
Hybridization and geometry of \[{\left[ {Ni{{\left( {CN} \right)}_4}} \right]^{2 - }}\] are:
A.$s{p^2}d$ and tetrahedral
B. $s{d^3}$ and square planar
C. $s{p^3}$ and tetrahedral
D. $ds{p^2}$ and square planar
Answer
558.6k+ views
Hint:To solve this question, we must first understand the basic concepts about Hybridization in Coordination Compounds. Then we need to assess the geometrical properties of the Coordinate complexes then only we can conclude the correct answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:Before we move forward with the solution of this given question, let us first understand some basic concepts:
Hybridization: Redistribution of the energy of orbitals of individual atoms to give orbitals of equivalent energy happens when two atomic orbitals combine to form hybrid orbital in a molecule. This process is called hybridization. The new orbitals thus formed are known as hybrid orbitals.
Step 1: Consider the molecule \[{\left[ {Ni{{\left( {CN} \right)}_4}} \right]^{2 - }}\] : It has a square planar geometry formed by $ds{p^2}$ hybridization and not tetrahedral by $s{p^3}$ . \[{\left[ {Ni{{\left( {CN} \right)}_4}} \right]^{2 - }}\] is diamagnetic, so $N{i^{2 + }}$ ion has $3{d^8}$ outer configuration with two unpaired electrons. For the formation by $s{p^3}$ hybridization, the $3d$ orbital would remain unaffected, consequently, the complex would be paramagnetic like $N{i^{2 + }}$ ion itself.
Step 2: And we know that, for the formation of square planar structure by $ds{p^2}$ hybridization, two unpaired d-electrons are paired up due to energy made available by the approach of ligands, making one of the $3d$ orbitals empty. By this, there is no unpaired electron and the complex would be diamagnetic.
Step 3: The hybridization is as follows:
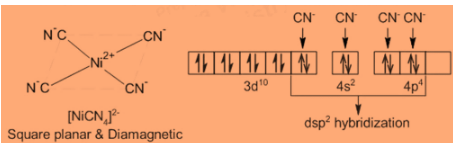
So, clearly we can conclude that the correct answer is Option D.
Note:During the process of hybridization, the atomic orbitals of similar energy are mixed together such as the mixing of two ‘s’ orbitals or two ‘p’ orbital’s or mixing of an ‘s’ orbital with a ‘p’ orbital or ‘s’ orbital with a ‘d’ orbital.
Complete step-by-step answer:Before we move forward with the solution of this given question, let us first understand some basic concepts:
Hybridization: Redistribution of the energy of orbitals of individual atoms to give orbitals of equivalent energy happens when two atomic orbitals combine to form hybrid orbital in a molecule. This process is called hybridization. The new orbitals thus formed are known as hybrid orbitals.
Step 1: Consider the molecule \[{\left[ {Ni{{\left( {CN} \right)}_4}} \right]^{2 - }}\] : It has a square planar geometry formed by $ds{p^2}$ hybridization and not tetrahedral by $s{p^3}$ . \[{\left[ {Ni{{\left( {CN} \right)}_4}} \right]^{2 - }}\] is diamagnetic, so $N{i^{2 + }}$ ion has $3{d^8}$ outer configuration with two unpaired electrons. For the formation by $s{p^3}$ hybridization, the $3d$ orbital would remain unaffected, consequently, the complex would be paramagnetic like $N{i^{2 + }}$ ion itself.
Step 2: And we know that, for the formation of square planar structure by $ds{p^2}$ hybridization, two unpaired d-electrons are paired up due to energy made available by the approach of ligands, making one of the $3d$ orbitals empty. By this, there is no unpaired electron and the complex would be diamagnetic.
Step 3: The hybridization is as follows:

So, clearly we can conclude that the correct answer is Option D.
Note:During the process of hybridization, the atomic orbitals of similar energy are mixed together such as the mixing of two ‘s’ orbitals or two ‘p’ orbital’s or mixing of an ‘s’ orbital with a ‘p’ orbital or ‘s’ orbital with a ‘d’ orbital.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




