
How many times does $18$ go into $60?$
Answer
556.5k+ views
Hint: Read the question twice which states that $60$ divided by $18$. Here we will first frame the given expression and then divide to find the remainder and the resultant required value.
Complete step-by-step solution:
To find the number of $18$which can go in $60$, it can be known by
$\dfrac{{60}}{{18}}$
Start division –
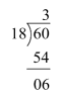
Hence, $18$ can go maximum three times and $6$will be left over.
It can be expressed as: $3\dfrac{6}{{18}}$
Common factors from the numerator and the denominator cancel each other.
$3\dfrac{6}{{18}} = 3\dfrac{1}{3}$
This is the required solution.
Alternative method:
The above problem can be solved by using the multiples method.
First just note down the multiples of the divisor that is $18$
Multiples of $18$ are $18,36,54$
There can be only three multiples of $18$which are less than $60$
Subtract last multiple from $60$
Which gives $6$ left over and hence can be expressed as $3\dfrac{6}{{18}}$
Common factors from the numerator and the denominator cancel each other.
$3\dfrac{6}{{18}} = 3\dfrac{1}{3}$
This is the required solution.
Additional Information: Prime factorization is the process of finding which prime numbers can be multiplied together to make the original number, where prime numbers are the numbers greater than $1$ and which are not the product of any two smaller natural numbers. For Example: $2,{\text{ 3, 5, 7,}}......$ $2$ is the prime number as it can have only $1$ factor. Factors are the number $1$and the number itself.
Note: Be good in multiples and division. Since it is the most important fundamental to solve and simplify any mathematical expression. Remember multiples till twenty numbers. Always convert the given number in the prime numbers and then find the common factors in the numerator and the denominator and then remove them.
Complete step-by-step solution:
To find the number of $18$which can go in $60$, it can be known by
$\dfrac{{60}}{{18}}$
Start division –
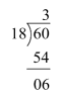
Hence, $18$ can go maximum three times and $6$will be left over.
It can be expressed as: $3\dfrac{6}{{18}}$
Common factors from the numerator and the denominator cancel each other.
$3\dfrac{6}{{18}} = 3\dfrac{1}{3}$
This is the required solution.
Alternative method:
The above problem can be solved by using the multiples method.
First just note down the multiples of the divisor that is $18$
Multiples of $18$ are $18,36,54$
There can be only three multiples of $18$which are less than $60$
Subtract last multiple from $60$
Which gives $6$ left over and hence can be expressed as $3\dfrac{6}{{18}}$
Common factors from the numerator and the denominator cancel each other.
$3\dfrac{6}{{18}} = 3\dfrac{1}{3}$
This is the required solution.
Additional Information: Prime factorization is the process of finding which prime numbers can be multiplied together to make the original number, where prime numbers are the numbers greater than $1$ and which are not the product of any two smaller natural numbers. For Example: $2,{\text{ 3, 5, 7,}}......$ $2$ is the prime number as it can have only $1$ factor. Factors are the number $1$and the number itself.
Note: Be good in multiples and division. Since it is the most important fundamental to solve and simplify any mathematical expression. Remember multiples till twenty numbers. Always convert the given number in the prime numbers and then find the common factors in the numerator and the denominator and then remove them.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




