
What is the hybridization of $Ni$ in $Ni{(Dmg)_2}$?
Answer
507k+ views
Hint: Mixing and recasting of orbitals of a same atom with nearly the same energy to form new equivalent orbitals with definite orientation and maximum symmetry in space is known as hybridization. The geometry of a molecule depends upon its hybridization.
Complete answer:
The structure of $Ni{(Dmg)_2}$ is as follows:
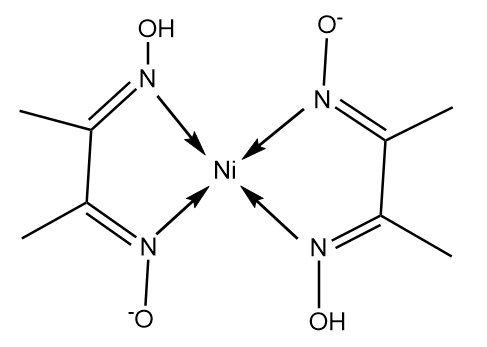
Nickel in the given complex exist in its $ + 2$ oxidation state and electronic configuration of nickel is represented as follows:
Atomic number of nickel $ = 28$
At ground state, the electronic configuration of Ni $ = [Ar]3{d^8}4{s^2}$
At $ + 2$ oxidation state, the atom will lose two electrons from the valence shell and the electronic configuration will be as follows:
$N{i^{ + 2}} = [Ar]3{d^8}4{s^0}$
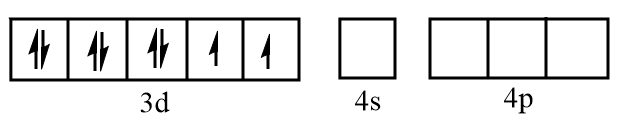
Sketch of orbitals of $N{i^{2 + }}$ are represented as follows:
Now, Dmg i.e., dimethylglyoxime as a ligand form a bond through nitrogen atoms, so it is considered as a strong field ligand and force the unpaired electrons to pair up. Thus, the incoming electrons will be filled in the inner d orbital and vacant s and p orbitals respectively as shown in the figure below:
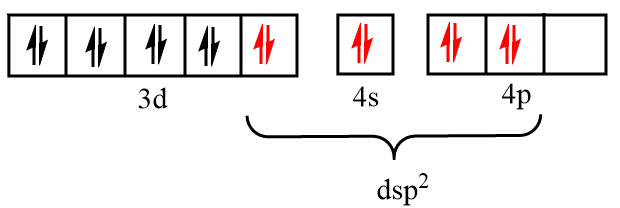
Therefore, the hybridization state of nickel in the given complex is $ds{p^2}$.
Note:
Remember that hybridization is the major factor to decide the geometry of a coordination complex. As the hybridization of the complex is found to be $ds{p^2}$, so the equivalent geometry of the complex is square planar as the inner d-orbital is involved in the bonding. However, the type of ligand decides the magnetic property of the complex. Here, the ligand was stable because of chelation and hydrogen bonding, so pairing of electrons takes place and no unpaired electron is left in the orbitals. Thus, the complex is diamagnetic in nature.
Complete answer:
The structure of $Ni{(Dmg)_2}$ is as follows:

Nickel in the given complex exist in its $ + 2$ oxidation state and electronic configuration of nickel is represented as follows:
Atomic number of nickel $ = 28$
At ground state, the electronic configuration of Ni $ = [Ar]3{d^8}4{s^2}$
At $ + 2$ oxidation state, the atom will lose two electrons from the valence shell and the electronic configuration will be as follows:
$N{i^{ + 2}} = [Ar]3{d^8}4{s^0}$
Sketch of orbitals of $N{i^{2 + }}$ are represented as follows:

Now, Dmg i.e., dimethylglyoxime as a ligand form a bond through nitrogen atoms, so it is considered as a strong field ligand and force the unpaired electrons to pair up. Thus, the incoming electrons will be filled in the inner d orbital and vacant s and p orbitals respectively as shown in the figure below:

Therefore, the hybridization state of nickel in the given complex is $ds{p^2}$.
Note:
Remember that hybridization is the major factor to decide the geometry of a coordination complex. As the hybridization of the complex is found to be $ds{p^2}$, so the equivalent geometry of the complex is square planar as the inner d-orbital is involved in the bonding. However, the type of ligand decides the magnetic property of the complex. Here, the ligand was stable because of chelation and hydrogen bonding, so pairing of electrons takes place and no unpaired electron is left in the orbitals. Thus, the complex is diamagnetic in nature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




