybridised.
3. Diamond behaves as an insulator because there are no free electrons for the conduction of electricity.
4. It has a crystal structure and therefore is very hard. It exists in cubic and octahedral crystal structure.
5. The molecular arrangement of the carbon molecules are three dimensional in nature because of the tetrahedral geometry. Thus, it has rigid structure.
Hybridization on the carbon atoms in diamond is $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{3}}$, which is option ‘c’.
Additional Information: Uses of diamond:
(1) As diamonds are durable and hard, that’s why diamonds are used in cutting, drilling, grinding and polishing.
(2) Diamond is exclusively used in jewellery especially in engagement rings due to shine and lustre.
Note: The structure of diamond is large and does not have any specific molecular formula. Due to no specific formula, the hybridization cannot be found in any particular formula. So, actually hybridization found checking the structure of a single unit of diamond. Diamonds have repetitive same units. So, hybridization of diamond is $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{3}}$.
Complete step by step answer:
Diamond is one of the allotrope of carbon other than graphite and coal. Diamond is entirely made of carbon atoms and in the cubic crystal lattice of diamond, carbon atoms are arranged. This arrangement of carbon is obtained due to high pressure and immense heat.
Let us discuss the physical properties of diamond and structure formation of diamond:
1. The hybridisation of carbon here is $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{3}}$. Thus, it has a tetrahedral structure.
Its structural unit is like

2. All four valencies of carbon atom are satisfied, as it is $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{3}}$hybridised.
3. Diamond behaves as an insulator because there are no free electrons for the conduction of electricity.
4. It has a crystal structure and therefore is very hard. It exists in cubic and octahedral crystal structure.
5. The molecular arrangement of the carbon molecules are three dimensional in nature because of the tetrahedral geometry. Thus, it has rigid structure.
Hybridization on the carbon atoms in diamond is $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{3}}$, which is option ‘c’.
Additional Information: Uses of diamond:
(1) As diamonds are durable and hard, that’s why diamonds are used in cutting, drilling, grinding and polishing.
(2) Diamond is exclusively used in jewellery especially in engagement rings due to shine and lustre.
Note: The structure of diamond is large and does not have any specific molecular formula. Due to no specific formula, the hybridization cannot be found in any particular formula. So, actually hybridization found checking the structure of a single unit of diamond. Diamonds have repetitive same units. So, hybridization of diamond is $\text{s}{{\text{p}}^{3}}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




