
Human infection of blood fluke occurs through
(a) Metacercaria
(b) Miracidium
(c) Capsule
(d) Cercaria
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: Human infection of blood fluke occurs through a larva that is formed by multiplication of sporocysts in their life cycle. Hundreds of these larvae are shed by snails to continue their life cycle. They enter human skin and shed their forked tail.
Complete answer:
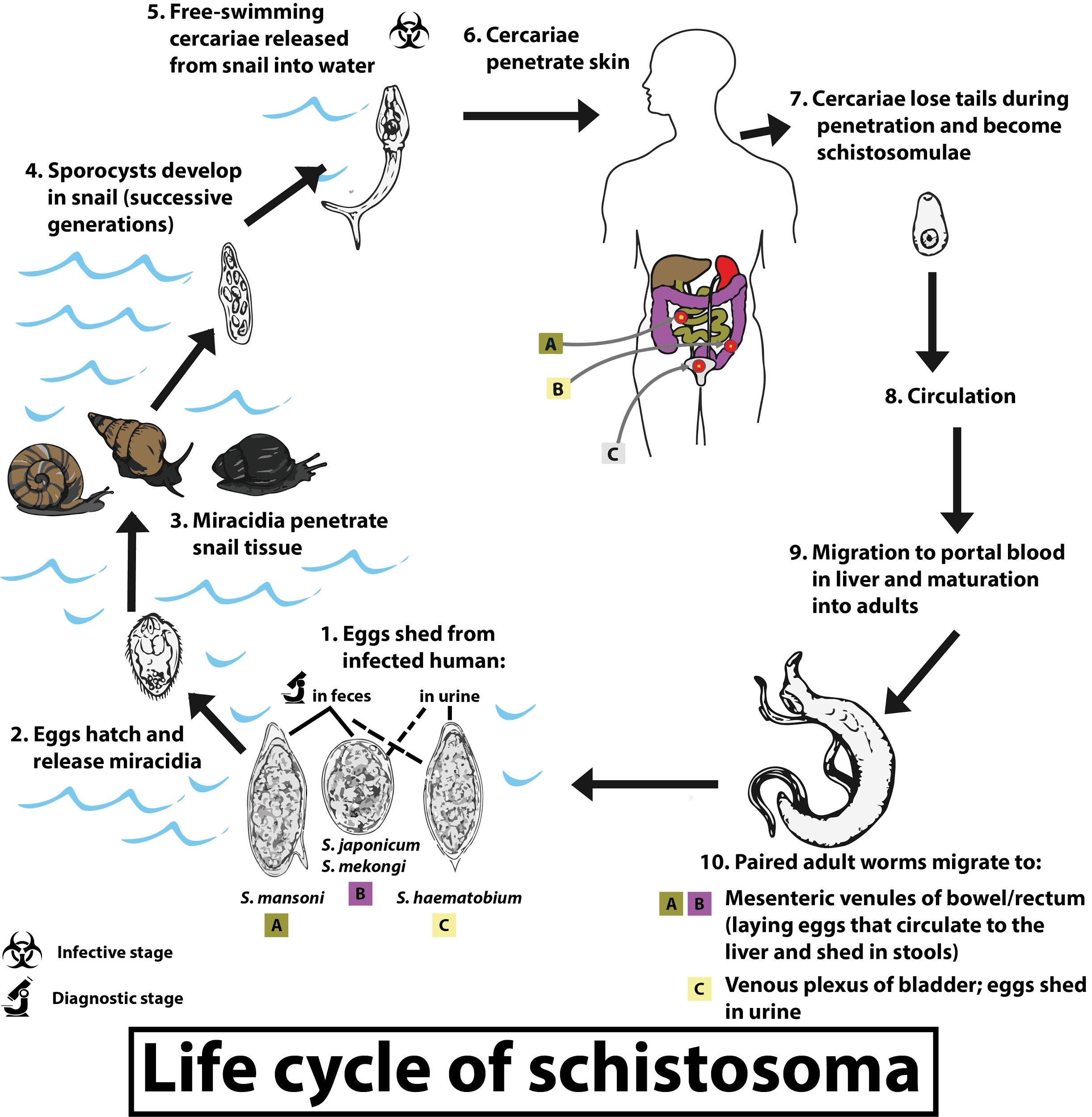
Human infection of blood fluke occurs through cercaria which comes under the Phylum Platyhelminthes and class called trematode. Trematodes are multicellular, eukaryotic helminths. They include two groups of parasitic flatworms commonly called flukes. They complete their life cycle in two hosts namely snails and mammals. Their life cycle involves free-swimming larvae called ‘cercaria’. These larvae are given off by infected snails that act as their intermediate host. Further cercaria either penetrates the skin of their definitive host i.e. human beings as seen in blood flukes or are ingested in the form of encysted ‘metacercariae’ through various edible plants and animals. After entering the human beings, the larvae develop into adult males and females, (schistosomes) or hermaphrodites (other flukes). Schistosomes or hermaphrodites then produce eggs that pass out in host excreta. When in contact with freshwater these eggs hatch into miracidium which again infects the snails.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Cercaria.’
Note: -The scientific name of blood fluke is ‘Schistosoma.’
-It lives in the vesicles of the intestine and urinary bladder in humans.
-Other than blood flukes all other trematodes show a different mode of infection. They enter their definitive host by ingestion of metacercariae through contaminated food.
-Miracidium hatching test can be used to diagnose infection by schistosomes.
Complete answer:
Human infection of blood fluke occurs through cercaria which comes under the Phylum Platyhelminthes and class called trematode. Trematodes are multicellular, eukaryotic helminths. They include two groups of parasitic flatworms commonly called flukes. They complete their life cycle in two hosts namely snails and mammals. Their life cycle involves free-swimming larvae called ‘cercaria’. These larvae are given off by infected snails that act as their intermediate host. Further cercaria either penetrates the skin of their definitive host i.e. human beings as seen in blood flukes or are ingested in the form of encysted ‘metacercariae’ through various edible plants and animals. After entering the human beings, the larvae develop into adult males and females, (schistosomes) or hermaphrodites (other flukes). Schistosomes or hermaphrodites then produce eggs that pass out in host excreta. When in contact with freshwater these eggs hatch into miracidium which again infects the snails.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Cercaria.’
Note: -The scientific name of blood fluke is ‘Schistosoma.’
-It lives in the vesicles of the intestine and urinary bladder in humans.
-Other than blood flukes all other trematodes show a different mode of infection. They enter their definitive host by ingestion of metacercariae through contaminated food.
-Miracidium hatching test can be used to diagnose infection by schistosomes.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




