
How was benzene discovered$?$
Answer
548.1k+ views
Hint: Benzene is an aromatic hydrocarbon having the molecular formula ${C_6}{H_6}$. The benzene molecule is composed of six $C$ atoms joined in a planar ring with one $H$ atom attached to each. It is the parent compound of numerous important aromatic compounds and is a colourless liquid with characteristic odour.
Complete step-by-step answer:The word benzene is derived from "gum benzoin" or benzoin resin, an aromatic resin which is known to European pharmacists and perfumers. Soon an acidic material was derived from benzoin by the process of sublimation, and named flowers of benzoin, or benzoic acid. The hydrocarbon thus derived from benzoic acid was named benzin, benzol, or benzene.
Michael Faraday first isolated and identified benzene in $1825$ from the oily residue derived from the production of illuminating gas, giving it the name bicarburet of hydrogen.
In $1834$ German chemist Eilhardt Mitscherlich heated benzoic acid with lime and produced benzene.
In $1845$ German chemist A.W. von Hofmann isolated benzene from coal tar.
German chemists Joseph Loschmidt in $1861$ and August Kekule von Stradonitz in $1866$ independently proposed a cyclic arrangement of six carbons with alternating single and double bonds. Kekule subsequently modified his structural formula to one in which oscillation of the double bonds gave two equivalent structures in rapid equilibrium.
In $1931$ American chemist Linus Pauling suggested that benzene had a single structure, which was a resonance hybrid of the two Kekule structures.
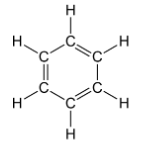
The structure of benzene can be represented as:
Note: It is used primarily as a precursor to the manufacture of chemicals with more complex structure, such as ethyl benzene and cumene, of which billions of kilograms are produced annually. It is highly toxic and is a known carcinogen; exposure to it may cause leukemia. As a result, there are strict controls on benzene emissions.
Complete step-by-step answer:The word benzene is derived from "gum benzoin" or benzoin resin, an aromatic resin which is known to European pharmacists and perfumers. Soon an acidic material was derived from benzoin by the process of sublimation, and named flowers of benzoin, or benzoic acid. The hydrocarbon thus derived from benzoic acid was named benzin, benzol, or benzene.
Michael Faraday first isolated and identified benzene in $1825$ from the oily residue derived from the production of illuminating gas, giving it the name bicarburet of hydrogen.
In $1834$ German chemist Eilhardt Mitscherlich heated benzoic acid with lime and produced benzene.
In $1845$ German chemist A.W. von Hofmann isolated benzene from coal tar.
German chemists Joseph Loschmidt in $1861$ and August Kekule von Stradonitz in $1866$ independently proposed a cyclic arrangement of six carbons with alternating single and double bonds. Kekule subsequently modified his structural formula to one in which oscillation of the double bonds gave two equivalent structures in rapid equilibrium.
In $1931$ American chemist Linus Pauling suggested that benzene had a single structure, which was a resonance hybrid of the two Kekule structures.
The structure of benzene can be represented as:

Note: It is used primarily as a precursor to the manufacture of chemicals with more complex structure, such as ethyl benzene and cumene, of which billions of kilograms are produced annually. It is highly toxic and is a known carcinogen; exposure to it may cause leukemia. As a result, there are strict controls on benzene emissions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




