
What is the hybridization of the central metal atom in the following: $P{H_3},P{H_4}^ + $
Answer
564.3k+ views
Hint: We know that Hybridization involves the mixing of atomic orbitals of an atom (generally a central atom) to generate a new set of atomic orbitals which is called the hybrid orbitals. Hence to find the hybridization of the central metal atom we need to first write the electronic configuration and then draw the orbitals in which the bonded atom will be filled.
Complete step-by-step answer: The atomic number of phosphorous is $15$ hence its electronic configuration will be: $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^3}$
Here the valence orbitals will take part in hybridization i.e. $3{s^2}3{p^3}$
So, for $P{H_3}$
The orbitals will be filled as
$3s$
$3p$
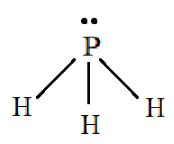
Here the two electrons in $3s$orbital are the lone pair of electrons present on phosphorus and the three hydrogen atoms are filled in the $3p$ orbital. Ideally the molecule should show $s{p^3}$ hybridization but this does not happen. $P{H_3}$ will not show any hybridization as it is considered to be a Drago molecule. Drago molecules do not have any hybridization and have the least bond angle. The geometry will be that of a trigonal pyramidal because there exists a lone pair-bond pair repulsion.
Structure of $P{H_3}$:
For $P{H_4}^ + $:
$3s$
$3p$
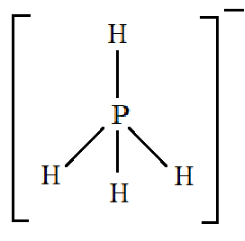
Here we see that since four atoms of hydrogen are present so it will occupy the $3s$ orbital as well as the $3p$ orbital. So, all the four sub orbitals are bonded with hydrogen atoms hence the hybridization will be $s{p^3}$ and hence it will have a geometry of tetrahedral.
Structure of $P{H_4}^ + $:
Note: To understand the Drago molecule you need to understand the Drago’s rule. The rule states that hybridization will not take place if:
1.The central atom belongs to the third or higher period.
2.The central atom possesses a lone pair of electrons.
3.The electronegativity of the terminal atom is less than the carbon atom.
Complete step-by-step answer: The atomic number of phosphorous is $15$ hence its electronic configuration will be: $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^3}$
Here the valence orbitals will take part in hybridization i.e. $3{s^2}3{p^3}$
So, for $P{H_3}$
The orbitals will be filled as
| $ \uparrow \downarrow $ |
$3s$
| $ \uparrow $ | $ \uparrow $ | $ \uparrow $ |
$3p$
Here the two electrons in $3s$orbital are the lone pair of electrons present on phosphorus and the three hydrogen atoms are filled in the $3p$ orbital. Ideally the molecule should show $s{p^3}$ hybridization but this does not happen. $P{H_3}$ will not show any hybridization as it is considered to be a Drago molecule. Drago molecules do not have any hybridization and have the least bond angle. The geometry will be that of a trigonal pyramidal because there exists a lone pair-bond pair repulsion.
Structure of $P{H_3}$:

For $P{H_4}^ + $:
| $ \uparrow $ |
$3s$
| $ \uparrow $ | $ \uparrow $ | $ \uparrow $ |
$3p$
Here we see that since four atoms of hydrogen are present so it will occupy the $3s$ orbital as well as the $3p$ orbital. So, all the four sub orbitals are bonded with hydrogen atoms hence the hybridization will be $s{p^3}$ and hence it will have a geometry of tetrahedral.
Structure of $P{H_4}^ + $:

Note: To understand the Drago molecule you need to understand the Drago’s rule. The rule states that hybridization will not take place if:
1.The central atom belongs to the third or higher period.
2.The central atom possesses a lone pair of electrons.
3.The electronegativity of the terminal atom is less than the carbon atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




