
What is the hybrid state of the central atom in the following? \[P{F_5},{\text{ }}C{O_2},{\text{ }}B{F_4}^ - \]
Answer
506.7k+ views
Hint: You need to find hybridization of the central atom in the following compounds. For this, you should know the structure of the compounds. Also, you need to be aware of the central atom and the surrounding atoms in any molecule.
Complete answer: We are given three molecules here which are \[P{F_5},{\text{ }}C{O_2},{\text{ }}B{F_4}^ - \]. We have to find out the hybrid state of the central atom. That means we have to find out the hybridization of the central atom. For finding hybridization we are going to use the formula:
$\Rightarrow H = \dfrac{1}{2}[V + X - C + A]$
Where V is the number of valence electrons of the central atom, X is the number of monovalent atoms around the central atom, C is the charge on the cation and A is the charge on the anion.
For hybridization we have the table as follows:
So one by one let us find out the hybrid state of the central atom. The hybrid state is found out in the following manner:
\[P{F_5}\]
Structure of \[P{F_5}\]is
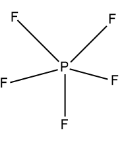
The central atom is P. the number of valence electrons (V) in P are $5$, number of monovalent atoms(X) are $5$ and there is no charge on the molecule so C and A will be $0$. Hence by using the formula we have:
$\Rightarrow H = \dfrac{1}{2}[V + X - C + A]$
$ = \dfrac{1}{2}[5 + 5 - 0 + 0]$
$ = \dfrac{{10}}{2} = 5$
According to the table value of H is $5$ therefore the hybrid state of P in \[P{F_5}\] is sp3d
\[C{O_2}\] The structure of the molecule is a:
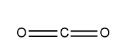
In central atom C, V is $4$, X is $0$ and there is no charge on the molecule so C and A will be $0$.
$0$. Hence by using the formula we have:
$\Rightarrow H = \dfrac{1}{2}[V + X - C + A]$
$= \dfrac{1}{2}[4 + 0 - 0 + 0]$
$ = \dfrac{4}{2} = 2$
From the table value of H is $2$ therefore the hybrid state of C in \[C{O_2}\] is sp
\[B{F_4}^ - \]
The structure of the molecule is as follows:
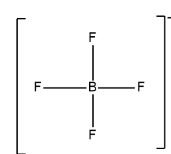
In central atom B, V is $3$, X is $4$ and no charge on cation so C is $0$ and charge on anion A will be $ - 1$.
$0$. Hence by using the formula we have:
$\Rightarrow H = \dfrac{1}{2}[V + X - C + A]$
$H = \dfrac{1}{2}[3 + 4 - 0 + \left( { - 1} \right)]$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}[3 + 4 + 1]$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{8}{2} = 4$
From the table value of H is $4$ therefore the hybrid state of B in \[B{F_4}^ - \] is $sp^3$
Note:
In \[C{O_2}\] we see that the number of monovalent atoms is two; this is because oxygen is a divalent as it forms two bonds to complete its octet. There is another method by which the hybrid state or the hybridization of the central atom can be found out, it is known as a VSEPR theory which also gives you the shape of the particular molecule.
Complete answer: We are given three molecules here which are \[P{F_5},{\text{ }}C{O_2},{\text{ }}B{F_4}^ - \]. We have to find out the hybrid state of the central atom. That means we have to find out the hybridization of the central atom. For finding hybridization we are going to use the formula:
$\Rightarrow H = \dfrac{1}{2}[V + X - C + A]$
Where V is the number of valence electrons of the central atom, X is the number of monovalent atoms around the central atom, C is the charge on the cation and A is the charge on the anion.
For hybridization we have the table as follows:
| Value of H | $2$ | $3$ | $4$ | $5$ |
| Type of hybridization | \[sp\] | \[s{p^2}\] | \[s{p^3}\] | \[s{p^3}d\] |
So one by one let us find out the hybrid state of the central atom. The hybrid state is found out in the following manner:
\[P{F_5}\]
Structure of \[P{F_5}\]is

The central atom is P. the number of valence electrons (V) in P are $5$, number of monovalent atoms(X) are $5$ and there is no charge on the molecule so C and A will be $0$. Hence by using the formula we have:
$\Rightarrow H = \dfrac{1}{2}[V + X - C + A]$
$ = \dfrac{1}{2}[5 + 5 - 0 + 0]$
$ = \dfrac{{10}}{2} = 5$
According to the table value of H is $5$ therefore the hybrid state of P in \[P{F_5}\] is sp3d
\[C{O_2}\] The structure of the molecule is a:

In central atom C, V is $4$, X is $0$ and there is no charge on the molecule so C and A will be $0$.
$0$. Hence by using the formula we have:
$\Rightarrow H = \dfrac{1}{2}[V + X - C + A]$
$= \dfrac{1}{2}[4 + 0 - 0 + 0]$
$ = \dfrac{4}{2} = 2$
From the table value of H is $2$ therefore the hybrid state of C in \[C{O_2}\] is sp
\[B{F_4}^ - \]
The structure of the molecule is as follows:

In central atom B, V is $3$, X is $4$ and no charge on cation so C is $0$ and charge on anion A will be $ - 1$.
$0$. Hence by using the formula we have:
$\Rightarrow H = \dfrac{1}{2}[V + X - C + A]$
$H = \dfrac{1}{2}[3 + 4 - 0 + \left( { - 1} \right)]$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}[3 + 4 + 1]$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{8}{2} = 4$
From the table value of H is $4$ therefore the hybrid state of B in \[B{F_4}^ - \] is $sp^3$
Note:
In \[C{O_2}\] we see that the number of monovalent atoms is two; this is because oxygen is a divalent as it forms two bonds to complete its octet. There is another method by which the hybrid state or the hybridization of the central atom can be found out, it is known as a VSEPR theory which also gives you the shape of the particular molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




